Abstract.
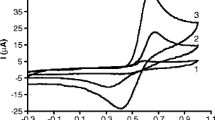
Cinnamtannin B1 (trimeric proanthocyanidin), which is identified and isolated from the effective fraction of the root of Lindera aggregata (Sims) Kosterm, is one kind of condensed tannin used as an effective antipyrotic and antitumor agent. Its electrochemical response can be obtained at a pyrolytic graphite electrode. Consequently, an easily performed and sensitive method for the determination of cinnamtannin B1 is developed. The detection limit is estimated to be 1.0 × 10−7 M with the linear determination range of 2.0 × 10−7 M to 1.8 × 10−6 M. Five replicate analyses of 1.0 × 10−6 M cinnamtannin B1 yields an RSD value of 2.1%. Since the working electrode does not need to be modified with any other species, it is very stable, repeatable and easily treated, and this method therefore potentially useful in real sample analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Chen, T., Hoshi, T. et al. Electrochemical Determination of Cinnamtannin B1 with a Pyrolytic Graphite Electrode. Microchim Acta 150, 73–76 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-005-0329-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-005-0329-4