Abstract
Introduction
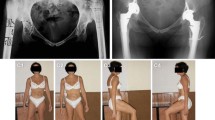
The aim of this study has been to present outcomes after cementless arthroplasty for developmental dysplasia Crowe type IV of the hip, with transverse subtrochanteric shortening osteotomy and using the S-ROM stem.
Methods
We evaluated radiographs, functional scores and complications in a consecutive series of 23 patients (28 hips) with high dislocation of the hip. The average age of patients at surgery was 49.9 (range 22–68) years. The operations were performed between 2007 and 2013. Patients were assessed retrospectively–clinically and radiographically during the year 2018.
Results
The mean follow-up period was 94 (range 60–134) months. The average Harris hip score improved from 39.9 to 84.0. The mean leg length discrepancy decreased from 5 cm preoperatively to 1.4 cm at the final follow-up. All acetabular components were implanted into the true acetabulum, and all prostheses were stable at the latest examination. No neurovascular damage was recorded. We have identified specific complications in seven hips (25%) in total: Intraoperative femoral fracture required fixation in four hips; three hips (10.7%) needed revision: Recurrent dislocation, with the need for cup reorientation, occurred in two hips (in one of them, this was followed by the subsequent need for resection of heterotopic ossification); there was one aseptic stem loosening with the need of one-stage revision. All the osteotomies healed within 8 months.
Conclusion
Hip arthroplasty with transverse shortening femoral osteotomy, using S-ROM stem, is an acceptable, but not complication-free treatment method in patients with Crowe type IV developmental hip dysplasia, in the midterm.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sofu H, Sahin V, Gürsu S et al (2013) Cementless total hip arthroplasty in patients with Crowe Type IV developmental dysplasia. Hip Int 23(5):472
Argenson JN, Flecher X, Parratte S, Aubaniac JM (2007) Anatomy of the dysplastic hip and consequences for total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 465(12):40–45
Liu S, Zuo J, Li Z et al (2017) Study of three-dimensional morphology of the proximal femur in developmental adult dysplasia of the hip suggests that the on-shelf modular prosthesis may not be an ideal choice for patients with Crowe type IV hips. Int Orthop 41(4):707–713
Georgiades G, Babis GC, Kourlaba G, Hartofilakidis G (2010) Effect of cementless acetabular component orientation, position, and containment in total hip arthroplasty for congenital hip disease. J Arthroplast 25(7):1143–1150
Desteli EE, Imren Y, Tan E et al (2015) Clinical results of cementless total hip arthroplasty with shortening osteotomy for high dislocation with developmental dysplasia. Acta Orthop Belg 81(1):30–35
Li L, Yu M, Yang C, Gu G (2016) Total hip arthroplasty (S-ROM stem) and subtrochanteric osteotomy for Crowe type IV developmental dysplasia of the hip. Indian J Orthop 50(2):195–200
Ollivier M, Abdel MP, Krych AJ et al (2016) Long-term results of total hip arthroplasty with shortening subtrochanteric osteotomy in Crowe IV developmental dysplasia. J Arthroplast 31(8):1756–1760
Zagra L, Bianchi L, Mondini A et al (2015) Oblique femoral shortening osteotomy in total hip arthroplasty for high dislocation in patients with hip dysplasia. Int Orthop 39(9):1797–1802
Muratli KS, Karatosun V, Uzun B, Celik S (2014) Subtrochanteric shortening in total hip arthroplasty: biomechanical comparison of four techniques. J Arthroplast 29(4):836–842
Makita H, Inaba Y, Hirakawa K, Saito T (2007) Results of total hip arthroplasties with femoral shortening for Crowe´s group IV dislocated hips. J Arthoplast 22(1):32–38
Zeng WN, Liu JL, Wang FY et al (2017) Total hip arthroplasty for patients with Crowe type IV developmental dysplasia of the hip: ten years results. Int J Surg 42(6):17–21
Macheras GA, Koutsostathis SD, Lepetsos P et al (2014) THA following deformities due to congenital dislocation of the hip joint. Hip Int 24(Suppl. 10):29–32
Sonohata M, Tajima T, Kitajima M et al (2012) Total hip arthroplasty combined with double-chevron subtrochanteric osteotomy. J Orthop Sci 17(4):382–389
Tözün IR, Akgül T, Şensoy V, Kilicoglu ÖI (2016) The results of monoblock stem with step-cut femoral shortening osteotomy for developmentally dislocated hips. Hip Int 26(3):270–277
Mutlu T, Çiçek H, Yalçin N et al (2016) How do different designs of femoral stem affects total hip arthroplasty applied to Crowe type III and type IV dysplastic hips. Hip Int 26(4):374–379
Wang D, Li LL, Wang HY et al (2017) Long-term results of cementless total hip arthroplasty with subtrochanteric shortening osteotomy in Crowe type IV developmental dysplasia. J Arthoplast 32(4):1211–1219
Tamegai H, Otani T, Fujii H et al (2013) A modified S-ROM stem in primary total hip arthroplasty for developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Arthroplast 28(10):1741–1745
Mattingly DA (2005) The S-ROM modular femoral stem in dysplasia of the hip. Orthopedics 28(9 suppl):1069–1073
Drexler M, Dwyer T, Marmor M et al (2013) Nineteen year results of THA using modular 9 mm S-ROM femoral component in patients with small femoral canals. J Arthroplast 28(9):1667–1670
Crowe JF, Mani VJ, Ranawat CS (1979) Total hip replacement in congenital dislocation and dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Jt Surg Am 61(1):15–23
Harris WH (1969) Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Jt Surg Am 51(4):737–755
Dorr LD, Faugere MC, Mackel AM et al (1993) Structural and cellular assessment of bone quality of proximal femur. Bone 14:231–242
Gruen TA, McNeice GM, Amstutz HC (1979) “Modes of failure” of cemented stem-type femoral components: a radiographic analysis of loosening. Clin Orthop 141(6):17–27
DeLee J, Charnley J (1976) Radiological demarcation of cemented sockets in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 121(11):20–32
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioural sciences, 2nd edn. Lawrence Elbaum, Hillsdale
Hua WB, Yang SH, Xu WH et al (2015) Total hip arthroplasty with subtrochanteric femoral shortening osteotomy for high hip dislocation. Orthop Surg 7(2):112–118
Çatma MF, Ünlü S, Öztürk A et al (2016) Femoral shortening osteotomy in total hip arthroplasty for severe dysplasia: a comparison of two fixation techniques. Int Orthop 40(11):2271–2276
Bruce WJ, Rizkallah SM, Kwon YM, Goldberg JA (2000) A new technique of subtrochanteric shortening in total hip in total hip arthroplasty: surgical technique and results of 9 cases. J Arthroplast 15(5):617–626
Onodera S, Majima T, Ito H et al (2006) Cementless total hip arthroplasty using the modular S-ROM prosthesis combined with corrective proximal femoral osteotomy. J Arthroplast 21(5):664–669
Park MS, Kim KH, Jeong WC (2007) Transverse subtrochanteric shortening osteotomy in primary total hip arthroplasty for patients with severe hip developmental dysplasia. J Arthroplast 22(7):1031–1036
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by AZV MZ CR Project No. 15-31269A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Human and animal rights
Every institution involved in this work has approved the human protocol for this investigation.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from the participants, and all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Necas, L., Hrubina, M., Melisik, M. et al. Cementless hip arthroplasty and transverse shortening femoral osteotomy with the S-ROM stem for Crowe type IV developmental dysplasia. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 29, 1025–1033 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-019-02400-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-019-02400-y