Abstract
Aims
The aim is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP4-I: sitagliptin, saxagliptin, linagliptin, vildagliptin and alogliptin) in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods
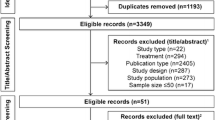
We searched the Cochrane Library, PubMed, EMBASE, Chinese Biomedical Database (CBM), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and the Wanfang Database from inception to April, 2018. Randomized controlled trials were included if they compared the different versions of DPP4-I with each other or with placebo in treatment of type 2 diabetes. Bayesian network meta-analysis and pairwise meta-analysis were performed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the different kinds of DPP4-I and placebo. The data were analyzed using STATA 12.0 and WinBUGS1.4 software.
Results
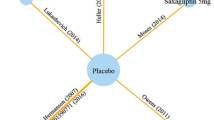
We identified 58 eligible studies (with 31356 patients) involving 14 treatment arms. Indirect comparison results showed that except for alogliptin, a decrease was found for all DPP4-I versus the placebo for hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) with vildagliptin50 twice daily (BID) showing the highest probability. Linagliptin5 once daily (QD) decreased the level of fasting plasma glucose (FPG) the most for all DPP4-I versus the placebo; when comparing them with each other, alogliptin25QD was more effective when compared with sitagliptin100QD and vildaglipti50BID; linagliptin5qd had the highest decrease impact on body mass index (BMI). Except for hypoglycemia and upper respiratory tract infection (URTI), there are no statistical significance on incidence of adverse events and the body weight when DPP4-I are compared with each other or with placebo.
Conclusion
Our network meta-analysis presents the associations of DPP4-I versus placebos on HbA1c, FPG, 2 h postprandial blood glucose (2HPPG), BMI, body weight and adverse events. DPP4-I have a lowering effect on the glycemic level (HbA1c, FPG), especially vildaglipti50BID and linagliptin10QD, respectively. Besides, linagliptin5QD has the greatest probabilities of reducing BMI. In addition, DPP4-I were associated with not increasing the incidence of adverse events. Among them, vildagliptin100QD and sitagliptin100QD have the lowest probability in reducing the incidence of hypoglycemia and URTI, respectively.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Diabetes facts and figures. Brussels. International Diabetes Federation (2018). https://www.idf.org/ news/94:new-idf-figures-show-continued -increase-in-diabetes-across-the-globe,-reiterating-the-need-for-urgent-action.html. Accessed 1 Jan 2018
International Diabetes Federation. IDFDIABETESATLAS, 7th edn. http://www.idf.org/files/idf_publications/idf_diabetes_atlas_EN/idf_diabetes_atlas_EN/assets/common/downloads/publication.pdf. Accessed 01 Jan 2018
Deacon CF (2011) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a comparative review. Diabetes Obes Metab 13:17–18
Holst JJ, Deacon CF (1998) Inhibition of the activity of dipeptidyl peptidase IV as a treatment for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 47:1663–1670
Thornberry NA, Weber AE (2007) Discovery of JANUVIA (sitagliptin), a selective dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Curr Top Med Chem 7:557–568
Tahrani AA, Piya MK, Barnett AH (2009) Saxagliptin: a new DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Adv Ther 26:249–262
Ckhardt ME, Angkop EL, Mark M et al (2007) 8-[(3R)-3-aminopiperidin-1-yl]-7-(but-2-yn-1-yl)-3-methyl-1-[(4-methylquinazolin-2-yl) methyl]-3, 7-dihydro-1H-purine-2, 6-dione a highly potent, selective, long-acting, and orally bioavailable DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type-2 diabetes. Med Chem 50:6450–6453
Feng J, Zhang ZY, Wallace MB (2007) Discovery of alogliptin: a potent, selective, bioavailable, and efficacious inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Med Chem 50:2297–2300
Gerrald KR, Van SE, Wines RC et al (2012) Saxagliptin and sitagliptin in adult patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab 14(6):481–492
Wan LY, Zhang C, Guo WH et al (2013) Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Advers Drug React J 15(6):306–313
Ying L, Yu MZ, Xu XZ et al (2015) Efficacy and safety of linagliptin for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Chin J Evid Based Med 15(9):1068–1077
