Abstract
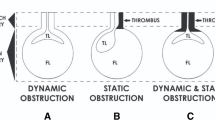
Cerebral malperfusion in association with acute type A aortic dissection is uncommon but can have a considerable effect on the outcome of treatment. Successful treatment requires the individual and effective removal of each of the factors associated with malperfusion. In addition to the conventional surgical procedures, endovascular treatment has become an option for restoring perfusion. However, artificial perfusion and/or surgical procedures can lead to new malperfusion, which is not necessarily apparent to surgeons and which is difficult to predict. Thus, a number of modalities need to be applied to monitoring the current status of perfusion to enable timely treatment. Since each of the diagnostic modalities has its merits and demerits, one should use them effectively while being mindful of the pitfalls. In addition, a delay in the diagnosis in the pre-hospital stage is an important determinant of the surgical outcomes of aortic dissection. Portable echocardiography, which has been recently developed, may be useful for improving this situation. However, an early diagnosis largely depends on the physician’s awareness and basic echocardiography skills. Surgeons should make general physicians aware of this message.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bossone E, Corteville DC, Harris KM, Suzuki T, Fattori R, Hutchison S, et al. Stroke and outcomes in patients with acute type A aortic dissection. Circulation. 2013;128(11 Suppl 1):S175–9.
Girdauskas E, Kuntze T, Borger MA, Falk V, Mohr FW. Surgical risk of preoperative malperfusion in acute type A aortic dissection. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009;138:1363–9.
Krüger T, Weigang E, Hoffmann I, Blettner M, Aebert H. Cerebral protection during surgery for acute aortic dissection type A: results of the German Registry for Acute Aortic Dissection Type A (GERAADA). Circulation. 2011;124:434–43.
Haldenwang PL, Wahlers T, Himmels A, Wippermann J, Zeriouh M, Kröner A, et al. Evaluation of risk factors for transient neurological dysfunction and adverse outcome after repair of acute type A aortic dissection in 122 consecutive patients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012;42:e115–20.
Harrington DK, Ranasinghe AM, Shah A, Oelofse T, Bonser RS. Recommendations for haemodynamic and neurological monitoring in repair of acute type A aortic dissection. Anesthesiol Res Pract. 2011;2011:949034.
Masuda M, Kuwano H, Okumura M, Amano J, Arai H, Endo S, et al. Thoracic and cardiovascular surgery in Japan during 2012: annual report by The Japanese Association for Thoracic Surgery. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;62:734–64.
Mészáros I, Mórocz J, Szlávi J, Schmidt J, Tornóci L, Nagy L, et al. Epidemiology and clinicopathology of aortic dissection. Chest. 2000;117:1271–8.
Pocar M, Passolunghi D, Moneta A, Mattioli R, Donatelli F. Coma might not preclude emergency operation in acute aortic dissection. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;81:1348–51.
Iliescu VA, Dorobantu LF, Stiru O, Bubenek S, Miclea I, Rugina M, et al. Combined cardiac-neurosurgical treatment of acute aortic dissection, stroke, and coma. Tex Heart Inst J. 2008;35:200–2.
Pocar M, Passolunghi D, Moneta A, Donatelli F. Recovery of severe neurological dysfunction after restoration of cerebral blood flow in acute aortic dissection. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010;10:839–41.
Morimoto N, Okada K, Okita Y. Lack of neurologic improvement after aortic repair for acute type A aortic dissection complicated by cerebral malperfusion: predictors and association with survival. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;142:1540–4.
Nakamura Y, Tagusari O, Ichikawa Y, Morita A. Impact of immediate aortic repair on early and midterm neurologic status in patients with acute type A aortic dissection complicated by cerebral malperfusion. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;92:336–8.
Tsukube T, Hayashi T, Kawahira T, Haraguchi T, Matsukawa R, Kozawa S, et al. Neurological outcomes after immediate aortic repair for acute type A aortic dissection complicated by coma. Circulation. 2011;124(11 Suppl):S163–7.
Tsukube T, Haraguchi T, Okada Y, Matsukawa R, Kozawa S, Ogawa K, et al. Long-term outcomes after immediate aortic repair for acute type A aortic dissection complicated by coma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;148:1013–8.
