Abstract
Purpose
It is predictable that since distal gastrectomy (DG) with Billroth I anastomosis involves no procedures caudal to transverse colon, the effects of the surgical wound are the main cause of adhesive obstruction. Thus, it is an appropriate operation to test the efficiency of a synthetic absorbable adhesion barrier (Seprafilm).
Methods
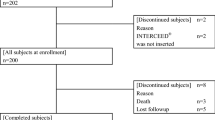
The subjects were 282 patients diagnosed with gastric cancer who underwent open DG with Billroth I anastomosis between 2001 and August, 2005. Seprafilm was not used in any patients operated on before April, 2003 (n = 169), but it was used in all patients operated on from May 2003 onward (n = 113). We retrospectively compared the incidences of adhesive obstruction in the Seprafilm group and the non-Seprafilm group.
Results
The cumulative incidence of adhesive obstruction was significantly lower in the Seprafilm group than in the non-Seprafilm group (P = 0.021). The respective incidences of adhesive obstruction 2 years after surgery were 0.9% and 6.5%. Multivariate analysis of the occurrence of adhesive obstruction revealed no significant differences in sex, age, body mass index, operation time, blood loss, or degree of lymph-node dissection; however, it revealed a significant difference in relation to the use of Seprafilm (P = 0.049).
Conclusion
In this series, Seprafilm reduced the incidence of adhesive obstruction after DG significantly; however, a prospective randomized study will be necessary to confirm this result.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker JM, Dayton MT, Fazio VW, Beck DE, Stryker SJ, Wexner SD, et al. Prevention of postoperative abdominal adhesions by a sodium hyaluronate-based bioresorbable membrane: a prospective, randomized, double-blind multicenter study. J Am Coll Surg 1996;183:297–306.
Diamond MP, The Seprafilm Adhesion Study Group. Reduction of adhesions after uterine myomectomy by Seprafilm membrane (HAL-F): a blinded, prospective, randomized, multicenter clinical study. Fertil Steril 1996;66:904–910.
Salum MR, Lam DT, Wexner SD, Pikarsky A, Khurrum M, Weiss EG, et al. Does limited placement of bioresorbable membrane of modified sodium hyaluronate and carboxymethylcellulose (Sepra-film) have possible short-term beneficial impact? Dis Colon Rectum 2001;44:706–712.
Vrijland WW, Tseng LNL, Eijkman HJM, Hop WCJ, Jakimowicz JJ, Leuguit P, et al. Fewer intraperitoneal adhesions with use of hyaluronic acid-carboxymethylcellulose membrane: a randomized clinical trial. Ann Surg 2002;235:193–199.
Kusunoki M, Ikeuchi H, Yanagi H, Noda M, Tonouchi H, Mohri Y, et al. Bioresorbable hyaluronate-carboxymethylcellulose membrane (Seprafilm) in surgery for rectal carcinoma: a prospective randomized clinical trial. Surg Today 2005;35:940–945.
Fazio VW, Cohen Z, Fleshman JW, Goor H, Bauer JJ, Wolff BG, et al. Reduction in adhesive small-bowel obstruction by Seprafilm adhesion barrier after intestinal resection. Dis Colon rectum 2005;49:1–11.
Hayashi S, Takayama T, Masuda H, Kochi M, Ishii Y, Matsuda M, et al. Bioresorbable membrane to reduce postoperative small bowel obstruction in patients with gastric cancer. A randomized clinical trial. Ann Surg 2008;247:766–770.
Takahashi T, Saikawa Y, Yoshida M, Otani Y, Kubota T, Kumai K, et al. Mechanical-stapled versus hand-sutured anastomosis in Billroth-I reconstruction with distal gastrectomy. Surg Today 2007;122-6.
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma. 2nd English edition. Gastric Cancer 1998;1:10–24.
Beck DE, Opelka FG, Bailey HR, Rauth SM, Pashos CL. Incidence of small-bowel obstruction and adhesiolysis after open colorectal and general surgery. Dis Colon Rectum 1999;42:241–248.
Nashimoto A, Morota T, Yabuzaki Y, Tsutiya Y, Tanaka O, Sasaki T. Investigation of postoperative ileus after gastrectomy and prevention of ileus by limited surgery for early gastric cancer. Jpn J Gastroenterol Surg 2000;33:1445–1460.
Shimizu K, Yoshida K, Hirai T, Touge T. relationship between surgical approach and postoperative ileus in gastric cancer. Nippon Rynsyogeka Gakkai Zasshi 2003;64:801–804.
Koyama N, Yoshida H, Yamashita N, Kojima T, Nakayama K, Watanabe M, et al. Postoperative bowel obstruction after gastrectomy and prevention of abdominal adhesions by sodium hyaluronate-based bioresorbable membrane. Gekarinsho 2003;89:481–484.
Harris DA, Topley N. Peritoneal adhesion. Br J Surg 2008;95:271–272.
Fujita J, Tsukahara Y, Ikeda K, Akagi K, Kan K, Hata S, et al. Evaluation of omentum preserving gastrectomy for advanced gastric cancer 2003;36:1151–1158.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawamura, H., Yokota, R., Yokota, K. et al. A sodium hyaluronate carboxymethylcellulose bioresorbable membrane prevents postoperative small-bowel adhesive obstruction after distal gastrectomy. Surg Today 40, 223–227 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-008-4059-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-008-4059-1