Bafeta A, Trinquart L, Seror R, Ravaud P (2014) Reporting of results from network meta-analyses: methodological systematic review. BMJ 348:g1741
Higgins JPT, Green S (2011) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0 [EB/OL]. The Cochrane Collaboration. http://www.cochrane-handbook.org. Accessed 3 Feb 2018
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6:e1000097
Chaimani A, Higgins JP, Mavridis D et al (2013) Graphical tools for network meta-analysis in STATA. PLoS One 8:e76654
Higgins JP, Altman DG (2008) Assessing risk of bias in included studies[M]/Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: Cochrane book series. John Wiley, Hoboken, pp 187–241
Dersimonian R, Kacker R (2007) Random-effects model for meta-analysis of clinical trials: an update. Contemp Clin Trials 28(2):105
Hartung J, Knapp G (2001) A refined method for the meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials with binary outcome. Stat Med 20:3875–3889
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21:1539–1558
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327:557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Bulpitt C (1988) Subgroup analysis. Lancet 332(8601):31–34
Valkenhoef GV, Kuiper J (2016) Network meta-analysis using bayesian methods[M]/evidence synthesis for decision making in healthcare. John Wiley, Hoboken, pp 76–93
Lu G, Ades AE (2004) Combination of direct and indirect evidence in mixed treatment comparisons. Stat Med 23:3105–3124
Dias S, Sutton AJ, Ades AE et al (2013) Evidence synthesis for decision making 2: a generalized linear modeling framework for pairwise and network metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials. Med Decis Making 33:607–617
Gelman A, Rubin DB (1992) Inference from iterative simulation using multiple sequences. Stat Sci 7:457–472
Salanti G, Ades AE, Ioannidis JP (2011) Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: an overview and tutorial. J Clin Epidemiol 64(2):163–171
Donegan S, Williamson P, D’Alessandro U, Tudur-Smith C (2013) Assessing key assumptions of network meta-analysis: a review of methods. Res Synth Methods 4:291–323
Spiegelhalter DJ, Best NG, Carlin BP, Van Der Linde A (2002) Bayesian measures of model complexity an fit. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Methodol) 64:583–639
Tian JH, Zhang J, Ge L, Yang KH, Song FJ (2017) The methodological and reporting quality of systematic reviews from China and the USA are similar. J Clin Epidemiol 85:50–58
Xiaoyan C, Jing W, Xiaochun H, Yuyu T, Shunyou D, Yingyu F (2016) Effects of vildagliptin versus saxagliptin on daily acute glucose fluctuations in Chinese patients with T2DM inadequately controlled with a combination of metformin and sulfonylurea. Curr Med Res Opin 6:1–6
Koyanagawa N, Miyoshi H, Ono K et al (2016) Comparative effects of vildagliptin and sitagliptin determined by continuous glucose monitoring in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocr J 63(8):747
Asti A, D’Alessandro A, Zito FP et al (2016) Sitagliptin versus saxagliptin in decompensated type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Italian J Med 10(1):36
Huang HH, Xu WQ et al (2015) Comparative study on the efficacy of saxagliptin and vildagliptin in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. Jiangxi Med J 2015(9):859–860
Chen P (2015) Clinical efficacy of DPP-IV inhibitor combined with metformin on type 2 diabetes mellitus. North Pharmaceutical (9):88–89
Tang YZ, Wang G, Jiang ZH et al (2015) Efficacy and safety of vildagliptin, sitagliptin, and linagliptin as add-on therapy in Chinese patients with T2DM inadequately controlled with dual combination of insulin and traditional oral hypoglycemic agent. Diabetol Metab Syndrome 7(1):91
Kothny W, Lukashevich V, Foley JE et al (2015) Comparison of vildagliptin and sitagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and severe renal impairment: a randomised clinical trial. Diabetologia 58(9):2020–2026
Göke R, Eschenbach P, Dütting ED (2015) Efficacy of vildagliptin and sitagliptin in lowering fasting plasma glucose: results of a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Metabol 41(3):244–247
Li LY, He X, Xie M et al (2014) Comparative study on the efficacy of Sitagliptin and saxagliptin in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. 14(6):11–12.