Rylski B, Urbanski PP, Siepe M, Beyersdorf F, Bachet J, Gleason TG, et al. Operative techniques in patients with type A dissection complicated by cerebral malperfusion. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014;46:156–66.
Ren Z, Wang Z, Hu R, Wu H, Deng H, Zhou Z et al. Which cannulation (axillary cannulation or femoral cannulation) is better for acute type A aortic dissection repair? A meta-analysis of nine clinical studies. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014. (Epub ahead of print).
Shimokawa T, Takanashi S, Ozawa N, Itoh T. Management of intraoperative malperfusion syndrome using femoral artery cannulation for repair of acute type A aortic dissection. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;85:1619–24.
Orihashi K, Sueda T, Okada K, Imai K. Detection and monitoring of complications associated with femoral or axillary arterial cannulation for surgical repair of aortic dissection. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2006;20:20–5.
Imanaka K, Kawata M, Matsuoka T, Yamabi H. Uncertainty of axillary artery perfusion during surgery for acute aortic dissection. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014;97:1781–2.
Luciani N, Anselmi A, Glieca F, Lauria G, de Geest R, Possati G. Femoral cannulation with long arterial cannula in aortic dissection. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;93:e45–7.
Orihashi K, Sueda T, Okada K, Imai K. Newly developed aortic dissection in the abdominal aorta after femoral arterial perfusion. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;79:1945–9.
Moizumi Y, Motoyoshi N, Sakuma K, Yoshida S. Axillary artery cannulation improves operative results for acute type a aortic dissection. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;80:77–83.
Tiwari KK, Murzi M, Bevilacqua S, Glauber M. Which cannulation (ascending aortic cannulation or peripheral arterial cannulation) is better for acute type A aortic dissection surgery? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010;10:797–802.
Pasic M, Schubel J, Bauer M, Yankah C, Kuppe H, Weng YG, et al. Cannulation of the right axillary artery for surgery of acute type A aortic dissection. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2003;24:231–5.
Do YW, Kim GJ, Park I, Cho JY, Lee JT. Direct axillary arterial cannulation using Seldinger’s technique in aortic dissection. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;44:338–42.
Hillebrand J, Konerding MA, Koch M, Kaufmann T, Steinseifer U, Moritz A, et al. Anatomic and flow dynamic considerations for safe right axillary artery cannulation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013;146:467–71.
Attaran S, Safar M, Saleh HZ, Field M, Kuduvalli M, Oo A. Cannulating a dissecting aorta using ultrasound-epiaortic and transesophageal guidance. Heart Surg Forum. 2011;14:E373–5.
Inoue Y, Takahashi R, Ueda T, Yozu R. Synchronized epiaortic two-dimensional and color Doppler echocardiographic guidance enables routine ascending aortic cannulation in type A acute aortic dissection. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;141:354–60.
Khaladj N, Shrestha M, Peterss S, Strueber M, Karck M, Pichlmaier M, et al. Ascending aortic cannulation in acute aortic dissection type A: the Hannover experience. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008;34:792–6.
Matsushita A, Manabe S, Tabata M, Fukui T, Shimokawa T, Takanashi S. Efficacy and pitfalls of transapical cannulation for the repair of acute type A aortic dissection. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;93:1905–9.
Orihashi K, Sueda T, Okada K, Takahashi S. Compressed true lumen in the innominate artery: a pitfall of right axillary arterial perfusion in acute aortic dissection. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009;137:242–3.
Igarashi T, Takahashi S, Takase S, Yokoyama H. Intraoperative thrombectomy for occluded carotid arteries in patients with acute aortic dissection: report of two cases. Surg Today. 2014;44:1177–9.
Orihashi K. Malperfusion in acute type A aortic dissection: unsolved problem. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;95:1570–6.
Ueyama K, Otaki K, Koyama M, Kamiyama H. Urgent simultaneous revascularization of the carotid artery and ascending aortic replacement for type A acute aortic dissection with cerebral malperfusion. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;55:284–6.
Urbanski PP. Carotid artery cannulation in acute aortic dissection with malperfusion. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006;131:1398–9.
