Abstract
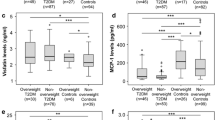
Obesity, insulin resistance (IR), and progressive decline in pancreatic β-cell function are major features of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Altered adipokines contribute to obesity-induced IR. Hence understanding of adipokines’ relation to obesity and glycemic control could be useful to improve disease outcomes. We aimed at determination of serum retinol binding protein-4 (RBP-4), lipocalin-2 (LCN-2), insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), and its binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) levels in T2DM patients with the impact of obesity and glycemic control on them and their relation to β-cell function. Serum insulin, RBP-4, LCN-2, IGF-I, and IGFBP-3 estimated by ELISA were examined in 32 T2DM patients and age- and sex-matched 20 healthy controls. Significant elevation was observed in serum RBP-4 (P < 0.001), LCN-2 (P < 0.01), and IGF-I/IGFBP-3 molar ratio (P < 0.05) in T2DM patients in comparison with healthy controls. There was no significant difference in them between nonobese and obese diabetics. However, RBP-4 and IGF/IGFBP-3 molar ratio were higher in uncontrolled than in controlled diabetic patients at P < 0.001 and P < 0.01, respectively. Moreover, RBP-4, LCN-2, and IGF-I/IGFBP-3 molar ratio were negatively correlated with β-cell function. In conclusion, serum RBP-4 and IGF-I/IGFBP-3 molar ratio but not LCN-2 were prominently elevated with poor glycemic control rather than obesity in T2DM patients. Whereas, declining β-cell function is associated with elevation of serum RBP-4, LCN-2 as well as IGF-I/IGFBP-3 molar ratio.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
IDF (2009) Diabetes atlas, 4th edn. International Diabetes Federation. Available at: www.diabetesatlas.org
Li L, Wang C, Bao Y, Wu H, Lu J, Xiang K et al (2009) Serum retinol-binding protein 4 is associated with insulin secretion in Chinese people with normal glucose tolerance. J Diabetes 1:125–130
Tschoner A, Sturm W, Engl J, Kaser S, Laimer M, Laimer E et al (2008) Retinol-binding Protein 4, visceral fat, and the metabolic syndrome: effects of weight loss. Obesity 16:2439–2444
Law I, Xu A, Lam K, Berger T, Mak T, Vanhoutte P et al (2010) Lipocalin-2 deficiency attenuates insulin resistance associated with aging and obesity. Diabetes 59:4872–4882
Lee J, Im J, Park K, Lee H, Shim J, Lee D (2009) Retinol binding protein 4 and insulin resistance in apparently healthy elderly subjects. Clinica Chimica Acta 400:30–32
Yang Q, Graham T, Mody N, Preitner F, Peroni O, Zabolotny J et al (2005) Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature 436:356–362
Graham T, Yang Q, Bluher M, Hammarstedt A, Ciaraldi T, Henry R et al (2006) Retinol-binding protein 4 and insulin resistance in lean, obese, and diabetic subjects. N Engl J Med 354:2552–2563
Cho Y, Youn B, Lee H, Lee N, Min S, Kwak S et al (2006) Plasma retinol-binding protein-4 concentrations are elevated in human subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 29:2457–2461
Janke J, Engeli S, Boschmann M, Adams F, Bohnke J, Luft F et al (2006) Retinol-binding protein 4 in human obesity. Diabetes 55:2805–2810
Yao-Borengasser A, Varma V, Bodles AM et al (2007) Retinol binding protein 4 expression in humans: relationship to insulin resistance, inflammation, and response to pioglitazone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:2590–2597
Promintzer M, Krebs M, Todoric J, Luger A, Bischof M, Nowotny P et al (2007) Insulin resistance is unrelated to circulating retinol binding protein and protein C inhibitor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:4306–4312
Flo T, Smith K, Sato S, Rodriguez D, Holmes M, Strong R et al (2004) Lipocalin 2 mediates an innate immune response to bacterial infection by sequestrating iron. Nature 432:917–921
Jayaraman A, Roberts K, Yoon J, Yarmush D, Duan X, Lee K et al (2005) Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a discriminatory marker of the hepatocyte-secreted protein response to IL-1: a proteomic analysis. Biotechnol Bioeng 91:502–515
Fujino R, Tanaka K, Morimatsu M, Tamura K, Kogo H, Hara T (2006) Spermatogonial cell-mediated activation of an IkappaBzeta-independent NF-kappaB pathway in sertoli cells induces transcription of the lipocalin-2 gene. Mol Endocrinol 4:904–915
Wang Y, Lam K, Kraegen E, Sweeney G, Zhang J, Tso A et al (2007) Lipocalin-2 is an inflammatory marker closely associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and hyperglycemia in humans. Clin Chem 53:34–41
Panidis D, Tziomalos K, Koiou E, Kandaraki E, Tsourdi E, Delkos D et al (2010) The effects of obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome on serum lipocalin-2 levels: a cross-sectional study. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 8:151
Denley A, Cosgrove L, Booker G, Wallace J, Forbes B (2005) Molecular interactions of the IGF system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16:421–439
