Abstract
Aims
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) induce weight loss and reduction in adipose tissue, but the effects of GLP-1 RA on the distribution of fat deposits have been poorly investigated.
Methods
In 25 patients with type 2 diabetes (16 females and 9 males, mean age 63.5 ± 8.8 years), treated with GLP-1 RA (exenatide, n. 12; liraglutide, n.13), both before and 3 months after starting treatment, an abdominal ultrasonographic scan, with Doppler of renal arteries, and echocardiography were performed. Subcutaneous fat width (peri-umbilical and sub-xiphoid), deep fat deposits (pre-aortic, peri-renal, and epicardial), and renal resistive index (RI) were evaluated.
Results
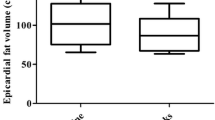
GLP-1 RA induced highly significant (p < 0.001) decrease in BMI and in fat thickness at all the assessed sites, without differences between exenatide and liraglutide treatment. A slight decrease in RI (p = 0.055) was also found. The percent changes of fat thickness was different between sites (p < 0.025), and the changes in subcutaneous deposits showed no significant correlation (p = 0.064) with those of deep fat deposits.
Conclusions
A short course of treatment with GLP-1 RA, besides weight loss, induces a redistribution of adipose tissue deposits, possibly contributing to a better cardiovascular risk profile in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jendle J, Nauck MA, Matthews DR, Frid A, Hermansen K, Düring M, Zdravkovic M, Strauss BJ, Garber AJ, on the behalf of the LEAD-2 and LEAD-3 Study Groups (2009) Weight loss with liraglutide, a once-daily human glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue for type 2 diabetes treatment as monotherapy or added to metformin, is primarily as a result of a reduction in fat tissue. Diabetes Obes Metab 11:1163–1172
De Fronzo RA, Ratner RE, Han J, Kim DD, Fineman MS, Baron AD (2005) Effects of exenatide (exendin-4) on glycemic control and weight over 30 weeks in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 28:1092–1100
Kim D, MacConell L, Zhuang D, Kothare PA, Trautman M, Fineman M, Taylor K (2007) Effects of once-weekly dosing of a long-acting release formulation of exenatide on glucose control and body weight in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 30:1487–1493
Vilsbøll T, Zdravkovic M, Le-Thi T, Krarup T, Schmitz O, Courreges JP, Verhoeven R, Buganova I, Madsbad S (2007) Liraglutide, a long-acting human glucagon-like peptide-1 analog, given as monotherapy significantly improves glycemic control and lowers body weight without risk of hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 30:1608–1610
Vilsbøll T, Christensen M, Junker AE, Knop FK, Gluud LL (2012) Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on weight loss: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 344:d7771. doi:10.1136/bmj.d7771
Williamson DF, Pamuk E, Thun M, Flanders D, Byers T, Heath C (1995) Prospective study of intentional weight loss and mortality in never-smoking overweight US white women aged 40–64 years. Am J Epidemiol 141:1128–1141
Chaston TB, Dixon JB (2008) Factors associated with percent change in visceral versus subcutaneous abdominal fat during weight loss: findings from a systemic review. Int J Obes 32:619–628
Després JP (2011) Excess visceral adipose tissue/ectopic fat. J Am Coll Cardiol 57:1887–1889
Bazzocchi A, Diano D, Ponti F, Salizzoni E, Albisinni U, Marchesini G, Battista G (2014) A 360-degree overview of body composition in healthy people: relationships among anthropometry, ultrasonography, and dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. Nutrition 30:696–701
Kawai T, Kamide K, Onishi M, Yamamoto-Hanasaki H, Baba Y, Hongyo K, Shimaoka I, Tatara Y, Takeya Y, Ohishi M, Rakugi H (2011) Usefulness of the resistive index in renal Doppler ultrasonography as an indicator of vascular damage in patients with risks of atheroscerosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:3256–3262
Società Italiana di Diabetologia—Associazione Medici Diabetologi (2014) Standard italiani per la cura del diabete mellito. http://www.standarditaliani.it
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Greene T, Coresh J, CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) (2009) A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 150:604–612
Suzuki R, Watanabe S, Hirai Y, Akiyama K, Nishide T, Matsushima Y, Murayama H, Ohshima H, Shinomiya M, Shirai K, Saito Y, Yoshida S, Saisho H, Ohto M (1993) Abdominal wall fat index, estimated by ultrasonography, for assessment of the ratio of visceral fat to subcutaneous fat in the abdomen. Am J Med 95:309–314
Kawasaki S, Aoki K, Hasegawa O, Numata K, Tanaka K, Shibata N, Shimada S, Okamura A, Terauchi Y (2008) Sonographic evaluation of visceral fat by measuring para- and perirenal fat. J Clin Ultrasound 36:129–133
