Abstract
Aims
Circulatory microRNAs (c-miRNAs) exert important roles in the molecular dysregulation of cardio-metabolic diseases. However, little is known whether dysregulated miRNA expression occurs when risk factors are elevated, as in the metabolic syndrome (MetS). This study quantified c-miRNA expression in individuals with MetS compared to healthy, further examining the relationship of gene pathways with the underlying pathogenesis.
Methods
Expression of 26 miRNAs was quantified in plasma from 40 women (20 healthy and 20 MetS) and 39 men (20 healthy and 19 MetS) by qPCR. In silico analysis was performed to investigate biological effects of the dysregulated miRNAs. Dysregulated miRNA expression was further validated in an independent cohort of 20 women (10 healthy and 10 MetS).
Results
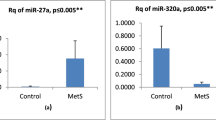
Regression model adjusted for age and sex identified miR-15a-5p, miR-17-5p, miR-370-3p and miR-375 as important predictors of MetS presence. Analysis of predictive miRNAs in the validation cohort strengthened the relationship with miR-15a-5p and miR-17-5p expression. These miRNAs share genes involved in the regulation of metabolic pathways including insulin, wnt, fatty acid metabolism and AMPK.
Conclusions
miR-15a-5p and miR-17-5p were identified as predictive biomarkers of MetS, irrespective of sexes, further demonstrating the relationship of c-miRNAs to known pathways of metabolic disturbances present in cardio-metabolic diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paniagua JA (2016) Nutrition, insulin resistance and dysfunctional adipose tissue determine the different components of metabolic syndrome. World J Diabetes 7:483–514. https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v7.i19.483
Martyn JAJ, Kaneki M, Yasuhara S (2008) Obesity-induced insulin resistance and hyperglycemia: etiologic factors and molecular mechanisms. Anesthesiology 109:137–148. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181799d45
Fernández-Hernando C, Ramírez CM, Goedeke L, Suárez Y (2013) MicroRNAs in metabolic disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300144
Mehta R, Otgonsuren M, Younoszai Z et al (2016) Circulating miRNA in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and coronary artery disease. BMJ Open Gastroenterol 3:e000096. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjgast-2016-000096
McGregor RA, Choi MS (2011) microRNAs in the regulation of adipogenesis and obesity. Curr Mol Med 11:304–316
Victoria B, Nunez Lopez YO, Masternak MM (2017) MicroRNAs and the metabolic hallmarks of aging. Mol Cell Endocrinol 455:131–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2016.12.021
Zhao Y, Song Y, Yao L et al (2017) Circulating microRNAs: promising biomarkers involved in several cancers and other diseases. DNA Cell Biol 36:77–94. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2016.3426
Rome S (2015) Use of miRNAs in biofluids as biomarkers in dietary and lifestyle intervention studies. Genes Nutr 10:33
Li M, Zhang J (2015) Circulating microRNAs: potential and emerging biomarkers for diagnosis of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Biomed Res Int 2015:730535
Calderari S, Diawara MR, Garaud A, Gauguier D (2017) Biological roles of microRNAs in the control of insulin secretion and action. Physiol Genomics 49(1):1–10
Deiuliis JA (2016) MicroRNAs as regulators of metabolic disease: pathophysiologic significance and emerging role as biomarkers and therapeutics. Int J Obes (Lond) 40:88–101. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.170
Párrizas M, Novials A (2016) Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for metabolic disease. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 30:591–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2016.08.001
Frost RJA, Olson EN (2011) Control of glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity by the Let-7 family of microRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:21075–21080. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1118922109
Heneghan HM, Miller N, McAnena OJ et al (2011) Differential miRNA expression in omental adipose tissue and in the circulation of obese patients identifies novel metabolic biomarkers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:E846–E850. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2010-2701
Poy MN, Eliasson L, Krutzfeldt J et al (2004) A pancreatic islet-specific microRNA regulates insulin secretion. Nature 432:226–230. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03076
Wang Y-T, Tsai P-C, Liao Y-C et al (2013) Circulating microRNAs have a sex-specific association with metabolic syndrome. J Biomed Sci 20:72. https://doi.org/10.1186/1423-0127-20-72
Sharma S, Eghbali M (2014) Influence of sex differences on microRNA gene regulation in disease. Biol Sex Differ 5:3
Cleeman JI, Smith SC, Alberti KGMM et al (2009) Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome. Circulation 120:1640–1645. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.109.192644
Osei-Yeboah J, Owiredu WKBA, Norgbe GK et al (2017) The prevalence of metabolic syndrome and its components among people with type 2 diabetes in the Ho municipality, Ghana: a cross-sectional study. Int J Chronic Dis 2017:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8765804
D’Souza RF, Markworth JF, Aasen KMM et al (2017) Acute resistance exercise modulates microRNA expression profiles: combined tissue and circulatory targeted analyses. PLoS ONE 12:e0181594. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181594
Shah JS, Soon PS, Marsh DJ (2016) Comparison of methodologies to detect low levels of hemolysis in serum for accurate assessment of serum microRNAs. PLoS ONE 11:e0153200. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0153200
