Abstract
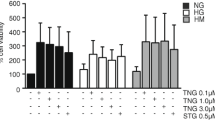
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) is an enzyme that is produced by endothelial cells in different districts and circulates in plasma. Patients with type 2 diabetes show a reduction in active Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) that could be due to impairment of secretion or its degradation or both. GLP-1 is rapidly inactivated in vivo, mainly by the DPP-4. Some authors suggest that Metformin has no direct inhibitory effect on DPP-4 activity and that Metformin and the other biguanides enhance GLP-1 secretion; others suggest a possible role of Metformin in the inhibition of the DPP-4 activity. In order to better elucidate the role of insulin sensitizers on the modulation of GLP-1 circulating levels, DPP-4 activity and mRNA expression were measured in cultured human aortic endothelial cells (HAEC) and human microvascular dermal endothelial cells (HMVEC) exposed to high glucose, Metformin and Rosiglitazone. Present data show that hyperglycemia is capable of increasing in a significant manner the DPP-4 activity only in microvascular endothelial cells. Rosiglitazone is able to modulate in a negative manner the expression of DPP-4 but not its activity in macrovascular endothelial cells, while at 24 h of exposure it is able to increase significantly DPP-4 activity but not its expression in microvascular endothelial cells. Metformin at 48 h only in microvascular endothelial cells is able to reduce in a significant manner (p = 0.01) the activity of DPP-4 but not its expression. The modulation of DPP-4 is site specific.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holst JJ, Deacon CF (1998) Inhibition of the activity of dipeptidyl-peptidase IV as a treatment for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 47:1663–1670
Dubový P, Kukletová MA (1992) Histochemical study by light and electron microscopy of the distribution of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV activity in the human dental pulp. Arch Oral Biol 37(1):1–6
Mentlein R, Gallwitz B, Schmidt WE (1993) Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV hydrolyses gastric inhibitory polypeptide, glucagon-like peptide-1-(7–36) amide, peptide histidine methionine, and is responsible for their degradation in human serum. Eur J Biochem 214:829–835
Augustyns K, Bal G, Thonus G, Belyaev A, Zhang XM, Bollaert W, Lambeir AM, Durinx C, Goossens F, Haemers A (1998) The unique properties of dipeptidyl-peptidase IV (DPP IV/CD 26) and the therapeutic potential of DPP-IV inhibitors. Curr Med Chem 6:311–327
Meneilly GS, Demuth HU, McIntosh CH, Pederson RA (2000) Effect of ageing and diabetes on glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and dipeptidyl peptidase IV responses to oral glucose. Diabet Med 17:346–350
Visboll T, Krarup T, Deacon CF, Madsbad S, Holst JJ (2001) Reduced postprandial concentration of intact biologically active glucagon-like peptide-1 in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes 50:609–613
Mannucci E, Pala L, Ciani S, Bardini G, Pezzatini A, Sposato I, Cremasco F, Ognibene A, Rotella CM (2005) Hyperglycaemia increases dipeptidyl peptidase IV activity in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 48(6):1168–1172
Pala L, Mannucci E, Pezzatini A, Ciani S, Sardi J, Raimondi L, Ognibene A, Cappadona A, Vannelli BG, Rotella CM (2003) Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV expression and activity in human glomerular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 310:28–31
Mannucci E, Ognibene A, Cremasco F, Bardini G, Mencucci A, Pierazzuoli E, Ciani S, Fanelli A, Messeri G, Rotella CM (2000) Glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 and leptin concentrations in obese patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 17(10):713
Mannucci E, Ognibene A, Cremasco F, Bardini G, Mencucci A, Pierazzuoli E, Ciani S, Messeri G, Rotella CM (2001) Effects of metformin on glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and leptin levels in obese non-diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 24:489–494
Lindsay JR, Duffy NA, McKillop AM, Ardill J, O’Harte FP, Flatt PR, Bell PM (2005) Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV activity by oral metformin in Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 22(5):654–657
Green BD, Irwin N, Duffy NA, Gault VA, O’harte FP, Flatt PR (2006) Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV activity by metformin enhances the antidiabetic effects of glucagon-like peptide-1. Eur J Pharmacol 547(1-3):192–199
Yasuda N, Inoue T, Nagakura T, Yamazaki K, Kira K, Saeki T, Tanaka I (2002) Enhanced secretion of glucagon-like peptide 1 by biguanide compounds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 298(5):779–784
Hinke SA, Kühn-Wache K, Hoffmann T, Pederson RA, McIntosh CH, Demuth HU (2002) Metformin effects on dipeptidylpeptidase IV degradation of glucagon-like peptide-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 291(5):1302–1308
Duffy NA, Green BD, Irwin N, Gault VA, McKillop AM, O’Harte FP, Flatt PR (2007) Effects of antidiabetic drugs on dipeptidyl peptidase IV activity: nateglinide is an inhibitor of DPP IV and augments the antidiabetic activity of glucagon-like peptide-1. Eur J Pharmacol 568(1-3):278–286
Rotella CM, Giannini S, Galli G, Cresci B, Tanini A (1996) Role of endothelial cells in the pathogenesis of diabetic microangiopathy DNM 9:273–289
Benvenuti S, Cellai I, Luciani P, Deledda C, Baglioni S, Giuliani C, Saccardi R, Mazzanti B, Dal Pozzo S, Mannucci E, Peri A, Serio M (2007) Rosiglitazone stimulates adipogenesis and decreases osteoblastogenesis in human mesenchymal stem cells. J Endocrinol Invest 30(9):RC26–RC30
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and the 2 − ΔΔCt. Methods 25:402–408
Durinx C, Neels H, Van der Auwera JC, Naelaerts K, Scharpe S, De Meester I (2001) Reference values for plasma dipeptidyl-peptidase IV activity and their association with other laboratory parameters. Clin Chem Lab Med 39:155–158
Mannucci E, Tesi F, Bardini G, Ognibene A, Petracca MG, Ciani S, Pezzatini A, Brogi M, Dicembrini I, Cremasco F, Messeri G, Rotella CM (2004) Effects of metformin on glucagon-like peptide-1 levels in obese patients with and without Type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Nutr Metab 17(6):336–342
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the Ministry of Scientific Research (PRIN and 60% founds MIUR).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pala, L., Pezzatini, A., Dicembrini, I. et al. Different modulation of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 activity between microvascular and macrovascular human endothelial cells. Acta Diabetol 49 (Suppl 1), 59–63 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-010-0195-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-010-0195-3