Abstract
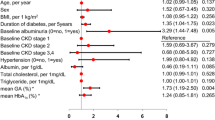
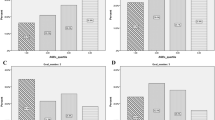
We measured serum concentrations of advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs) in patients with type 2 diabetes, to elucidate the mechanisms underlying the elevated serum concentrations of AGEs and to clarify the relationship between serum AGE concentrations and the development of microangiography and macroangiopathy. Serum AGEs were significantly higher in diabetic patients than in age-matched control subjects (p < 0.0001). In diabetic patients, serum AGEs were positively correlated with HbA1c (r = 0.47, p < 0.0001), urinary albumin excretion (UAE) (r = 0.42, p < 0.0001), diabetes duration (r = 0.31, p = 0.0030), and fasting plasma glucose (r = 0.34, p = 0.0010). Multiple regression analysis disclosed that only the HbA1c and UAE levels independently correlated with serum AGE levels. Serum AGEs in diabetic patients with progressive retinopathy and overt nephropathy were significantly higher than in those with less severe retinopathy and nephropathy. Serum AGEs were significantly higher in the diabetic patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) than in those without CHD. These results suggest that the HbA1c and UAE levels are independent risk factors for increased serum AGE concentrations in type 2 diabetic patients, and that higher serum AGE concentrations are associated with increased severity of diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy. Serum AGE concentrations may be a useful marker not only for the severity of diabetic microangiopathy but also for the development of CHD in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 May 2000 / Accepted in revised form: 5 September 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aso, Y., Inukai, T., Tayama, K. et al. Serum concentrations of advanced glycation endproducts are associated with the development of atherosclerosis as well as diabetic microangiopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol 37, 87–92 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005920070025
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005920070025