Abstract
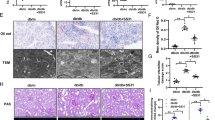
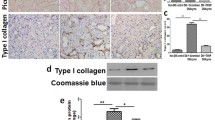
Although mitochondrial reduction-oxidation (redox) stress and increase in membrane permeability play an important role in diabetic-associated renal microvasculopathies, it is unclear whether the intra-renal mitochondrial oxidative stress induces mitochondrial protein modifications, leading to increase mitochondrial membrane permeability. The hypothesis is that mitochondrial oxidative stress induces mitochondrial protein modification and leakage in the mitochondrial membrane in type-2 diabetes. The present study was conducted to determine the involvement of intra-renal mitochondrial oxidative stress in mitochondrial protein modifications and modulation of membrane permeability in the setting of type-2 diabetes. Diabetes was induced by 6-week regimen of a high calorie and fat diet in C57BL/6J mice (Am J Physiol 291:F694–F701, 2006). Subcellular fractionation was carried out in kidney tissue from wild type and diabetic mice. All fractions were highly enriched in their corresponding marker enzyme. Subcellular protein modifications were determined by Western blot and 2-D proteomics. The results suggest that diabetes-induced oxidative stress parallels an increase in NADPH oxidase-4 (NOX-4) and decrease in superoxide dismutase-1, 2 (SOD-1, 2) expression, in mitochondrial compartment. We observed loss of mitochondrial membrane permeability as evidenced by leakage of mitochondrial cytochrome c and prohibitin to the cytosol. However, there was no loss in control tissue. The 2-D Western blots for mitochondrial post-translational modification showed an increase in nitrotyrosine generation in diabetes. We conclude that diabetes-induced intra-renal mitochondrial oxidative stress is reflected by an increase in mitochondrial membrane permeability and protein modifications by nitrotyrosine generation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mustad VA, Demichele S, Huang YS, Mika A, Lubbers N, Berthiaume N, Polakowski J, Zinker B (2006) Differential effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on metabolic control and vascular reactivity in the type 2 diabetic ob/ob mouse. Metabolism 55:1365–1374
Merzouk S, Hichami A, Madani S, Merzouk H, Berrouiguet AY, Prost J, Moutairou K, Chabane-Sari N, Khan NA (2003) Antioxidant status and levels of different vitamins determined by high performance liquid chromatography in diabetic subjects with multiple complications. Gen Physiol Biophys 22:15–27
Tyagi N, Sedoris KC, Steed M, Ovechkin AV, Moshal KS, Tyagi SC (2005) Mechanisms of homocysteine-induced oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289:H2649–H2656
Moshal KS, Tyagi N, Moss V, Henderson B, Steed M, Ovechkin A, Aru GM, Tyagi SC (2005) Early induction of matrix metalloproteinase-9 transduces signaling in human heart end stage failure. J Cell Mol Med 9:704–713
Turko IV, Li L, Aulak KS, Stuehr DJ, Chang JY, Murad F (2003) Protein tyrosine nitration in the mitochondria from diabetic mouse heart. Implications to dysfunctional mitochondria in diabetes. J Biol Chem 278:33972–33977
Rodriguez WE, Tyagi N, Joshua IG, Passmore JC, Fleming JT, Falcone JC, Tyagi SC (2006) Pioglitazone mitigates renal glomerular vascular changes in high-fat, high-calorie-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291:F694–F701
Yoo C, Song C, Kim B, Hong H, Lee H (2004) Glycated albumin induces superoxide generation in mesangial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 14:361–368
Allen DA, Harwood S, Varagunam M, Raftery MJ, Yaqoob MM (2003) High glucose-induced oxidative stress causes apoptosis in proximal tubular epithelial cells and is mediated by multiple caspases. FASEB J 17:908–910
Marti HP (2000) Role of matrix metalloproteinases in mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis. Kidney Blood Press Res 23:199–201
Oancea E, Teruel MN, Quest AF, Meyer T (1998) Green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged cysteine-rich domains from protein kinase C as fluorescent indicators for diacylglycerol signaling in living cells. J Cell Biol 140:485–498
Fumo P, Kuncio GS, Ziyadeh FN (1994) PKC and high glucose stimulate collagen alpha 1 (IV) transcriptional activity in a reporter mesangial cell line. Am J Physiol 267:F632–F638
Koya D, Jirousek MR, Lin YW, Ishii H, Kuboki K, King GL (1997) Characterization of protein kinase C beta isoform activation on the gene expression of transforming growth factor-beta, extracellular matrix components, and prostanoids in the glomeruli of diabetic rats. J Clin Invest 100:115–126
Inoguchi T, Sonta T, Tsubouchi H, Etoh T, Kakimoto M, Sonoda N, Sato N, Sekiguchi N, Kobayashi K, Sumimoto H, Utsumi H, Nawata H (2003) Protein kinase C-dependent increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in vascular tissues of diabetes: role of vascular NAD(P)H oxidase. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:S227–S232
Babior BM (1999) NADPH oxidase: an update. Blood 93:1464–1476
Armstrong JS (2006) Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization: the sine qua non for cell death. Bioessays 28:253–260
Huang L, Tang D, Yappert MC, Borchman D (2006) Oxidation-induced changes in human lens epithelial cells 2. Mitochondria and the generation of reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Biol Med 41:926–936
Peng X, Mehta R, Wang S, Chellappan S, Mehta RG (2006) Prohibitin is a novel target gene of vitamin D involved in its antiproliferative action in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 66:7361–7369
Prabhakar SS (2004) Role of nitric oxide in diabetic nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 24:333–344
Tilton RG, Kawamura T, Chang KC, Ido Y, Bjercke RJ, Stephan CC, Brock TA, Williamson JR (1997) Vascular dysfunction induced by elevated glucose levels in rats is mediated by vascular endothelial growth factor. J Clin Invest 99:2192–2202
Whiteman M, Chua YL, Zhang D, Duan W, Liou YC, Armstrong JS (2006) Nitric oxide protects against mitochondrial permeabilization induced by glutathione depletion: role of S-nitrosylation? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 339:255–262
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by American Heart Association Post-Doctoral training grant (award # 0625579B) to K.S.M. and N.I.H. Grants HL-71010, HL-74185, HL-88012 and NS-51568 to SCT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
G. K. Kartha and K. S. Moshal have contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kartha, G.K., Moshal, K.S., Sen, U. et al. Renal mitochondrial damage and protein modification in type-2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol 45, 75–81 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-008-0025-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-008-0025-z