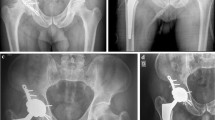
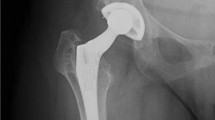
Abstract
Introduction
Clinical outcomes of total hip arthroplasty (THA) to treat rapidly destructive coxarthrosis (RDC) have been reported, but to our knowledge, there have been no studies comparing implants. The aim of this study was to examine the effectiveness of acetabular reconstruction for RDC by comparing the clinical results of THA using a Kerboull-type plate with an uncemented cup.
Patients and methods
Among 921 primary THAs performed between 2006 and 2014, 27 were performed for the treatment for RDC using a Kerboull-type plate or a conventional uncemented cup. A Kerboull-type plate for acetabular reinforcement device was used in 13 hips and an uncemented cup in 14 hips. The mean follow-up period was 61.2 months.
Results
The duration of surgery was 156.8 ± 36.4 min in the Kerboull-type plate group and 103.3 ± 14.4 min in the uncemented cup group, being significantly longer in the former (P = 0.0002). In the Kerboull-type plate group and the uncemented cup group, the 5-year survival rates were 100 and 83.9 %, respectively. Recurrent dislocation was observed in two cases in which the posterior approach had been used.
Conclusions
In our study, the loosening of the acetabular components was noted in 14.3 % of uncemented cup-applied cases, but no loosening was noted in any Kerboull-type plate-applied case. Therefore, for RDC, in which objective evaluation of fragile bone quality is difficult, the use of the Kerboull-type plate, which disperses weight-bearing of the acetabular, may be an effective means to achieve early functional recovery as well as a long-term favorable outcome.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Postel M, Kerboull M (1970) Total prosthetic replacement in rapidly destructive arthrosis of the hip. Clin Orthop 72:138–144
Rosenberg ZS, Shankman S, Steiner GC, Kastenbaum DK, Norman A, Lazansky MG (1992) Rapid destructive osteoarthritis: clinical, radiographic, and pathologic features. Radiology 182:213–216
Bock GW, Garcia A, Weisman MH, Major PA, Lyttle D, Haghighi P, Greenway GD, Resnick D (1993) Rapidly destructive hip disease: clinical and imaging abnormalities. Radiology 186:461–466
Peters K, Doets C (2009) Midterm results of cementless total hip replacement in rapidly destructive arthroplasty and a review of the literature. Hip Int 19:352–358
Kuo A, Ezzet KA, Patil S, Colwell CW Jr (2009) Total hip arthroplasty in rapidly destructive osteoarthritis of the hip: a case series. HSS J 5:117–119
Charrois O, Kahwaji A, Rhami M, Inoue K, Courpied JP (2002) Outcome after total hip arthroplasty performed for rapidly progressive hip destruction. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 88:236–244
Charrois O, Kahwaji A, Vastel L, Rosencher N, Courpied JP (2001) Blood loss in total hip arthroplasty for rapidly destructive coxarthrosis. Int Orthop 25:22–24
Kawai T, Tanaka C, Ikenaga M, Kanoe H, Okudaira S (2010) Total hip arthroplasty using Kerboull-type acetabular reinforcement device for rapidly destructive coxarthrosis. J Arthroplasty 25:432–436
Kerboull M, Hamadouche M, Kerboull L (2000) The Kerboull acetabular reinforcement device in major acetabular reconstructions. Clin Orthop 378:155–168
Kawanabe K, Akiyama H, Onishi E, Nakamura T (2007) Revision total hip replacement using the Kerboull acetabular reinforcement device with morsellised or bulk graft. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89:26–31
Baba T, Shitoto K (2010) Revision of total hip arthroplasty using the Kerboull and KT plates. Int Orthop 34:341–347
Paprosky WG, Perona PG, Lawrence JM (1994) Acetabular defect classification and surgical reconstruction in revision arthroplasty. A 6-year follow-up evaluation. J Arthroplasty 9:33–44
Haenle M, Schlüter S, Ellenrieder M, Mittelmeier W, Bader R (2013) Treatment of acetabular defects during revision total hip arthroplasty—preliminary clinical and radiological outcome using bone substitute materials. Hip Int 23:46–53
Oonishi H, Yamamoto M, Ishimaru H, Tsuji E, Kushitani S, Aono M, Ukon Y (1989) The effect of hydroxyapatite coating on bone growth into porous titanium alloy implants. J Bone Joint Surg Br 71:213–216
Oonishi H (1991) Orthopaedic applications of hydroxyapatite. Biomaterials 12:171
Mibe J, Imakiire A, Watanabe T, Fujie T (2005) Results of total hip arthroplasty with bone graft and support ring for protrusio acetabuli in rheumatoid arthritis. J Orthop Sci 10:8–14
DeLee JG, Chanley J (1976) Radiological demarcation of cemented socket in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop 121:20–32
Boutry N, Paul C, Leroy X, Fredoux D, Migaud H, Cotten A (2002) Rapidly destructive osteoarthritis of the hip: MR imaging findings. Am J Roentgenol (AJR) 179:657–663
Watanebe W, Itoi E, Yamada S (2002) Early MRI findings of rapidly destructive coxarthrosis. Skelet Radiol 31:35–38
Ogawa K, Kitajima M, Shigematsu M, Hotokebuchi T (2004) Clinical Perioperative outcome of total hip arthroplasty in rapidly destructive coxarthrosis (in Japanese). Orthop Traumatol 53:895–898
Ishii S, Masuda T, Matsuba Y, Ban K, Beppu M (2013) Short term results of total hip arthroplasty for the rapidly destructive coxarthrosis (in Japanese). Jpn J Replace Arthroplasty 43:437–438
Baba T, Shitoto K, Kaneko K (2013) Bipolar hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fracture using the direct anterior approach. World J Orthop 4:85–89
Homma Y, Baba T, Sano K, Ochi H, Matsumoto M, Kobayashi K, Yuasa T, Maruyama Y, Kaneko K (2015) Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve injury with the direct anterior approach for total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. doi:10.1007/s00264-015-2942-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by the medical research ethics committee at our university.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual patients in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baba, T., Homma, Y., Ochi, H. et al. Total hip arthroplasty using a Kerboull-type plate for rapidly destructive coxarthrosis: comparison with uncemented acetabular component. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 26, 189–194 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-015-1738-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-015-1738-7