Abstract
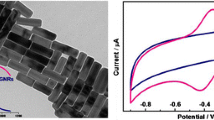
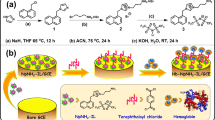
Hemoglobin (Hb) was immobilized on CdS:Mn nanoparticles (NPs) capped with citrate to obtain an amperometric biosensor for determination of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The NPs were prepared from aqueous solution via a precipitation method. The UV-vis spectra of the film with Hb on the NPs and of free Hb solutions suggested that Hb retained its bioactivity and native conformation in the film. In buffer of pH 7.0, the sensor film exhibited a pair of quasi-reversible redox peaks originating from the Hb-heme Fe(III)/Fe(II) redox couple. The formal potential of Hb varied linearly with the increase of pH from 3.0 to 9.0 with a slope of −46 mV·pH−1, this indicating that one proton participates in the redox reaction. The electron transfer rate constant (ks) is 2.2 s−1, suggesting that the NPs provide a benign microenvironment for Hb to undergo direct electron transfer. Despite the absence of an electron mediator, the biosensor displays an analytical performance which is better than any others described in previous reports. Hence, the NPs may provide a simple and alternative approach towards electrochemical biosensors.

The CdS:Mn NPs capped with citrate may provide a benign microenvironment for Hb to undergo direct electron transfer so that the electrochemical detection could be improved.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas ME, Luo W, Zhu LH, Zou J, Tang HQ (2010) Fluorometric determination of hydrogen peroxide in milk by using a Fenton reaction system. Food Chem 120:327–331
Yue HF, Bu X, Huang MH, Young J, Raglione T (2009) Quantitative determination of trace levels of hydrogen peroxide in crospovidone and a pharmaceutical product using high performance liquid chromatography with coulometric detection. Int J Pharm 375:33–40
Prakash PA, Yogeswaran U, Chen SM (2009) A review on direct electrochemistry of catalase for electrochemical sensors. Sensors 9:1821–1844
Ribeiro JPN, Segundo MA, Reis S, Lima JLFC (2009) Spectrophotometric FIA methods for determination of hydrogen peroxide: application to evaluation of scavenging capacity. Talanta 79:1169–1176
Chang Q, Zhu LH, Jiang GD, Tang HQ (2009) Sensitive fluorescent probes for determination of hydrogen peroxide and glucose based on enzyme-immobilized magnetite/silica nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem 395:2377–2385
Hu XF, Han HY, Hua LJ, Sheng ZH (2010) Electro generated chemiluminescence of blue emitting ZnSe quantum dots and its biosensing for hydrogen peroxide. Biosens Bioelectron 25:1843–1846
Zou GZ, Ju HX (2004) Electro generated chemiluminescence from a CdSe nanocrystal film and it sensing application in aqueous solution. Anal Chem 76:6871–6876
Guo HL, Liu DY, Yu XD (2009) Direct electrochemistry and electro catalysis of hemoglobin on nanostructured gold colloid-silk fibroin modified glassy carbon electrode, X.H. Xia. Sens Actuators, B, Chem 139:598–603
Lu LM, Zhang L, Zhang XB, Wu ZS, Huan SY, Shen GL, Yu RQ (2010) A MgO nanoparticles composite matrix-based electrochemical biosensor for hydrogen peroxide with high sensitivity. Electroanalysis 22:471–477
George S, Lee HK (2009) Direct electrochemistry and electro catalysis of hemoglobin in nafion/carbon nanochip film on glassy carbon electrode. J Phys Chem B 113:15445–15454
Hong JM, Dai ZH (2009) Amperometric biosensor for hydrogen peroxide and nitrite based on globin immobilized on one-dimensional gold nanoparticle. Sens Actuators, B, Chem 140:222–226
Kapralov A, Vlasova II, Feng WH, Maeda A, Walson K, Tyurin VA, Aneja RK, Carcillo J, Bayir H, Kagan VE (2009) Peroxidase activity of hemoglobin. Haptoglobin complexes covalent aggregation and oxidative stress in plasma and macrophages. J Biol Chem 284:30395–30407
Gu HY, Yu AM, Chen HY (2001) Direct electron transfer and characterization of hemoglobin immobilized on a Au colloid-cysteamine-modified gold electrode. J Electroanal Chem 516:119–126
Liu Y, Jiang QY, Lu SY, Zhang Y, Gu HY (2009) Immobilization of hemoglobin on the gold colloid modified glassy carbon electrode for preparing a novel hydrogen peroxide biosensor. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 29:418–427