Zalewski K, Misiek M, Kowalik A et al (2017) Normalizers for microRNA quantification in plasma of patients with vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia lesions and vulvar carcinoma. Tumor Biol 39:101042831771714. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010428317717140
Bignotti E, Calza S, Tassi RA et al (2016) Identification of stably expressed reference small non-coding RNAs for microRNA quantification in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma tissues. J Cell Mol Med 20:2341–2348. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12927
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.73
Backes C, Kehl T, Stöckel D et al (2017) miRPathDB: a new dictionary on microRNAs and target pathways. Nucl Acids Res 45:D90–D96. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw926
Stöckel D, Kehl T, Trampert P et al (2016) Multi-omics enrichment analysis using the GeneTrail2 web service. Bioinformatics 32:1502–1508. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv770
Sliwinska A, Kasinska MA, Drzewoski J (2017) MicroRNAs & metabolic disorders—where are we heading? Arch Med Sci 13:885–896. https://doi.org/10.5114/aoms.2017.65229
Chen Y, Tian L, Wan S et al (2016) MicroRNA-17-92 cluster regulates pancreatic beta-cell proliferation and adaptation. Mol Cell Endocrinol 437:213–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2016.08.037
Li H, Li T, Wang S et al (2013) miR-17-5p and miR-106a are involved in the balance between osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res 10:313–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scr.2012.11.007
Wang Q, Li YC, Wang J et al (2008) miR-17-92 cluster accelerates adipocyte differentiation by negatively regulating tumor-suppressor Rb2/p130. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:2889–2894. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0800178105
Kamalden TA, Macgregor-Das AM, Kannan SM et al (2017) Exosomal microRNA-15a transfer from the pancreas augments diabetic complications by inducing oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 27:913–930. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2016.6844
Martinez-Sanchez A, Rutter GA, Latreille M (2017) miRNAs in β-cell development, identity, and disease. Front Genet 7:226. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2016.00226
Sun L-L, Jiang B-G, Li W-T et al (2011) MicroRNA-15a positively regulates insulin synthesis by inhibiting uncoupling protein-2 expression. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 91:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2010.11.006
Rawal S, Munasinghe PE, Nagesh PT et al (2017) Down-regulation of miR-15a/b accelerates fibrotic remodelling in the Type 2 diabetic human and mouse heart. Clin Sci 131:847–863. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20160916
Guo L, Zhang Q, Ma X et al (2017) miRNA and mRNA expression analysis reveals potential sex-biased miRNA expression. Nature 7:39812. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39812
Pérez-Cremades D, Mompeón A, Gómez XV et al (2018) MiRNA as a new regulatory mechanism of estrogen vascular action. Int J Mol Sci 19:473
Ameling S, Kacprowski T, Chilukoti RK et al (2015) Associations of circulating plasma microRNAs with age, body mass index and sex in a population-based study. BMC Med Genomics 8:61. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-015-0136-7
Wang H, Peng R, Wang J et al (2018) Circulating microRNAs as potential cancer biomarkers: the advantage and disadvantage. Clin Epigenet 10:59
Sun T, Fu M, Bookout AL et al (2009) MicroRNA let-7 regulates 3T3-L1 adipogenesis. Mol Endocrinol 23:925–931. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2008-0298
Jones A, Danielson KM, Benton MC et al (2017) miRNA signatures of insulin resistance in obesity. Obesity 25:1734–1744. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.21950
Burgess KS, Philips S, Benson EA et al (2015) Age-related changes in microRNA expression and pharmacogenes in human liver. Clin Pharmacol Ther 98:205–215. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.145
Noren Hooten N, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M et al (2010) microRNA expression patterns reveal differential expression of target genes with age. PLoS ONE 5:e10724. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010724
Dluzen DF, Noren Hooten N, Zhang Y et al (2016) Racial differences in microRNA and gene expression in hypertensive women. Sci Rep 6:35815. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep35815
Huang RS, Gamazon ER, Ziliak D et al (2011) Population differences in microRNA expression and biological implications. RNA Biol 8:692–701. https://doi.org/10.4161/rna.8.4.16029
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge all the participants involved in this study.
Funding
This study was supported by AgResearch Limited through the Strategic Science Investment Fund (Nutritional strategies for an aging population, Contracts A19079 and A21246).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CJM, DCS, AMM, BD, SP and IR designed the research. CJM, AMM, FR, RFD and BD conducted the discovery phase, and SP and IR coordinated the validation phase. FR, CJM and VS conducted the statistical analysis. FR wrote the paper. All authors provided content and feedback on the manuscript. DCS has primary responsibility for the final content of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Southern Health and Disability Ethics Committee (14/STH/184 and 16/STH/23) and University of Auckland Human Participants and Ethics Committee (014501).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Managed by Massimo Federici.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramzan, F., D’Souza, R.F., Durainayagam, B.R. et al. Circulatory miRNA biomarkers of metabolic syndrome. Acta Diabetol 57, 203–214 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-019-01406-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-019-01406-6