Abstract
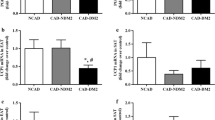
Lipoprotein receptor expression plays a crucial role in the pathophysiology of adipose tissue in in vivo models of diabetes. However, there are no studies in diabetic patients. The aims of this study were to analyze (a) low-density lipoprotein receptor–related protein 1 (LRP1) and very low-density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR) expression in epicardial and subcutaneous fat from type 2 diabetes mellitus compared with nondiabetic patients and (b) the possible correlation between the expression of these receptors and plasmatic parameters. Adipose tissue biopsy samples were obtained from diabetic (n = 54) and nondiabetic patients (n = 22) undergoing cardiac surgery before the initiation of cardiopulmonary bypass. Adipose LRP1 and VLDLR expression was analyzed at mRNA level by real-time PCR and at protein level by Western blot analysis. Adipose samples were also subjected to lipid extraction, and fat cholesterol ester, triglyceride, and free cholesterol contents were analyzed by thin-layer chromatography. LRP1 expression was higher in epicardial fat from diabetic compared with nondiabetic patients (mRNA 17.63 ± 11.37 versus 7.01 ± 4.86; P = 0.02; protein 11.23 ± 7.23 versus 6.75 ± 5.02, P = 0.04). VLDLR expression was also higher in epicardial fat from diabetic patients but only at mRNA level (231.25 ± 207.57 versus 56.64 ± 45.64, P = 0.02). No differences were found in the expression of LRP1 or VLDLR in the subcutaneous fat from diabetic compared with nondiabetic patients. Epicardial LRP1 and VLDLR mRNA overexpression positively correlated with plasma triglyceride levels (R 2 = 0.50, P = 0.01 and R 2 = 0.44, P = 0.03, respectively) and epicardial LRP1 also correlated with plasma glucose levels (R 2 = 0.33, P = 0.03). These results suggest that epicardial overexpression of certain lipoprotein receptors such as LRP1 and VLDLR expression may play a key role in the alterations of lipid metabolism associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sironi AM, Gastaldelli A, Mari A, Ciociaro D, Positano V, Buzzigoli E, Ghione S, Turchi S, Lombardi M, Ferrannini E (2004) Visceral fat in hypertension: influence on insulin resistance and beta-cell function. Hypertension 44:127–133
Kankaanpää M, Lehto HR, Pärkkä JP, Komu M, Viljanen A, Ferrannini E, Knuuti J, Nuutila P, Parkkola R, Iozzo P (2006) Myocardial triglyceride content and epicardial fat mass in human obesity: relationship to left ventricular function and serum free fatty acid levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:4689–4695
Mahabadi AA, Massaro JM, Rosito GA, Levy D, Murabito JM, Wolf PA, O’Donnell CJ, Fox CS, Hoffmann U (2009) Association of pericardial fat, intrathoracic fat, and visceral abdominal fat with cardiovascular disease burden: the Framingham Heart Study. Eur Heart J 30:850–856
Iacobellis G, Ribaudo MC, Assael F, Vecci E, Tiberti C, Zappaterreno A, Di Mario U, Leonetti F (2003) Echocardiographic epicardial adipose tissue is related to anthropometric and clinical parameters of metabolic syndrome: a new indicator of cardiovascular risk. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:5163–5168
Mazurek T, Zhang L, Zalewski A, Mannion JD, Diehl JT, Arafat H, Sarov-Blat L, O’Brien S, Keiper EA, Johnson AG, Martin J, Goldstein BJ, Shi Y (2003) Human epicardial adipose tissue is a source of inflammatory mediators. Circulation 108:2460–2466
Baker AR, Silva NF, Quinn DW, Harte AL, Pagano D, Bonser RS, Kumar S, McTernan PG (2006) Human epicardial adipose tissue expresses a pathogenic profile of adipocytokines in patients with cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol 13(5):1
Djaberi R, Schuijf JD, van Werkhoven JM, Nucifora G, Jukema JW, Bax JJ (2008) Relation of epicardial adipose tissue to coronary atherosclerosis. Am J Cardiol 102:1602–1607
Taguchi R, Takasu J, Itani Y, Yamamoto R, Yokoyama K, Watanabe S, Masuda Y (2001) Pericardial fat accumulation in men as a risk factor for coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 157:203–209
Salgado-Somoza A, Teijeira-Fernández E, Fernández AL, González-Juanatey JR, Eiras S (2010) Proteomic analysis of epicardial and subcutaneous adipose tissue reveals differences in proteins involved in oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 299:H202–H209
Rijzewijk LJ, van der Meer RW, Smit JW, Diamant M, Bax JJ, Hammer S, Romijn JA, de Roos A, Lamb HJ (2008) Myocardial steatosis is an independent predictor of diastolic dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Am Coll Cardiol 52:1793–1799
