Abstract
Aims
Ficolin-3, a soluble molecule of the innate immune system, has a primary role in the activation of the lectin pathway in the complement system. Considering that inflammatory mechanisms are involved in complement activation and take part in the pathophysiology of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), we conducted this study to explore the link between serum ficolin-3 and DPN in diabetic patients.
Methods
A total of 466 diabetic patients were enrolled in this cross-sectional study. DPN was evaluated by neurological symptoms, neurological signs, neurothesiometer and electromyogram. The concentration of serum ficolin-3 was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Results
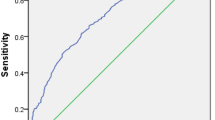
The concentration of serum ficolin-3 was lower in DPN patients compared with non-DPN patients (18.73 ± 4.75 vs. 26.69 ± 5.68 ng/mL, P < 0.001). In addition, it was found negatively correlated to the vibration perception threshold (r = −0.158; P = 0.025). The results of multiple regression analysis of DPN indicated that age, diabetes duration, serum ficolin-3 were all independent impact factors for DPN (P < 0.05). Patients were then assigned into quartiles according to the serum ficolin-3 levels, and the prevalence of DPN ascended as the concentration of ficolin-3 descended (Trend analysis, P < 0.001). Compared with ficolin-3 Quartile 1 (referent), the risk of DPN was significantly greater in Quartile 2 (OR 2.76; 95 % CI 1.56–4.88; P < 0.001), Quartile 3 (OR 3.02; 95 % CI 1.69–5.40; P < 0.001) and Quartile 4 (OR 6.84; 95 % CI 3.39–13.80; P < 0.001).
Conclusions
Lower ficolin-3 level is independently associated with DPN, and it may be a potential biomarker for DPN.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li J, Zhang H, Xie M, Yan L, Chen J, Wang H (2013) NSE, a potential biomarker, is closely connected to diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Care 36:3405–3410
Zychowska M, Rojewska E, Przewlocka B, Mika J (2013) Mechanisms and pharmacology of diabetic neuropathy-experimental and clinical studies. Pharmacol Rep 65:1601–1610
Morano S, Tiberti C, Cristina G, Sensi M, Cipriani R, Guidobaldi L et al (1999) Autoimmune markers and neurological complications in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Hum Immunol 60:848–854
Mika J, Osikowicz M, Rojewska E, Korostynski M, Wawrzczak-Bargiela A, Przewlocki R et al (2009) Differential activation of spinal microglial and astroglial cells in a mouse model of peripheral neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 623:65–72
Collins MP, Periquet-Collins I, Sahenk Z, Killel JT (2010) Direct immunofluoresence in vasculitic neuropathy: specificity of vascular immune deposits. Muscle Nerve 42:62–69
Walport MJ (2001) Complement: first of two parts. N Engl J Med 344:1058–1066
Walport MJ (2001) Complement: second of two parts. N Engl J Med 344:1140–1144
Garred P, Honoré C, Ma YJ, Munthe-Fog L, Hummelshøj T (2009). MBL2, FCN1, FCN2 and FCN3-The genes behind the initiation of the lectin pathway of complement. Mol Immunol 46:2737–2744
Ma YJ, Skjoedt MO, Garred P (2013) Collectin-11/MASP complex formation triggers activation of the lectin complement pathway—the fifth lectin pathway initiation complex. J Innate Immun 5:242–250
Munthe-Fog L, Hummelshoj T, Ma YJ, Hansen BE, Koch C, Madsen HO et al (2008) Characterization of a polymorphism in the coding sequence of FCN3 resulting in a Ficolin-3 (Hakata antigen) deficiency state. Mol Immunol 45:2660–2666
Hein E, Honoré C, Skjoedt MO, Munthe-Fog L, Hummelshøj T, Garred P (2010) Functional analysis of ficolin-3 mediated complement activation. PLoS ONE 5:e15443
Chen H, Lu J, Chen X, Yu H, Zhang L, Bao Y et al (2012) Low serum levels of the innate immune component ficolin-3 is associated with insulin resistance and predicts the development of type 2 diabetes. J Mol Cell Biol 4:256–257
Rosoklija GB, Dwork AJ, Younger DS, Karlikaya G, Latov N, Hays AP (2000) Local activation of the complement system in endoneurial microvessels of diabetic neuropathy. Acta Nenropathol 99:55–62
American Diabetes Association (2014) Standards of medical care in diabetes—2014. Diabetes Care 37(Suppl 1):S14–S80
Ziegler D, Hanefeld M, Ruhnau KJ, Meißner HP, Lobisch M, Schütte K et al (1995) the ALADIN Study Group: treatment of symptomatic diabetic peripheral neuropathy with the anti-oxidant α-lipoic acid: a 3-week multicentre randomized controlled trial (ALADIN Study). Diabetologia 38:1425–1433