Sakaguchi G, Komiya T, Tamura N, Obata S, Masuyama S, Kimura C, et al. Cerebral malperfusion in acute type A dissection: direct innominate artery cannulation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;129:1190–1.
Munakata H, Okada K, Kano H, Izumi S, Hino Y, Matsumori M, et al. Controlled earlier reperfusion for brain ischemia caused by acute type A aortic dissection. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;87:e27–8.
Kim SH, Song S, Kim SP, Lee J, Lee HC, Kim ES. Hybrid technique to correct cerebral malperfusion following repair of a type A aortic dissection. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;47:163–6.
Casana R, Tolva V, Majnardi AR, Bianchi PG, Addobati L, Bertoni GB, et al. Endovascular management of symptomatic cerebral malperfusion due to carotid dissection after type A aortic dissection repair. Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011;45:641–5.
Roseborough GS, Murphy KP, Barker PB, Sussman M. Correction of symptomatic cerebral malperfusion due to acute type I aortic dissection by transcarotid stenting of the innominate and carotid arteries. J Vasc Surg. 2006;44:1091–6.
Takahashi S, Katayama K, Takasaki T, Sueda T. Endovascular repair for retrograde type A aortic dissection with malperfusion. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2014. (Epub ahead of print).
Fukada J, Morishita K, Kawaharada N, Yamauchi A, Hasegawa T, Satsu T, et al. Isolated cerebral perfusion for intraoperative cerebral malperfusion in type A aortic dissection. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;75:266–8.
Andropoulos DB, Stayer SA, Diaz LK, Ramamoorthy C. Neurological monitoring for congenital heart surgery. Anesth Analg. 2004;99:1365–75.
Levy WJ, Levin S, Chance B. Near-infrared measurement of cerebral oxygenation: correlation with electroencephalographic ischemia during ventricular fibrillation. Anesthesiology. 1995;83:738–46.
Orihashi K, Sueda T, Okada K, Imai K. Near-infrared spectroscopy for monitoring cerebral ischemia during selective cerebral perfusion. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004;26:907–11.
Estrera AL, Garami Z, Miller CC 3rd, Sheinbaum R, Huynh TT, Porat EE, et al. Cerebral monitoring with transcranial Doppler ultrasonography improves neurologic outcome during repairs of acute type A aortic dissection. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;129:277–85.
Orihashi K, Matsuura Y, Sueda T, Shikata H, Morita S, Hirai S, et al. Flow velocity of central retinal artery and retrobulbar vessels during cardiovascular operations. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1997;114:1081–7.
Orihashi K, Matsuura Y, Sueda T, Shikata H, Watari M, Okada K. Clinical implication of orbital ultrasound monitoring during selective cerebral perfusion. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;71:673–7.
Pulido JN, Pallohusky BS, Park SJ, Cook DJ. Transcutaneous ultrasound measurements of carotid flow to monitor for cerebral malperfusion during type-A aortic dissection repair. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2013;27:728–30.
Augoustides JG, Kohl BA, Harris H, Pochettino A. Color-flow Doppler recognition of intraoperative brachiocephalic malperfusion during operative repair of acute type A aortic dissection: utility of transcutaneous carotid artery ultrasound scanning. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2007;21:81–4.
Orihashi K, Matsuura Y, Sueda T, Watari M, Okada K, Sugawara Y, et al. Aortic arch branches are no longer blind zone for transesophageal echocardiography: a new eye for aortic surgeons. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000;120:466–72.
Orihashi K, Sueda T, Okada K, Imai K. Left internal thoracic artery graft assessed by means of intraoperative transesophageal echocardiography. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;79:580–4.
Orihashi K, Sueda T, Okada K, Imai K. Malposition of selective cerebral perfusion catheter is not a rare event. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2005;27:644–8.
Kano M, Chikugo F, Shimahara Y, Urata M, Hayamizu T. Left axillary artery perfusion in surgery of type A aortic dissection. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;14:22–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orihashi, K. Cerebral malperfusion in acute aortic dissection. Surg Today 46, 1353–1361 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-016-1381-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-016-1381-x