Castellano J, Farré J, Fernandes J, Bayes-Genis A, Cinca J, Badimon L, Hove-Madsen L, Llorente-Cortés V (2011) Hypoxia exacerbates Ca(2+)-handling disturbances induced by very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 50:894–902
Cal R, Castellano J, Revuelta-López E, Aledo R, Barriga M, Farré J, Vilahur G, Nasarre L, Hove-Madsen L, Badimon L, Llorente-Cortés V (2012) Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 mediates hypoxia-induced very low density lipoprotein-cholesteryl ester uptake and accumulation in cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Res 94:469–479
Yagyu H, Lutz EP, Kako Y, Marks S, Hu Y, Choi SY, Bensadoun A, Goldberg IJ (2002) Very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) receptor-deficient mice have reduced lipoprotein lipase activity. Possible causes of hypertriglyceridemia and reduced body mass with VLDL receptor deficiency. J Biol Chem 277:10037–10043
Goudriaan JR, Tacken PJ, Dahlmans VE, Gijbels MJ, van Dijk KW, Havekes LM, Jong MC (2001) Protection from obesity in mice lacking the VLDL receptor. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21:1488–1493
Descamps O, Bilheimer D, Herz J (1993) Insulin stimulates receptor-mediated uptake of apoE-enriched lipoproteins and activated alpha 2-macroglobulin in adipocytes. J Biol Chem 268:974–981
Gauthier A, Vassiliou G, Benoist F, McPherson R (2003) Adipocyte low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein gene expression and function is regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. J Biol Chem 278:11945–11953
Hofmann SM, Zhou L, Perez-Tilve D, Greer T, Grant E, Wancata L, Thomas A, Pfluger PT, Basford JE, Gilham D, Herz J, Tschöp MH, Hui DY (2007) Adipocyte LDL receptor-related protein-1 expression modulates postprandial lipid transport and glucose homeostasis in mice. J Clin Invest 117:3271–3282
Llorente-Cortés V, Otero-Viñas M, Sánchez S, Rodríguez C, Badimon L (2002) Low-density lipoprotein upregulates low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein expression in vascular smooth muscle cells: possible involvement of sterol regulatory element binding protein-2-dependent mechanism. Circulation 106:3104–3110
Llorente-Cortés V, Costales P, Bernués J, Camino-Lopez S, Badimon L (2006) Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 negatively regulates low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein transcription. J Mol Biol 359:950–960
Costales P, Aledo R, Vérnia S, Das A, Shah VH, Casado M, Badimon L, Llorente-Cortés V (2010) Selective role of sterol regulatory element binding protein isoforms in aggregated LDL-induced vascular low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 expression. Atherosclerosis 213:458–468
Sendra J, Llorente-Cortés V, Costales P, Huesca-Gómez C, Badimon L (2008) Angiotensin II upregulates LDL receptor-related protein (LRP1) expression in the vascular wall: a new pro-atherogenic mechanism of hypertension. Cardiovasc Res 78:581–589
Bayes-Genis A, Soler-Botija C, Farré J, Sepúlveda P, Raya A, Roura S, Prat-Vidal C, Gálvez-Montón C, Montero JA, Büscher D, Izpisúa Belmonte JC (2010) Human progenitor cells derived from cardiac adipose tissue ameliorate myocardial infarction in rodents. J Mol Cell Cardiol 49:771–780
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Rydén L, Standl E, Bartnik M, Van den Berghe G, Betteridge J, de Boer MJ, Cosentino F, Jönsson B, Laakso M, Malmberg K, Priori S, Ostergren J, Tuomilehto J, Thrainsdottir I, Vanhorebeek I, Stramba-Badiale M, Lindgren P, Qiao Q, Priori SG, Blanc JJ, Budaj A, Camm J, Dean V, Deckers J, Dickstein K, Lekakis J, McGregor K, Metra M, Morais J, Osterspey A, Tamargo J, Zamorano JL, Deckers JW, Bertrand M, Charbonnel B, Erdmann E, Ferrannini E, Flyvbjerg A, Gohlke H, Juanatey JR, Graham I, Monteiro PF, Parhofer K, Pyörälä K, Raz I, Schernthaner G, Volpe M, Wood D; Task Force on Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases: executive summary (2007) The task force on diabetes and cardiovascular diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Eur Heart J 28:88–136
Gaborit B, Kober F, Jacquier A, Moro PJ, Cuisset T, Boullu S, Dadoun F, Alessi MC, Morange P, Clément K, Bernard M, Dutour A (2012) Assessment of epicardial fat volume and myocardial triglyceride content in severely obese subjects:relationship to metabolic profile, cardiac function and visceral fat. Int J Obes (Lond) 36:422–430
Yerramasu A, Dey D, Venuraju S, Anand DV, Atwal S, Corder R, Berman DS, Lahiri A (2012) Increased volume of epicardial fat is an independent risk factor for accelerated progression of sub-clinical coronary atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 220:223–230
