Abstract
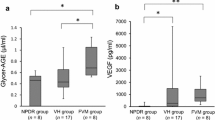
We determined the levels of the endogenous angiogenesis inhibitors soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (sVEGFR-1), thrombospondin (TSP)-1 and TSP-2 in the vitreous fluid from patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) and correlated their levels with clinical disease activity and the levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Vitreous samples from 30 PDR and 25 nondiabetic patients were studied by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. TSP-1 was not detected. VEGF and TSP-2 levels were significantly higher in PDR with active neovascularization compared with inactive PDR and nondiabetic patients (P < 0.001 for both comparisons). VEGF, sVEGFR-1 and TSP-2 levels were significantly higher in PDR with hemorrhage compared with PDR without hemorrhage and nondiabetic patients (P = 0.0063; 0.0144; <0.001, respectively). VEGF and sVEGFR-1 levels were significantly higher in PDR without traction retinal detachment (TRD) compared with PDR with TRD and nondiabetic patients (P = 0.038; 0.022, respectively). TSP-2 levels were significantly higher in PDR with TRD compared with PDR without TRD and nondiabetic patients (P < 0.001). There was a significant correlation between levels of VEGF and sVEGFR-1 (r = 0.427, P = 0.038). Our findings suggest that upregulation of sVEGFR-1 and TSP-2 may be a protective mechanism against progression of angiogenesis associated with PDR. TSP-2 might be associated with TRD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spranger J, Pfeiffer AP (2001) New concepts in pathogenesis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 109:S438–S450
Dawson DW, Volpert OV, Gillis P, Crawford SE, Xu H, Benedict W, Bouck NP (1999) Pigment epithelium-derived factor: a potent inhibitor of angiogenesis. Science 285:245–248
Matsunaga N, Chikaraishi Y, Izuta H, Ogata N, Shimazawa M, Matsumura M, Hara H (2008) Role of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 in the vitreous in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmology 115:1916–1922
Shibuya M (2006) Differential roles of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 and receptor-2 in angiogenesis. J Biochem Mol Biol 39:469–478
Wu FTH, Stefanini MO, Gabhann FM, Kontos CD, Annex BH, Popel AS (2010) A system biology perspective on sVEGFR-1: its biological function, pathogenic role and therapeutic use. J Cell Mol Med 14:528–552
Zhang X, Lawler J (2007) Thrombospondin-based antiangiogenic therapy. Microvasc Res 74:90–99
Aiello LP, Avery RL, Arrigg PG, Keyt BA, Jampel HD, Shah ST, Pasquale LR, Thieme H, Iwamoto MA, Park JE, Nguyen HV, Aiello LM, Ferrara N, King GL (1994) Vascular endothelial growth factor in ocular fluid in patients with diabetic retinopathy and other retinal disorders. N Engl J Med 331:1480–1487
Rota R, Riccioni T, Zaccarini M, Lamartina S, Gallo AD, Fusco A, Kovesdi I, Balestrazzi E, Abeni DC, Ali RR, Capogrossi MC (2004) Marked inhibition of retinal neovascularization in rats following soluble-flt-1 gene transfer. J Gene Med 6:992–1002
Kyriakides TR, Tam JW (1999) Bornstein. Accelerated wound healing in mice with a disruption of the thrombospondin 2 gene. J Invest Dermatol 113:782–787
Lin T-N, Kim G-M, Chen J-J, Cheung W-M, He YY, Hsu CY (2003) Differential regulation of thrombospondin-1 and thrombospondin-2 after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Stroke 34:177–186
Hawighorst T, Velasco P, Streit M, Hong Y-K, Kyriakides TR, Brown LF, Bornstein P, Detmar M (2001) Thrombospondin-2 plays a protective role in multistep carcinogenesis: a novel host anti-tumor defense mechanism. EMBO J 20:2631–2640
Streit M, Riccardi L, Velasco P, Brown LF, Hawighorst T, Bornstein P, Detmar M (1999) Thrombospondin-2: a potent endogenous inhibitor of tumor growth and angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:14888–14893