Yu CM, Guo JW, Gu HY (2009) Direct electrochemical behavior of hemoglobin at surface of Au@Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 166:215–220
Fan H, Pan ZQ, Gu HY (2010) The self-assembly, characterization and application of hemoglobin immobilized on Fe3O4@Pt core-shell nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 168:239–244
Sato K, Tachibana Y, Hattori S, Chiba T, Kuwabata S (2008) Polyacrylic acid coating of highly luminescent CdS nanocrystals for biological labeling applications. J Colloid Interface Sci 324:257–260
Wang XF, Zhou Y, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2009) Signal-on electrochemiluminescence biosensors based on CdS-carbon nanotube nanocomposite for the sensitive detection of choline and acetylcholine. Adv Funct Mater 19:1–7
Huang YX, Zhang WJ, Xiao H, Li GX (2005) An electrochemical investigation of glucose oxidase at a CdS nanoparticles modified electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 21:817–821
Hu DH, Wu HM, Liang JG, Han HY (2008) Study on the interaction between CdSe quantum dots and hemoglobin. Spectrochim Acta A 69:830–834
Sun W, Wang DD, Li GC, Zhai ZQ, Zhao RJ, Jiao K (2008) Direct electron transfer of hemoglobin in a CdS nanorods and nafion composite film on carbon ionic liquid electrode. Electrochim Acta 53:8217–8221
Zhou H, Gan X, Liu T, Yang QL, Li GX (2005) Effect of nano cadmium sulfide on the electron transfer reactivity and peroxidase activity of hemoglobin. J Biochem Biophys Methods 64:38–45
Shi CG, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2007) Electro generated chemiluminescence and electrochemical bi- functional sensors for H2O2 based on CdS nanocrystals/hemoglobin multilayers. J Electroanal Chem 610:186–192
Stouwdam JW, Janssen RAJ (2009) Electroluminescent Cu-doped CdS quantum dots. Adv Mater 21:2916–2920
Wang GL, Yu PP, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2009) A label-free photo electrochemical immunosensor based on water- soluble quantum dots. J Phys Chem C 113:11142–11148
ShanY XuJJ, Chen HY (2009) Distance-dependent quenching and enhancing of electrochemiluminescence from a CdS: Mn nanocrystal film by Au nanoparticles for highly sensitive detection of DNA. Chem Commun 8:905–907
Yang H, Holloway PH (2004) Efficient and photostable ZnS-Passivated CdS:Mn luminescent nanocrystals. Adv Funct Mater 14:152–156
Zheng N, Zhou X, Yang WY, Li XJ, Yuan ZB (2009) Direct electrochemistry and electro catalysis of hemoglobin immobilized in a magnetic nanoparticles-chitosan film. Talanta 79:780–786
Zhu JT, Shi CG, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2007) Direct electrochemistry and electro catalysis of hemoglobin on undoped nanocrystalline diamond modified glassy carbon electrode. Bioelectrochemistry 71:243–248
Chen SH, Yuan R, Chai YQ, Yin B, Xu Y (2008) Multilayer assembly of hemoglobin and colloidal gold nanoparticles on multiwall carbon nanotubes/chitosan composite for detecting hydrogen peroxide. Electroanalysis 20:2141–2147
Wu BY, Hou SH, Yin F, Li J, Zhao ZX, Huan JD, Chen Q (2007) Amperometric glucose biosensor based on layer-by-layer assembly of multilayer films composed of chitosan, gold nanoparticles and glucose oxidase modified Pt electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 22:838–844
http://www.chinanusa.com/query/enterp.asp?memid=S033720530894#company%20profile
Zong SZ, Cao Y, Ju HX (2007) Direct electron transfer of hemoglobin immobilized in multiwalled carbon nanotubes enhanced grafted collagen matrix for electro catalytic detection of hydrogen peroxide. Electroanalysis 19:841–846
Feng JJ, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2007) Direct electron transfer and electro catalysis of hemoglobin adsorbed on mesoporous carbon through layer-by-layer assembly. Biosens Bioelectron 22:1618–1624
Lesser C, Gao M, Kirstein S (1999) Highly luminescent thin films from alternating deposition of CdTe nanoparticles to polycations. Mater Sci Eng C 8–9:159–162
Xu YX, Hu CG, Hu SS (2008) A hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin in Hb-Ag sol films. Sens Actuators, B, Chem 130:816–822
