Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the effectiveness of resecting liver metastases of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), when performed in conjunction with imatinib treatment.
Methods
Forty-one patients with pathologically diagnosed GIST and liver metastases were randomly assigned to an operation group (neoadjuvant therapy + resection + adjuvant therapy with imatinib) or a nonoperation group (imatinib alone). Patients were monitored for up to 36 months, and survival was analyzed.
Results
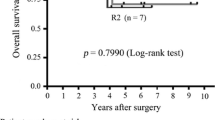
We monitored 39 patients throughout the 36-month follow-up period, recording 1- and 3-year survival rates of 100% and 89.5% in the operation group and 85% and 60% in the nonoperation group, respectively. There was a significant difference in overall survival between the operation and nonoperation groups (P = 0.03). Furthermore, resection improved the survival of patients who responded poorly to 6 months of preoperative imatinib treatment, compared with that of their counterparts in the nonoperation group (P = 0.04).
Conclusion
These findings suggest that surgical intervention in combination with imatinib treatment is more effective than imatinib alone against GIST liver metastases, with minimal complications and side effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eisenberg BL, Judson I. Surgery and imatinib in the management of GIST: emerging approaches to adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapy. Ann Surg Oncol 2004;11:465–475.
DeMatteo RP, Lewis JJ, Leung D, Mudan SS, Woodruff JM, Brennan MF. Two hundred gastrointestinal stromal tumors: recurrence patterns and prognostic factors for survival. Ann Surg 2000;231:51–58.
Demetri GD, von Mehren M, Blanke CD, Van den Abbeele AD, Eisenberg B, Roberts PJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of imatinib mesylate in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. N Engl J Med 2002;347:472–480.
Goss GA, Merriam P, Manola J, Singer S, Fletcher CD, Demetri GD. Clinical and pathological characteristics of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST). Prog Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 2000;19:599.
Joensuu H, Fletcher C, Dimitrijevic S, Silberman S, Roberts P, Demetri G. Management of malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Lancet Oncol 2002;3:655–664.
Ebihara Y, Okushiba S, Kawarada Y, Kitashiro S, Katoh H, Kondo S. Neoadjuvant imatinib in a gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the rectum: report of a case. Surg Today 2008;38:174–177.
Nowain A, Bhakta H, Pais S, Kanel G, Verma S. Isolated hepatic metastasis from a gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) 17 years after initial resection: need for long-term surveillance. J Clin Gastroenterol 2005;39:925.
Nunobe S, Sano T, Shimada K, Sakamoto Y, Kosuge T. Surgery including liver resection for metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors or gastrointestinal leiomyosarcomas. Jpn J Clin Oncol 2005;35:338–341.
Choi H, Charnsangavej C, Macapinlac H, Burgess M, Patel S, Chen L, et al. Correlation of computerized tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) in patients with metastatic GIST treated at a single institution with imatinib mesylate (abstract 3290). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 2003;22:819.
DeMatteo RP, Owzar K, Antonescu CR, Maki R, Demetri GD, McCarter M, et al. Efficacy of adjuvant imatinib mesylate following complete resection of localized, primary gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) at high risk of recurrence: The U.S. Intergroup phase II trial ACOSOG Z9000. American Society of Clinical Oncology 2008 Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium, 25–27 January 2008, Orlando, FL, 2008. A–8.
Zhan WH, China Gastrointestinal Cooperative Group. Efficacy and safety of adjuvant post-surgical therapy with imatinib in patients with high risk of relapsing GIST (abstract 10045). J Clin Oncol 2007;25:556.
DeMatteo RP, Ballman KV, Antonescu CR, Maki RG, Pisters PW, Demetri GD, et al. Adjuvant imatinib mesylate after resection of localised, primary gastrointestinal stromal tumour: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2009;373:1097–1104.
Eisenberg BL, Harris J, Blanke CD, Demetri GD, Heinrich MC, Watson JC, et al. Phase II trial of neoadjuvant/adjuvant imatinib mesylate (IM) for advanced primary and metastatic/recurrent operable gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST): early results of RTOG 0132/ACRIN 6665. J Surg Oncol 2009;99:42–47.
Andtbacka RH, Ng CS, Scaife CL, Cormier JN, Hunt KK, Pisters PW, et al. Surgical resection of gastrointestinal stromal tumors after treatment with imatinib. Ann Surg Oncol 2007;14:14–24.
Haller F, Detken S, Schulten HJ, Happel N, Gunawan B, Kuhlgatz J, et al. Surgical management after neoadjuvant imatinib therapy in gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GISTs) with respect to imatinib resistance caused by secondary KIT mutations. Ann Surg Oncol 2007;14:526–532.
Gold JS, DeMatteo RP. Neoadjuvant therapy for gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST): racing against resistance. Ann Surg Oncol 2007;14:1247–1248.
Blanke CD, Demetri GD, Von MM, Heinrich MC, Eisenberg B, Fletcher JA, et al. Long-term results from a randomized phase II trial of standard-versus higher-dose imatinib mesylate for patients with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors expressing KIT. J Clin Oncol 2008;26:620–625.
Blanke CD, Rankin C, Demetri GD, Ryan CW, von Mehren M, Benjamin RS, et al. Phase III randomized, intergroup trial assessing imatinib mesylate at two dose levels in patients with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors expressing the kit receptor tyrosine kinase: S0033. J Clin Oncol 2008;26:626–632.
Zalcberg JR, Verweij J, Casali PG, Cesne AL, Reichardt P, Blay JY, et al. Outcome of patients with advanced gastro-intestinal stromal tumours crossing over to a daily imatinib dose of 800 mg after progression on 400 mg. Eur J Cancer 2005;41:1751–1757.
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 2000;92:205–216.
Choi H, Charnsangavej C, Faria SC, Macapinlac HA, Burgess MA, Patel SR, et al. Correlation of computed tomography and positron emission tomography in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor treated at a single institution with imatinib mesylate: proposal of new computed tomography response criteria. J Clin Oncol 2007;25:1753–1759.
Gayed I, Vu T, Iyer R, Johnson M, Macapinlac H, Swanston N, et al. The role of 18F-FDG PET in staging and early prediction of response to therapy of recurrent gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Nucl Med 2004;45:17–21.
Goerres GW, Stupp R, Barghouth G, Hany TF, Pestalozzi B, Dizendorf E, et al. The value of PET, CT and in-line PET/CT in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumours: long-term outcome of treatment with imatinib mesylate. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2005;32:153–162.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, L., Zhang, MM., Ji, L. et al. Resection combined with imatinib therapy for liver metastases of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Surg Today 40, 936–942 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-009-4171-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-009-4171-x