Harmancey R, Wilson CR, Taegtmeyer H (2008) Adaptation and maladaptation of the heart in obesity. Hypertension 52:181–187
Sell H, Dietze-Schroeder D, Eckel J (2006) The adipocyte-myocyte axis in insulin resistance. Trends Endocrinol Metab 17:416–422
Cal R, Juan-Babot O, Brossa V, Roura S, Galvez-Monton C, Portoles M, Rivera M, Cinca J, Badimon L, Llorente-Cortes V (2012) Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 expression correlatos with cholesteryl ester accumulation in the myocardium of ischemic cardiomyopathy patients. J Transl Med 10:160
Castellano J, Aledo R, Sendra J, Costales P, Juan-Babot O, Badimon L, Llorente-Cortés V (2011) Hypoxia stimulates low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 expression through hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:1411–1420
Masson O, Chavey C, Dray C, Meulle A, Daviaud D, Quilliot D, Muller C, Valet P, Liaudet-Coopman E (2009) LRP1 receptor controls adipogenesis and is up-regulated in human and mouse obese adipose tissue. PLoS ONE 4:e7422
Clemente-Postigo M, Queipo-Ortuño MI, Fernandez-Garcia D, Gomez-Huelgas R, Tinahones FJ, Cardona F (2011) Adipose tissue gene expression of factors related to lipid processing in obesity. PLoS ONE 6:e24783
Corvera S, Graver DF, Smith RM, Insulin increases the cell surface concentration of alpha 2-macroglobulin receptors in 3T3-L1 adipocytes (1989) Altered transit of the receptor among intracellular endocytic compartments. J Biol Chem 264:10133–10138
Jedrychowski MP, Gartner CA, Gygi SP, Zhou L, Herz J, Kandror KV, Pilch PF (2010) Proteomic analysis of GLUT4 storage vesicles reveals LRP1 to be an important vesicle component and target of insulin signaling. J Biol Chem 285:104–114
Bogan JS (2012) Regulation of glucose transporter translocation in health and diabetes. Annu Rev Biochem 81:507–532
Dicker A, Le Blanc K, Aström G, van Harmelen V, Götherström C, Blomqvist L, Arner P, Rydén M (2005) Functional studies of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult human adipose tissue. Exp Cell Res 308:283–290
Iwasaki T, Takahashi S, Takahashi M, Zenimaru Y, Kujiraoka T, Ishihara M, Nagano M, Suzuki J, Miyamori I, Naiki H, Sakai J, Fujino T, Miller NE, Yamamoto TT, Hattori H (2005) Deficiency of the very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) receptors in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: insulin dependency of the VLDL receptor. Endocrinology 146:3286–3294
Takazawa T, Yamauchi T, Tsuchida A, Takata M, Hada Y, Iwabu M, Okada-Iwabu M, Ueki K, Kadowaki T (2009) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonist rosiglitazone increases expression of very low density lipoprotein receptor gene in adipocytes. J Biol Chem 284:30049–30057
Takahashi S, Sakai J, Fujino T, Hattori H, Zenimaru Y, Suzuki J, Miyamori I, Yamamoto TT (2004) The very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) receptor: characterization and functions as a peripheral lipoprotein receptor. J Atheroscler Thromb 11:200–208
Prawitt J, Niemeier A, Kassem M, Beisiegel U, Heeren J (2008) Characterization of lipid metabolism in insulin-sensitive adipocytes differentiated from immortalized human mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res 314:814–824
Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM (2006) Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 444:840–846
Biddinger SB, Kahn CR (2006) From mice to men: insights into the insulin resistance syndromes. Annu Rev Physiol 68:123–158
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by grants from Instituto de Salud Carlos III, REDINSCOR RD06/0003/0015 (V. Llorente-Cortés and O. Juan-Babot), FIS PI11/00747 cofinanced by Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (F.E.D.E.R) and by Fundació MARATÓ TV3 (080110). The authors thank Dr. Vicenç Martí (Interventional Cardiology Unit, Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau-UAB, Barcelona) by his help with data collection and statistics.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Guido Pozza.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasarre, L., Juan-Babot, O., Gastelurrutia, P. et al. Low density lipoprotein receptor–related protein 1 is upregulated in epicardial fat from type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and correlates with glucose and triglyceride plasma levels. Acta Diabetol 51, 23–30 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-012-0436-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-012-0436-8