Takihata M, Nakamura A, Terauchi Y et al (2014) Comparative study of three DPP-4 inhibitors, namely sitagliptin, vildagliptin, and alogliptin, in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients: the cosva randomized, controlled trial. Clin Diabetes Ther Posters 106:1024
Li CJ, Yu Q, Yu P et al (2014) Efficacy and safety comparison of add-on therapy with liraglutide, saxagliptin and vildagliptin, all in combination with current conventional oral hypoglycemic agents therapy in poorly controlled Chinese type 2 diabetes. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 122(8):469
Sakamoto M, Nishimura R, Irako T et al (2012) Comparison of vildagliptin twice daily vs. sitagliptin once daily using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): crossover pilot study (J-VICTORIA study). Cardiovasc Diabetol 11(1):92
Rizzo MR, Barbieri M, Marfella R, Paolisso G (2012) Reduction of oxidative stress and inflammation by blunting daily acute glucose fluctuations in patients with type 2 diabetes: role of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibition. Pathophysiol Complicat 35(10):2076–2082
Guerci B, Monnier L, Serusclat P et al (2012) Continuous glucose profiles with vildagliptin versus sitagliptin in add-on to metformin: results from the randomized optima study. Diabetes Metab 38(4):359–366
Wang W, Yang J, Yang G et al (2016) Efficacy and safety of linagliptin in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled by metformin: a multinational 24-week, randomized clinical trial. J Diabetes 8(2):229
Yang W, Xing X, Lv X et al (2015) Vildagliptin added to sulfonylurea improves glycemic control without hypoglycemia and weight gain in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes 7(2):174
Sheu WHH, Park SW, Yan G et al (2015) Linagliptin improves glycemic control after 1 year as add-on therapy to basal insulin in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Med Res Opin 31(3):1–34
Schmieder RE, Friedrich S, Kistner I et al (2015) Effects of linagliptin on early alterations of renal endothelial function in patients with type-2 diabetes. Nephrol Dial Transplant 30(suppl_3):iii11
Chantal M, Ravi SR, Daniel L et al (2015) A randomized clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of co-administration of sitagliptin with intensively titrated insulin glargine. Diabetes Ther 6(2):127
Leibowitz G, Cahn A, Bhatt DL et al (2015) Impact of treatment with saxagliptin on glycaemic stability and β-cell function in the SAVOR-TIMI 53 study. Diabetes Obes Metab 17(5):487
Laakso M, Rosenstock J, Groop PH et al (2015) Treatment with the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor linagliptin or placebo followed by glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes with moderate to severe renal impairment: a 52-week, randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Diabetes Care 38(2):15–17
Kohei K, Takashi K, Yasuo T et al (2015) Sitagliptin improves glycemic excursion after a meal or after an oral glucose load in Japanese subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes Obes Metab 17:11
Wu YF (2013) The effect of saxagliptin monotherapy on treating new type 2 diabetes. Doctoral dissertation, Zhejiang University
Yang W, Guan Y, Yue S et al (2012) The addition of sitagliptin to ongoing metformin therapy significantly improves glycemic control in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes 4(3):227–237
Rauch T, Graefe-Mody U, Deacon CF et al (2012) Linagliptin increases incretin levels, lowers glucagon, and improves glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Ther 3(1):10
Pan CY, Yang W, Tou C et al (2011) Efficacy and safety of saxagliptin in drug-naïve Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 28(3):217–224
Pan C, Xing X, Han P et al (2012) Efficacy and tolerability of vildagliptin as add-on therapy to metformin in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab 14(8):737–744
Minervini G, Iqbal N, Charbonnel B et al (2012) Efficacy and safety of saxagliptin in combination with insulin in patients with long-standing type 2 diabetes. Intern Med J 61:A290
Kothny W, Shao Q, Groop P et al (2012) One-year safety, tolerability and efficacy of vildagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate or severe renal impairment. Diabetes Obes Metab 14(11):1032–1039
Kawamori R, Inagaki N, Araki E et al (2011) Linagliptin monotherapy provides superior glycaemic control versus placebo or voglibose with comparable safety in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, placebo and active comparator-controlled, double-blind study. Diabetes Obes Metab 14(4):348–357
Gerosa D, Ragonesi PD, Anna C et al (2012) Vildagliptin action on some adipocytokine levels in type 2 diabetic patients: a 12-month, placebo-controlled study. Expert Opin Pharmacother 13(18):2581–2591
Derosa G, Carbone A, Franzetti I et al (2012) Effects of a combination of sitagliptin plus metformin vs metformin monotherapy on glycemic control, β-cell function and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 98(1):51–60
Barnett A, Huisman H, Jones R et al (2012) Efficacy and safety of linagliptin in elderly patients (≥ 70 Years) with type 2 diabetes. Can J Diabetes 36(5):S39