Sabir N, Sermez Y, Kazil S, Zencir M (2001) Correlation of abdominal fat accumulation and liver steatosis: importance of ultrasonographic and anthropometric measurements. Eur J Ultrasound 14:121–128
Sperandeo M, Varriale A, D’Amico G, Sperandeo G, Piattelli ML, De Cata A, Greco A, Prigigallo F, Annese MA, Cedrone L, Vendemiale G (2007) Intrarenal resistive index in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with and without microalbuminuria. Eur J Inflamm 5:103–110
Iacobellis G, Ribaudo MC, Assael F, Vecci E, Tiberti C, Zappaterreno A, Di Mario U, Leonetti F (2003) Echocardiographic epicardial adipose tissue is related to anthropometric and clinical parameters of metabolic syndrome: a new indicator of cardiovascular risk. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:5163–5168
Sperandeo M, Carnevale V, Muscarella S, Sperandeo G, Varriale A, Filabozzi P, Piattelli ML, D’Alessandro V, Copetti M, Pellegrini F, Dimitri L, Vendemiale G (2011) Clinical application of transthoracic ultrasonography in patients with pneumonia. Eur J Clin Invest 41:1–7
Bagger JI, Christensen M, Knop FK, Vilsbøl T (2011) Therapy for obesity based on gastrointestinal hormones. Rev Diabet Stud 8:339–347
Holst JJ, Deacon CF (2013) Is there a place for incretin therapies in obesity and prediabetes? Trends Endocrinol Metab 24:145–152
Sever MJ, Kocjan T, Pfeifer M, Kravos NA, Janez A (2014) Short-term combined treatment with liraglutide and metformin leads to significant weight loss in obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome and previous poor response to metformin. Eur J Endocrinol 170:451–459
Tchernof A, Despres JP (2013) Pathophysiology of human visceral obesity: an update. Physiol Rev 93:359–404
Bartelt A, Heeren J (2014) Adipose tissue browning and metabolic health. Nat Rev Endocrinol 10:24–36
Liu KH, Chan JL, Chan WB, Chan JCN, Chu CWW (2006) Mesenteric fat thickness is an independent determinant of metabolic syndrome and identifies subjects with increased carotid intima-media thickness. Diabetes Care 29:379–384
Liu J, Fox CS, Hickson DA, May WD, Hairston KG, Carr JJ, Taylor HA (2010) Impact of abdominal visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue on cardiometabolic risk factors: the Jackson Heart Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:5419–5426
Cetin DC, Nasr G (2014) Obesity in the elderly: more complicated than you think. Clev Clin J Med 81:51–61
Christensen DL, Faurholt-Jepsen D, Faerch K, Mwaniki DL, Boit MK, Kilonzo B, Tetens I, Friis H, Borch-Johnsen K (2014) Insulin resistance and beta-cell function in different ethnic groups in Kenya: the role of abdominal fat distribution. Acta Diabetol 51:53–60
The Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration (2011) Separate and combined associations of body-mass index and abdominal adiposity with cardiovascular disease: collaborative analysis of 58 prospective studies. Lancet 377:1085–1095
Ross R, Bradshaw AJ (2009) The future of obesity reduction: beyond weight loss. Nat Rev Endocrinol 5:319–326
Iacobellis G, Singh N, Wharton S, Sharma AM (2008) Substantial changes in epicardial fat thickness after weight loss in severely obese subjects. Obesity 16:1693–1697
Kim MK, Tomita T, Kim MJ, Sasai H, Maeda S, Tanaka K (2009) Aerobic exercise training reduces epicardial fat in obese men. J Appl Physiol 106:5–11
Bazzocchi A, Filonzi G, Ponti F, Amadori M, Sassi C, Salizzoni E, Albisinni U, Battista G (2013) The role of ultrasonography in the evaluation of abdominal fat: analysis of technical and methodological issues. Acad Radiol 20:1278–1285
Iacobellis G, Corradi D, Sharma AM (2005) Epicardial adipose tissue: anatomic, biomolecular and clinical relationships with the heart. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 2:536–543
Lorber D (2013) GLP-1 receptor agonists: effects on cardiovascular risk reduction. Cardiovasc Ther 31:238–249
Bacchi E, Negri C, Tarperi C, Baraldo A, Faccioli N, Milanese C, Zanolin ME, Lanza M, Cevese A, Bonora E, Schena F, Moghetti P (2014) Relationships between cardiorespiratory fitness, metabolic control, and fat distribution in type 2 diabetes subjects. Acta Diabetol 51:369–375
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Ethical standard
The protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee of Policlinico Umberto I Hospital, Sapienza University of Rome.
Human and animal rights disclosure
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5).
Informed consent disclosure
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Managed by Massimo Federici.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morano, S., Romagnoli, E., Filardi, T. et al. Short-term effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists on fat distribution in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: an ultrasonography study. Acta Diabetol 52, 727–732 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-014-0710-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-014-0710-z