Cleveland-Donovan K, Maile LA, Tsiaras WG, Tchkonia T, Kirkland JL, Boney CM (2010) IGF-I activation of the AKT pathway is impaired in visceral but not subcutaneous preadipocytes from obese subjects. Endocrinology 151(8):3752–3763
Jogie-Brahim S, Feldman D, Oh Y (2009) Unraveling insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 actions in human disease. Endocr Rev 30(5):417–437
Rajpathak S, Gunter M, Wylie-Rosett J, Ho G, Kaplan R, Muzumdar R, Rohan T, Strickler H (2009) The role of insulin-like growth factor-I and its binding proteins in glucose homeostasis and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 25:3–12
Lam C, Chen M, Lacey S, Yang Q, Sullivan L, Xanthakis V, Safa R, Smith H, Peng X, Sawyer D, Vasan R (2010) Circulating insulin-like growth factor-1 and its binding protein-3: metabolic and genetic correlates in the community. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30(7):1479–1484
Rajpathak S, McGinn A, Strickler H, Rohan T, Pollak M, Cappola A et al (2008) Insulin-like growth factor-(IGF)-axis, inflammation, and glucose intolerance among older adults. Growth Horm IGF Res 18:166–173
Trinder P (1969) Determination of glucose in blood using glucose oxidase with an alternative oxygen acceptor. Ann Clin Biochem 6:24–27
Abraham E, Huff T, Cope N, Wilson J, Bransome E, Huisman T (1978) Determination of the glycosylated hemoglobins (HbA1) with a new microcolumn procedure. Suitability of the technique for assessing the clinical management of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 27:931–937
Henry RJ (1974) Clinical chemistry, principles and techniques, 2nd edn. Harper and Row, New York, p 525
Siedel J, Hagele E, Ziegenhorn J, Wahlefeld A (1983) Reagent for the enzymatic determination of serum total cholesterol with improved lipolytic efficiency. Clin Chem 29:1075–1080
Richmond W (1973) Preparation and properties of a cholesterol oxidase from Nocardia sp. and its application to the enzymatic assay of total cholesterol in serum. Clin Chem 19(12):1350–1356
Burstein M, Scholnick HR, Morfin R (1970) Rapid method for the isolation of lipoproteins from human serum by precipitation with polyanions. J Lipid Res 11(6):583–595
Bergmeyer HU (1985) Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol VIII, 3rd edn. VCH Verlagsgesellschaft, Weinheim, pp 154–160
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
Wolpin B, Michaud D, Giovannucci E, Schernhammer E, Stampfer M, Manson J, Cochrane B, Rohan T, Ma J, Pollak M, Fuchs C (2007) Circulating insulin-like growth factor axis and the risk of pancreatic cancer in four prospective cohorts. Br J Cancer 97:98–104
Eckel RH, Kahn SE, Ferrannini E, Goldfine AB, Nathan DM, Schwartz MW, Smith RJ, Smith SR (2011) Obesity and type 2 diabetes: what can be unified and what needs to be individualized? Diabetes Care 34:1424–1430
Kanat M, Winnier D, Norton L, Arar N, Jenkinson C et al (2011) The relationship between β-cell function and glycated hemoglobin: results from the veterans administration genetic epidemiology study. Diabetes Care 34:1006–1010
Maedler K, Schulthess F, Bielman C, Berney T, Bonny C, Prentki M, Donath M, Roduit R (2008) Glucose and leptin induce apoptosis in human β-cells and impair glucose-stimulated insulin secretion through activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinases. FASEB J 22:1905–1913
Liu X, Hamnvik O, Petrou M, Gong H, Chamberland J et al (2011) Circulating lipocalin 2 is associated with body fat distribution at baseline but is not an independent predictor of insulin resistance: the prospective Cyprus metabolism study. Eur J Endocrinol 165:805–812
Thrailkill K, Moreau C, Cockrell G (2010) Disease and gender-specific dysregulation of NGAL and MMP-9 in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Endocrine 37(2):336–343
Bruun C, Heding PE, Ronn SG, Frobose H, Rhodes CJ, Mandrup-Poulsen T, Billestrup N (2009) Suppressor of cytokine signalling-3 inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced apoptosis and signalling in beta cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 311(1–2):32–38
Wabitsch M, Heinze E, Debatin KM, Blum WF (2000) IGF-I- and IGFBP-3-expression in cultured human preadipocytes and adipocytes. Horm Metab Res 32:555–559
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to appreciate the kind help of Prof. Dr. Mohamed Fahmy Abd-El Aziz, Prof. and Head of the Endocrinology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt, for facilitating clinical samples and their data collection. This research did not receive any specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sector.
Conflict of interest
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Mesallamy, H.O., Hamdy, N.M. & Sallam, Aa.M. Effect of obesity and glycemic control on serum lipocalins and insulin-like growth factor axis in type 2 diabetic patients. Acta Diabetol 50, 679–685 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-012-0373-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-012-0373-6