Tajima N, Kadowaki T, Odawara M et al (2011) Addition of sitagliptin to ongoing glimepiride therapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes over 52 weeks leads to improved glycemic control. Diabetol Int 2(1):32–44
Seino Y, Fujita T, Hiroi S et al (2011) Efficacy and safety of alogliptin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double-blind, dose-ranging comparison with placebo, followed by a long-term extension study. Curr Med Res Opin 27(9):1781–1792
Del PS, Barnett AH, Huisman H et al (2011) Effect of linagliptin monotherapy on glycaemic control and markers of β-cell function in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 13(3):258
Nowicki M, Rychlik I, Haller H et al (2011) Saxagliptin improves glycaemic control and is well tolerated in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal impairment. Diabetes Obes Metab 13(6):523
Nowicki M, Rychlik I, Haller H et al (2011) Long-term treatment with the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor saxagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal impairment: a randomised controlled 52-week efficacy and safety study. Int J Clin Pract 65(12):1230
Mcgill JB, Sloan L, Newman J et al (2013) Long-term efficacy and safety of linagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and severe renal impairment. A 1-year, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Care 36(2):237
Lukashevich V, Schweizer A, Shao Q et al (2011) Safety and efficacy of vildagliptin versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate or severe renal impairment: a prospective 24-week randomized placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 13(10):947–954
Lukashevich V, Schweizer A, Foley J, Shao Q, Groop PH, Kothny W et al (2011) Efficacy of vildagliptin therapy in combination with insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes and severe renal impairment. Diabetologia 54(Suppl1):S332
Kothny W, Schweizer A, Naik R, Groop PH, Shao Q, Lukashevich V et al (2011) Comparison of vildagliptin with placebo in a 24-week study of 221 patients with type 2 diabetes and severe renal impairment (eGFR < 30). Diabetologia. 54(Suppl1):S332
Newman J, Mcgill JB, Patel S, Friedrich C, Sauce C, Woerle HJ et al (2011) Long-term efficacy and safety of linagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and severe renal impairment. Diabetologia 54(Suppl1):S333
Horie Y, Kanada S, Watada H et al (2011) Pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and tolerability profiles of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor linagliptin: a 4-week multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IIa study in Japanese type 2 diabetes patients. Clin Ther 33(7):973
Dandona P, Makdissi A, Chang S et al (2011) Sitagliptin exerts an anti-inflammatory effect. Am Diabetes Assoc 60:A306
Barzilai N, Guo H, Mahoney EM et al (2011) Efficacy and tolerability of sitagliptin monotherapy in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Curr Med Res Opin 27(5):1049–1058
Garber AJ, Foley JE, Banerji MA et al (2010) Effects of vildagliptin on glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with a sulphonylurea. Diabetes Obes Metab 10(11):1047–1056
Defronzo RA, Fleck PR, Wilson CA et al (2008) Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor alogliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and inadequate glycemic control: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Care 31(12):2315–2317
Chan JC, Scott R, Arjona Ferreira JC et al (2008) Safety and efficacy of sitagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic renal insufficiency. Diabetes Obes Metab 10(7):545–555
Su Y, Lv LF, Li QZ, Zhao ZG (2014) A randomized controlled clinical trials for the treatment of type 2 diabetes by vildagliptin and alpha-glucosidase inhibitor. Chin J New Drugs 22:2655–2658
Lukashevich V, Kozlovski P, Foley J, Kothny W et al (2012) Vildagliptin combined with insulin reduces HBA1C without increasing risk of hypoglycemia and weight gain in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 61:A254
Moses RG, Kalra S, Brook D, Sockler J, Visvanathan J, Fisher SA (2012) Saxagliptin (SAXA) effectively reduces HbA1c and is well tolerated when added to a combination of metformin (MET) and sulfonylurea (SU). Clin Diabetes/Ther Posters 61:A282
Su Y, Lv LF, Li QZ, Zhao ZG, Su YL (2014) The clinical research on the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus by DPP-4 inhibitor. Chin J Diabetes 22(10):886–889
Ba J, Han P, Yuan G et al (2017) Randomized trial assessing the safety and efficacy of sitagliptin in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on sulfonylurea alone or combined with metformin. J Diabetes 09:667–676
Pan C, Han P, Ji Q, li C, Lu J et al (2017) Efficacy and safety of alogliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a multicentre randomized double-blind placebo-controlled phase 3 study in mainland China, Taiwan, and Hong Kong. J Diabetes 09:386–395
