Abstract
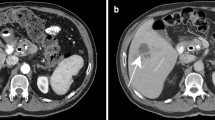
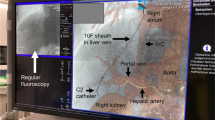
Microwave coagulation therapy (MCT) is one of the treatment modalities for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). A 67-year-old man with liver cirrhosis underwent MCT during a laparotomy for a deeply located HCC (2.5 cm in diameter) at the border of the anterior and posterior segments of the right hepatic lobe. Two weeks after MCT, he complained of abdominal fullness. Portal vein thrombosis (PVT) was diagnosed because he had massive ascites and an echogenic mass in the portal vein on abdominal ultrasonography. PVT was successfully treated by fibrinolytic therapy with a selective infusion of urokinase via the superior mesenteric artery (SMA). There have been few reports on PVT as a complication of MCT. Attention should be paid to the possible occurrence of PVT as a critical complication after MCT for liver tumors adjacent to the portal vein. Fibrinolytic therapy via the SMA is thus considered to be an effective approach for PVT after MCT.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: July 19, 1999 / Accepted: March 24, 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kojima, Y., Suzuki, S., Sakaguchi, T. et al. Portal Vein Thrombosis Caused by Microwave Coagulation Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Report of a Case. Surg Today 30, 844–848 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005950070071
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005950070071