Apelqvist J, Bakker K, van Houtum WH, Schaper NC (2008) International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot (IWGDF) Editorial Board. Practical guidelines on the management and prevention of the diabetic foot: based upon the International Consensus on the Diabetic Foot (2007) Prepared by the International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 24(Suppl 1):S181–S187
Shen J, Hu Y, Liu F, Zeng H, Li L, Zhao J et al (2013) Vibration perception threshold for sight-threatening retinopathy screening in type 2 diabetic outpatients. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 29:525–531
Xiaofu T (1995) Clinical EMG study. The Beijing University of Science and Technology China harmony Medical College unites the publishing house, Beijing
Dyck PJ (1988) Detection, characterization, and staging of polyneuropathy: assessed in diabetics. Muscle Nerve 11:21–32
Wilkinson CP, Ferris FL 3rd, Klein RE, Lee PP, Agardh CD, Davis M et al (2003) Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology 110:1677–1682
Mythili A, Kumar KD, Subrahmanyam KA, Venkateswarlu K, Butchi RGA (2010) Comparative study of examination scores and quantitative sensory testing in diagnosis of diabetic polyneuropathy. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 30:43–48
Young MJ, Breddy JL, Veves A, Boulton AJ (1994) The prediction of diabetic neuropathic foot ulceration using vibration perception thresholds. A prospective study. Diabetes Care 17:557–560
Shen J, Liu F, Zeng H, Wang J, Zhao JG, Zhao J et al (2012) Vibrating perception threshold and body mass index are associated with abnormal foot plantar pressure in type 2 diabetes outpatients. Diabetes Technol Ther 14:1053–1059
Prohászka Z, Munthe-Fog L, Ueland T, Gombos T, Yndestad A, Förhécz Z et al (2013) Association of ficolin-3 with severity and outcome of chronic heart failure. PLoS ONE 8:e60976
Füst G, Munthe-Fog L, Illes Z, Széplaki G, Molnar T, Pusch G et al (2011) Low ficolin-3 levels in early follow-up serum samples are associated with the severity and unfavorable outcome of acute ischemic stroke. J Neuroinflammation 8:185
Halmos A, Rigó J Jr, Szijártó J, Füst G, Prohászka Z, Molvarec A (2012) Circulating ficolin-2 and ficolin-3 in normal pregnancy and pre-eclampsia. Clin ExpImmunol 169:49–56
Fujita T, Hemmi S, Kajiwara M, Yabuki M, Fuke Y, Satomura A et al (2013) Complement-mediated chronic inflammation is associated with diabetic microvascular complication. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 29:220–226
Kim HJ, Cho EH, Yoo JH, Kim PK, Shin JS, Kim MR et al (2007) Proteome analysis of serum from type 2 diabetics with nephropathy. J Proteome Res 6:735–743
Zheng B, Li T, Chen H, Xu X, Zheng Z (2011) Correlation between ficolin-3 and vascular endothelial growth factor-to-pigment epithelium-derived factor ratio in the vitreous of eyes with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 152:1039–1043
Duchen LW, Anjorin MB, Watkins MD, Mackay MB (1980) Pathology of autonomic neuropathy in diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med 92:301–303
Graham AR, Johnson PC (1985) Direct immunofluorescence findings in peripheral nerve from patients with diabetic neuropathy. Ann Neurol 17:450–454
Qin X, Goldfine A, Krumrei N, Grubissich L, Acosta J, Chorev M et al (2004) Glycation inactivation of the complement regulatory protein CD59: a possible role in the pathogenesis of the vascular complications of human diabetes. Diabetes 53:2653–2661
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the grants from National Science Foundation of China (81270397 for Fang Liu, 81170759 for Lianxi Li).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights disclosure
All procedures in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation of Shanghai Jiao-Tong University Affiliated Sixth People’s Hospital and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5).
Informed consent disclosure
Statement of informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Managed by Massimo Federici.
X. Zhang and Y. Hu have contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Hu, Y., Shen, J. et al. Low levels of ficolin-3 are associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Acta Diabetol 53, 295–302 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-015-0780-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-015-0780-6