Shah A, Levesque K, Pierini E et al (2017) Effect of sitagliptin on glucose control in type 2 diabetes mellitus after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Diabetes Obes Metab 20:1–6
Tanaka K, Okada Y, Mori H et al (2017) Comparative analysis of the effects of alogliptin and vildagliptin on glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocr J 64(2):179–189
Wang W, Ning G, Ma J et al (2017) A randomized clinical trial of the safety and efficacy of sitagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled by acarbose alone. Curr Med Res Opin 33(4):693–699
Sun F, Wu S, Guo S et al (2015) Effect of GLP-1 receptor agonists on waist circumference among type 2 diabetes patients: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Endocrine 48(3):794–803
Sun F, Wu S, Guo S et al (2015) Impact of GLP-1 receptor agonists on blood pressure, heart rate and hypertension among patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 10(1):26–37
Jansen JP, Fleurence R, Devine B et al (2011) Interpreting indirect treatment comparisons and network meta-analysis for health-care decision making: report of the ISPOR task force on indirect treatment comparisons good research practices: part 1. Value Health 14(4):417–428
Cai L, Cai Y, Lu ZJ et al (2012) The efficacy and safety of vildagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Clin Pharm Ther 37(4):386
Bekiari E, Rizava C, Athanasiadou E et al (2015) Systematic review and meta-analysis of vildagliptin for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Endocrine 52(3):458–480
Singhfranco D, Mclaughlinmiddlekauff J, Elrod S et al (2012) The effect of linagliptin on glycaemic control and tolerability in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab 14(8):694–708
Bryzinski BHB (2015) A pooled analysis of the efficacy and safety of saxagliptin as monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Metab 06:4
Shin S-J (2012) Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and their effects on weight reduction. J Diabetes Investig 03:490–491
Resnick HE, Valsania P, Halter JB et al (2000) Relation of weight gain and weight loss on subsequent diabetes risk in overweight adults. J Epidemiol Commun Health 54(8):596–602
Ford ES, Williamson DF, Liu S (1997) Weight change and diabetes incidence: findings from a national cohort of US adults. Am J Epidemiol 146:214–222
Moghissi E, Ismailbeigi F, Devine RC (2013) Hypoglycemia: minimizing its impact in type 2 diabetes. Endocr Pract 19(3):1–33
Mbanya JC, Al-Sifri S, Abdel-Rahim A et al (2015) Incidence of hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with gliclazide versus DPP-4 inhibitors during Ramadan: a meta-analytical approach. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 109(2):226–232
Kim HM, Lim JS, Lee BW et al (2015) Optimal candidates for the switch from glimepiride to sitagliptin to reduce hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrinol Metab 30(1):84–91
Phung OJ, Scholle JM, Talwar M et al (2010) Effect of noninsulin antidiabetic drugs added to metformin therapy on glycemic control, weight gain and hypoglycemia in Type 2 diabetes. JAMA 303(14):1410–1418
Zhao Q, Hong D, Zheng D et al (2014) Risk of diarrhea in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with sitagliptin: a meta-analysis of 30 randomized clinical trials. Drug Des Dev Ther 8:2283
Bhattacharjee A, Gupta MC, Agrawal S (2016) Adverse drug reaction monitoring of newer oral anti-diabetic drugs—a pharmacovigilance perspective. Int J Pharmacol Res 6(04):142–151
Esposito K, Chiodini P, Maiorino MI et al (2014) Glycaemic durability with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of long-term randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open 4(6):e005442–e005442
Karagiannis T, Paschos P, Paletas K et al (2012) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors for treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the clinical setting: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 344:449–449
Caldwell DM, Ades AE, Higgins JPT (2005) Simultaneous comparison of multiple treatments: combining direct and indirect evidence. BMJ 331(7521):897–900
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the library of Lanzhou University for their database in accessing and acquiring the full texts. The authors are also grateful to the freelance editor for polishing and revising the language and the authors of the original studies included in this study.
Funding
No fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have indicated that they have no conflict of interest regarding the content of this article.
Human and animal rights statement
This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any studies with animals and humans performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Managed by Massimo Porta.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, J., Cheng, P., Ge, L. et al. The efficacy and safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors for type 2 diabetes: a Bayesian network meta-analysis of 58 randomized controlled trials. Acta Diabetol 56, 249–272 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-018-1222-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-018-1222-z