Noh Y-H, Matsuda K, Hong Y-K, Kunstfeld R, Riccardi L, Koch M, Oura H, Dadras SS, Streit M, Detmar M (2003) An N-terminal 80 kDa recombinant fragment of human thrombopsondin-2 inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor induced endothelial cell migration in vitro and tumor growth and angiogenesis in vivo. J Invest Dermatol 121:1536–1543
Koch M, Hussein F, Woeste A, Gründker C, Frontzek K, Emons G, Hawighorst T (2011) CD36-mediated activation of endothelial cell apoptosis by an N-terminal recombinant fragment of thrombospondin-2 inhibits breast cancer growth and metastasis in vivo. Breast Cancer Res Treat 128:337–346
MacLauchlan S, Skokos EA, Agah A, Zeng J, Tian W, Davidson JM, Bornstein P, Kyriakides TR (2009) Enhanced angiogenesis and reduced contraction in thrombospondin-2-null wounds is associated with increased levels of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and-9 and soluble VEGF. J Histochem Cytochem 57:301–313
Kyriakides TR, Zhu Y-H, Yang Z, Huynh G, Bornstein P (2001) Altered extracellular matrix remodeling and angiogenesis in sponge granulomas of thrombospondin 2-null mice. Am J Pathol 159:1255–1262
Krady MM, Zeng J, Yu J, MacLauchlan S, Skokos EA, Tian W, Bornstein P, Sessa WC, Kyriakides TR (2008) Thrombospondin-2 modulates extracellular matrix remodeling during physiological angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 173:879–891
Park YW, Kang YM, Butterfield J, Detmar M, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM (2004) Thrombospondin 2 functions as an endogenous regulator of angiogenesis and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Pathol 165:2087–2098
Armstrong LC, Björkblom B, Hankenson KD, Siadak AW, Stiles CE, Bornstein P (2002) Thrombospondin 2 inhibits microvascular endothelial cell proliferation by a caspase-independent mechanism. Mol Biol Cell 13:1893–1905
Simantov R, Febbraio M, Silverstein RL (2005) The antiangiogenic effect of thrombospondin-2 is mediated by CD36 and modulated by histidine-rich glycoprotein. Matrix Biol 24:27–34
Adri VC, Kupriyanova TA, Deryugina EI, Quigley JP (2007) Human neutrophils uniquely release TIMP-Free MMP-9 to provide a potent catalytic stimulator of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:20262–20267
Bergers G, Prekken R, McMahon G, Vu TH, Itoh T, Tamaki K, Tanzawa K, Thorpe P, Itohara S, Werb Z, Hanahan D (2000) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during carcinogenesis. Natl Cell Biol 2:737–744
Lee S, Jilani SM, Nikolova GV, Carpizo D, Iruela-Arispe ML (2005) Processing of VEGF-A by matrix metalloproteinases regulates bioavailability and vascular patterning in tumors. J Cell Biol 169:681–691
Abu El-Asrar AM, Struyf S, Kangave D, Geboes K, Van Damme J (2006) Chemokines in proliferative diabetic retinopathy and proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Eur Cytokine Netw 17:155–165
Ogata N, Ando A, Uyama M, Matsumura M (2001) Expression of cytokines and transcription factors in photocoagulated human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Graefes Arch Exp Ophthalmol 239:87–95
Xiao M, McLeod D, Cranley J, Williams G, Boulton M (1999) Growth factor staining patterns in the pig retina following retinal laser photocoagulation. Br J Ophthalmol 83:728–736
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ms. Connie B. Unisa-Marfil for secretarial work. This work was supported by Dr. Nasser Al-Rasheed Research Chair in Ophthalmology (Abu El-Asrar AM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abu El-Asrar, A.M., Nawaz, M.I., Kangave, D. et al. Angiogenesis regulatory factors in the vitreous from patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Acta Diabetol 50, 545–551 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-011-0330-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-011-0330-9