Summary.
Permeability is a physical property in rocks of extreme importance in energy engineering, civil and environmental engineering, and various areas of geology. Early on, fractures in fluid flow models were assumed to be rigid. However, experimental research and field data confirmed that stress-deformation behavior in fractures is a key factor governing their permeability tensor. Although extensive research was conducted in the past, the three-dimensional stress-permeability relationships, particularly in the inelastic deformation stage, still remain unclear. In this paper, laboratory experiments conducted on large concrete blocks with randomly distributed fractures and rock core samples are reported to investigate fluid flow and permeability variations under uniaxial, biaxial and triaxial complete stress-strain process. Experimental relationships among flowrate, permeability and fracture aperture in the fractured media are investigated. Results show that the flowrate and stress/aperture exhibit “cubic law” relationship for the randomly distributed fractures.
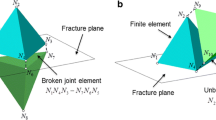
A permeability-aperture relationship is proposed according to the experimental results. Based on this relationship, stress-dependent permeability in a set of fractures is derived in a three-dimensional domain by using a coupled stress and matrix-fracture interactive model. A double porosity finite element model is extended by incorporating such stress-dependent permeability effects. The proposed model is applied to examine permeability variations induced by stress redistributions for an inclined borehole excavated in a naturally fractured formation. The results indicate that permeability around underground openings depends strongly on stress changes and orientations of the natural fractures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Bai D. Elsworth (1994) ArticleTitleModeling of subsidence and stress-dependent hydraulic conductivity for intact and fractured porous media Rock Mech. Rock Engng. 27 IssueID4 209–234 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01020200
M. Bai Y. Abousleiman L. Cui J. Zhang (1999) ArticleTitleDual-porosity poroelastic modelling of generalized plane strain Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 36 1087–1094 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1365-1609(99)00065-9
N. Barton S. Bandis K. Bakhtar (1985) ArticleTitleStrength, deformation and conductity coupling of rock joints Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 22 231–245 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0148-9062(85)93227-9
W. F. Bawden J. H. Curran J.-C. Roegiers (1980) ArticleTitleInfluence of fracture deformation on secondary permeability – a numerical approach Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 17 265–279 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0148-9062(80)90809-8
J. Bear C.-F. Tsang G. de Marsily (1993) Flow and contaminant transport in fractured rock Academic Press San Diego
A. J. Bolton (2000) ArticleTitleSome measurements of permeability and effective stress on a heterogeneous soil mixture: implications for recovery of inelastic strains Engng. Geol. 57 95–104 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0013-7952(00)00019-3
Bradley, W. B. (1979) Failure of inclined boreholes, Trans. ASME 101, 232–239.
Cammarata, G., Fidelibus, C., Cravero, M., Barla, G. (2006) The hydro-mechanically coupled response of rock fractures. Rock Mech. Rock Engng. DOI 10.1007/s00603-006-0081-z
M. S. Diederichs (2003) ArticleTitleRock fracture and collapse under low confinement conditions Rock Mech. Rock Engng. 36 IssueID5 339–381 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00603-003-0015-y
A. F. Gangi (1978) ArticleTitleVariation of whole- and fractured-porous-rock permeability with confining pressure Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 15 249–257 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0148-9062(78)90957-9
R. E. Goodman (1976) Methods of geological engineering in discontinuous rocks West Publishing New York
J. Heiland (2003) ArticleTitleLaboratory testing of coupled hydro-mechanical processes during rock deformation Hydrogeology J. 11 122–141
Iwai, K. (1976): Fundamental studies of fluid flow through a single fracture. Ph.D. dissertation, Univ. of California, Berkeley.
J. C. Jaeger N. G. W. Cook (1979) Fundamentals of rock mechanics EditionNumber3 Chapman & Hall London
Jones, F. O. (1975): A laboratory study of the effects of confining pressure on fracture flow and storage in carbonate rocks. J Petrol. Technol. Jan., 21–27.
