Abstract
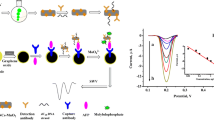
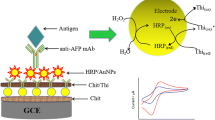
The application of gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical immunoassays have been extensively studied for the detection of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), but most often they exhibit low sensitivity. We describe the fabrication of a new electrochemical immunoassay for signal amplification of the antigen-antibody reaction combined with the nanogold-based bio-barcode technique. Hepatitis B surface antibody (HBsAb) was initially immobilized on a nanogold/thionine/DNA-modified gold electrode, and then a sandwich-type immunoassay format was employed for the detection of HBsAg using nanogold-codified horseradish peroxidase-HBsAb conjugates as secondary antibodies. Under optimal conditions, the current response of the sandwich-type immunocomplex relative to the H2O2 system was proportional to HBsAg concentration in the range from 0.5 to 650 ng·mL−1 with a detection limit of 0.1 ng·mL−1 (S/N = 3). The precision, reproducibility and stability of the immunosensor were acceptable. Subsequently, the immunosensors were used to assay HBsAg in human serum specimens. Analytical results were in agreement with those obtained by the standard chemiluminescence enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shah U, Kelly D, Chang M, Fujisawa T, Heller S, Gonzalez-Peralta R, Jara P, Mieli-Vergani G, Mohan N, Murray K (2009) Management of chroninc hepatitis B in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 48:399
Nokhodian Z, Kassaian N, Ataei B, Javadi A, Shoaei P, Farajzadegan Z, Adibi P (2009) Hepatitis B markers in Isfahan, Central Iran: a population-based study. Hepatitis Monthly 9:12
Sheikh SM (2009) Hepatitis B and C: value of universal antenatal screening. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 19:179
Al-Wayli HM (2009) Prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen in a Saudi hospital polulation. Saudi Med J 30:448
Zhang J, Wang J, Zhu J, Xu J, Chen H, Xu D (2008) An electrochemical impedimetric arrayed immunosensor based on indium tin oxide electrodes and silver-enhanced gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 163:63
Tang D, Xia B (2008) Electrochemical immunosensor and biochemical analysis for carcinoembryonic antigen in clinical diagnosis. Microchim Acta 163:41
Ryu K, Kazuma M, Bjorn R, Takehiko T, Takehiko K (2009) Integration of immunoassay into extended nanospace. Microchim Acta 164:307
Amine A, Brett C, Palleschi G (2008) Third international workship on biosensor for food safety and environmental monitoring Fez, Morocco, 18–20 October 2007. Microchim Acta 163:147
Wang L, Gan X (2009) Antibody-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for electrochemical immunoassay of fetoprotein in human serum. Microchim Acta 164:231
Tang D, Yuan R, Chai Y (2006) Magnetic core-shell Fe3O4@Ag nanoparticles coated carbon paste interface for studies of carcinoembryonic antigen in clinical immunoassay. J Phys Chem B 110:11640
AM Usamni, N Akmal (1994) Thin-layer flow-through enzyme immunosensor based on polycaprolactam net. Diagnositic Biosensor Polymers, ACS Symposim Series 556: 96
Yuan R, Tang D, Chai Y, Zhong X, Liu Y, Dai J (2004) Ultrasensitive potentiometric immunosensor based on SA and OCA techniques for immobilization of HBsAb with colloidal Au and polyvinyl butyral as matrixes. Langmuir 20:7240
Tang D, Li H, Liao J (2009) Ionic liquid and nanogold-modified immunosensing interface for electrochemical immunoassay of hepatitis B surface antigen in human serum. Microfluid Nanofluid 6:403
Vu B, Litvinov D, Willson R (2008) Gold nanoparticle effects in polymerase chain reaction favoring of smaller products by polymerase adsorption. Anal Chem 80:5462
Wang F, Hu S (2009) Electrochemical sensors based on metal and semicondutor nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 165:1
Zhang T, Yuan R, Chai Y, Liu K, Ling S (2009) Study on an immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles and a nano-calcium carbonate/Prussian blue modified glassy carbon electrode. Microchim Acta 165:53
Gun J, Rizkov D, Lev O, Abouzar M, Poghossian A, Schoning M (2009) Oxygen plasma-treated gold nanoparticle-based field-effect devices as transducer structures for bio-chemical sensing. Microchim Acta 164:395
Thibault S, Aubriet H, Arnoult C, Ruch D (2008) Gold nanoparticles and a glucose oxidase based biosensor: an attempt to follow-up and by XPS. Microchim Acta 163:211
Sadik O, Aluoch A, Zhou A (2009) Status of biomolecular recognition using electrochemical techniques. Biosens Bioelectron 24:2749
Kundu V, Mukherji S (2009) Novel U-bent fiber optic probe for localized surface plasmon resonance based biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 24:2804
Das J, Aziz M, Yang H (2006) A nanocatalyst-based assay for proteins: DNA-free ultrasensitive electrochemical detection using catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol by gold-nanoparticle label. J Am Chem Soc 128:16022
Ambrosi A, Castaneda M, Killard A, Smyth M, Alegret S, Merkoci A (2007) Double-codified gold nanolabels for enhanced immunoanalysis. Anal Chem 79:5232
Wang J, Xu D, Polsky R (2002) Magnetically-induced solid-state electrochemical detection of DNA hybridization. J Am Chem Soc 124:4208
Pang DW, Abruna HD (2000) Interactions of benzyl viologen with surface-bound single- and double-stranded DNA. Anal Chem 72:4700
Tang D, Yuan R, Chai Y, Dai J, Zhong X, Liu Y (2004) A novel immunosensor based on immobilization of hepatitis B surface antibody on platinum electrode modified colloidal gold and polyvinyl butyral as matrices via electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Bioeletrochemistry 65:15
Bi S, Yan Y, Yang X, Zhang S (2009) Gold nanolabels for new enhanced chemiluminescence immunassay of alpha-fetoprotein based on magnetic beads. Chem Eur J 15:4704
Tang D, Zhong Z, Niessner R, Knopp D (2009) Multifunctional magnetic bead-based electrochemical immunoassay for the detection of aflatoxin B1 in food. Analyst . doi:10.1039/b902401h
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.30670628) and Military Medical Research Foundation of China (06MA188).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Wu and Zhong contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, S., Zhong, Z., Wang, D. et al. Gold nanoparticle-labeled detection antibodies for use in an enhanced electrochemical immunoassay of hepatitis B surface antigen in human serum. Microchim Acta 166, 269–275 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-009-0184-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-009-0184-9