Laviron E (1979) The use of linear potential sweep voltammetry and of a.c. Voltammetry for the study of the surface electrochemical reaction of strongly adsorbed systems and of redox modified electrodes. J Electroanal Chem 100:263–270
Cai CX, Chen J (2004) Direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase promoted by carbon nanotubes. Anal Biochem 325:285–292
Laviron E (1979) Adsorptive voltammetric determination of cisapride at a carbon nanotubes paste electrode. J Electroanal Chem 101:19–28
Mai ZB, Zhao XJ, Dai Z, Zou XY (2010) Direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin adsorbed on self-assembled monolayers with different head groups or chain length. Talanta 81:167–175
Cao DF, Hu NF (2006) Direct electron transfer between hemoglobin and pyrolytic graphite electrodes enhanced by Fe3O4 nanoparticles in their layer-by-layer self-assembly films. Biophys Chem 121:209–217
Huang H, He PL, Hu NF, Zeng YH (2003) Electrochemical and electro catalytic properties of myoglobin and hemoglobin incorporated in carboxymethyl cellulose films. Bioelectrochem 61:29–38
Lai GS, Zhang HL, Zhang DY (2008) A novel hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on hemoglobin immobilized on magnetic chitosan microspheres modified electrode. Sens Actuators, B, Chem 129:497–503
Xu Q, Wang JH, Wang Z, Wang HQ, Yang Q, Zhao YD (2009) Biosensor for hydrogen peroxide based on chitosan and nanoparticle complex film-modified glassy-carbon electrodes. Anal Lett 42:2496–2508
Wang Z, Xu Q, Wang HQ, Yin ZH, Yu JH, Zhao YD (2009) Direct electrochemistry and elctrocatalytic activity of hemoglobin at CdTe nanoparticle/nafion film-modified electrode. Anal Sci 25:773–777
Gao RF, Zheng JB (2009) Direct electrochemistry of myoglobin based on DNA accumulation on carbon ionic liquid electrode. Electrochem Commun 11:1527–1529
Sun W, Li XQ, Wang Y, Li X, Zhao CZ, Jiao K (2009) Direct electrochemistry of myoglobin in nafion and multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified carbon ionic liquid electrode. Bioelectrochemistry 75:170–175
Tan XC, Zhang JL, Tan SW, Zhao DD, Huang ZW, Mi Y, Huang ZY (2009) Amperometric hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on horseradish peroxidase immobilized on Fe3O4/chitosan modified glassy carbon electrode. Electroanalysis 21:1514–1520
Kafi AKM, Wu GS, Chen AC (2008) A novel hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on the immobilization of horseradish peroxidase onto Au-modified titanium dioxide nanotube arrays. Biosens Bioelectron 24:566–571
Feng JJ, Zhao G, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2005) Direct electrochemistry and electro catalysis of heme proteins immobilized on gold nanoparticles stabilized by chitosan. Anal Biochem 342:280–286
Hamer M, Carballo RR, Rezzano IN (2009) Electro catalytic reduction of hydrogen peroxide by nanostructured bimetallic films of metalloporphyrins. Electroanalysis 21:2133–2138
Acknowledgement
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers: 20675042; 20875051; 21075070; 81001263), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant number: BK2009152).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
EDS spectrum of CdS:Mn NPs capped with citrate. (DOC 60 kb)
Fig. S2
The UV-vis spectra of (a) CdS:Mn-CS modified ITO, (b) Hb in pH 6.0 phosphate buffer solution and (c) Hb-CdS:Mn-CS modified ITO. (DOC 450 kb)
Fig. S3
Cyclic voltammograms of Hb-CdS:Mn-CS modified GCE in pH 7.0 phosphate buffer solution at various scan rates: 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400 mV·s−1 (a-h). Inset: plots of cathodic and anodic peak currents vs. scan rate. (DOC 585 kb)
Fig. S4
CVs of Hb-CdS:Mn-CS-GCE in pH 7.0 phosphate buffer solution at 100 mV·s−1 in the presence of (a) 0, (b) 5 μ M H2O2, (c) 10 μ M H2O2 and (d)15 μ M H2O2. (DOC 313 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, ZQ., Fan, H., Shi, CG. et al. Direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin immobilized on CdS:Mn nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 173, 277–283 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0559-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0559-6