P. C. Kelsall J. B. Case C. R. Chabannes (1984) ArticleTitleEvaluation of excavation-induced changes in rock permeability Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 21 123–135 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0148-9062(84)91530-4
R. L. Kranz A. D. Frankel T. Engelder C. H. Schulz (1979) ArticleTitleThe permeability of whole and jointed Barre granite Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 16 225–234 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0148-9062(79)91197-5
C.-H. Lee I. Farmer (1993) Fluid flow in discontinuous rocks Chapman & Hall London
S. P. Li Y. S. Li Z. Y. Wu (1994) ArticleTitlePermeability-strain equations corresponding to the complete stress–strain path of Yinzhuang sandstone Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 31 383–391 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0148-9062(94)90906-7
C. Louis (1974) Rock hydraulics L. Müller (Eds) Rock mechanics Springer Wien New York 299–382
J. B. Martin N. A. Chandler (1994) ArticleTitleThe progressive fracture of Lac du Bonnet granite Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 31 643–659 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0148-9062(94)90005-1
K.-B. Min J. Rutqvist C.-F. Tsang L. Jing (2004) ArticleTitleStress-dependent permeability of fractured rock masses: a numerical study Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 41 1191–1210 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.05.005
R. Pusch (1989) ArticleTitleAlteration of the hydraulic conductivity of rock by tunnel excavation Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 26 79–83 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0148-9062(89)90528-7
Pyrak-Nolte, L. J., Myer, L. R., Cook, N. G. W., Witherspoon, P. A. (1987): Hydraulic and mechanical properties of natural fractures in low permeability rock. In: Herger, G., Vongpaisal, S. (eds.), Proc., 6th Int. Society of Rock Mech. vol. 2. Balkema, Rotterdam, 225–231.
K. G. Raven J. E. Gale (1985) ArticleTitleWater flow in a natural fracture as a function of stress and sample size Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 22 251–261 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0148-9062(85)92952-3
J. Rutqvist O. Stephansson (2003) ArticleTitleThe role of hydromechanical coupling in fractured rock engineering Hydrogeology J. 11 7–40
O. Schulze T. Popp H. Kern (2001) ArticleTitleDevelopment of damage and permeability in deforming rock salt Engng. Geol. 61 163–180 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0013-7952(01)00051-5
S. Sisavath X. D. Jing R. W. Zimmerman (2000) ArticleTitleEffect of stress on the hydraulic conductivity of rock pores Phys. Chem. Earth (A) 25 163–168 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1464-1895(00)00026-0
Y. W. Tsang P. A. Witherspoon (1981) ArticleTitleHydromechanical behavior of a deformable rock fracture subject to normal stress J. Geophys. Res. B86 9287–9298
M. E. Waite S. Ge H. A. Spetzler (1999) ArticleTitleA new conceptual model for fluid flow in discrete fractures: an experimental and numerical study J. Geophys. Res. 104 IssueIDB6 13049–13059 Occurrence Handle10.1029/1998JB900035
J. B. Walsh (1981) ArticleTitleEffect of pore pressure and confining stress on fracture permeability Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 18 429–435 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0148-9062(81)90006-1
J. A. Wang H. D. Park (2002) ArticleTitleFluid permeability of sedimentary rocks in a complete stress-strain process Engng. Geol. 63 291–300 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0013-7952(01)00088-6
P. A. Witherspoon J. S. Y. Wang K. Iwai J. E. Gale (1980) ArticleTitleValidity of cubic law for fluid flow in a deformable rock fracture Water Resour. Res. 16 IssueID6 1016–1024
Zhang, J. (2002): Dual-porosity approach to wellbore stability in naturally fractured reservoirs. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Oklahoma, Norman.
Zhang, J., Bai, M., Roegiers, J.-C., Wang, J., Liu, T. (2000): Experimental determination of stress-permeability relationship. In: Girand et al. (eds), Pacific Rocks 2000, Balkema, Rotterdam.
J. Zhang M. Bai J.-C. Roegiers (2003) ArticleTitleDual-porosity poroelastic analyses of wellbore stability Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 40 473–483 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1365-1609(03)00019-4
J. Zhang J.-C. Roegiers (2005) ArticleTitleDouble porosity finite element method for borehole modeling Rock Mech. Rock Engng. 38 217–242 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00603-005-0052-9
J. Zhang J.-C. Roegiers H. A. Spetzler (2004) ArticleTitleInfluences of stress on permeability around a borehole in fractured porous media Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 41 IssueID3 454 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.ijrmms.2003.12.116
W. Zhu T.-F. Wong (1997) ArticleTitleThe transition from brittle faulting to cataclastic flow: permeability evolution J. Geophys. Res. 102 IssueIDB2 3027–3041 Occurrence Handle10.1029/96JB03282
R. W. Zimmerman G. S. Bodvarsson (1996) ArticleTitleHydraulic conductivity of rock fractures Transp. Porous Media. 23 1–30 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00145263
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Standifird, W., Roegiers, JC. et al. Stress-Dependent Fluid Flow and Permeability in Fractured Media: from Lab Experiments to Engineering Applications. Rock Mech. Rock Engng. 40, 3–21 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-006-0103-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-006-0103-x