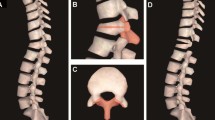
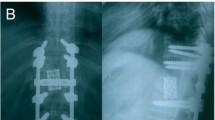
Abstract
Transpedicular closing wedge osteotomy (CWO) has become popular in correcting thoracic and lumbar kyphotic deformity (TLKD). Our study aims to evaluate the efficacy of CWO in treating TLKD of different etiologies. CWO was performed on 25 patients with thoracic and lumbar kyphosis, of whom 10 had ankylosing spondylitis, 10 had post-traumatic thoracolumbar fractures, and 5 had tuberculosis. Mean follow-up period was 24 months. Pre- and postoperative kyphotic Cobb angles and the horizontal distance between C7 and S1 in the lateral view were measured. Back pain and disability were assessed by visual analog score (VAS) and oswestry disability index (ODI). Postoperative complications were also recorded. Kyphotic deformity was successfully corrected, and 100 % osteotomic site fusion was obtained in all cases. Average operative duration was 255.6 min and blood loss was 1,675.6 ml. Average correction angels were 37.6°. The horizontal distance between C7 and S1 was 88.28 mm before the operation and 20.84 mm after the operation. Pre- and postoperative mean VAS of back pain in all cases was 7.6 and 2.6 respectively. Pre- and postoperative mean ODI was 61.8 and 27.32 receptively. Six complications were registered in six patients. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy is an effective and safe surgical method to correct thoracic and lumbar kyphosis of different etiologies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kiaer T, Gehrchen M (2010) Transpedicular closed wedge osteotomy in ankylosing spondylitis: results of surgical treatment and prospective outcome analysis. Eur Spine J 19:57–64
Sansur CA, Fu KM, Oskouian RJ, Jagannathan J, Kuntz C IV, Shaffrey CI (2008) Surgical management of global sagittal deformity in ankylosing spondylitis. Neurosurg Focus 24:E8
Schnake KJ, Kandziora F (2010) Correction of posttraumatic kyphosis of the thoracolumbar spine with modified pedicle subtraction osteotomy. Eur Spine J 19:2231–2232
Schoenfeld AJ, Wood KB, Fisher CF, Fehlings M, Oner FC, Bouchard K, Arnold P, Vaccaro AR, Sekhorn L, Harris MB, Bono CM (2010) Posttraumatic kyphosis: current state of diagnosis and treatment: results of a multinational survey of spine trauma surgeons. J Spinal Disord Tech 23:1–8
Rajasekaran S, Kanna RM, Shetty AP (2011) Closing-opening wedge osteotomy for severe, rigid, thoracolumbar post-tubercular kyphosis. Eur Spine J 20:343–348
Buchowski JM, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG (2010) Management of posttraumatic kyphosis after thoracolumbar injuries. Semin Spine Surg 22:92–102
Quiding H, Oksala E, Happonen RP, Lehtimäki K, Ojala T (1981) The visual analog scale in multiple-dose evaluations of analgesics. J Clin Pharmacol 21:424–429
Co YY, Eaton S, Maxwell MW (1993) The relationship between the St. Thomas and Oswestry disability scores and the severity of low back pain. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 16:14–18
Maskymowych WP (2004) Update in spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum 51:143–146
Van Royen BJ, De Gast A (1999) Lumbar osteotomy for correction of thoracolumbar kyphotic deformity in ankylosing spondylitis. A structured review of three methods of treatment. Ann Rheum Dis 58:399–406
Chen IH, Chien JT, Yu TC (2001) Transpedicular wedge osteotomy for correction of thoracolumbar kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis: experience with 78 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26:E354–E360
Chang KW, Chen YY, Lin CC, Hsu HL, Pai KC (2005) Closing wedge osteotomy versus opening wedge osteotomy in ankylosing spondylitis with thoracolumbar kyphotic deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30:1584–1593
Chang KW, Cheng CW, Chen HC, Chang KI, Chen TC (2008) Closing-opening wedge osteotomy for the treatment of sagittal imbalance. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33:1470–1477
Rajasekaran S, Vijay K, Shetty AP (2010) Single-stage closing-opening wedge osteotomy of spine to correct severe post-tubercularkyphotic deformities of the spine: a 3-year follow-up of 17 patients. Eur Spine J 19:583–592
Kawahara N, Tomita K, Baba H, Kobayashi T, Fujita T, Murakami H (2001) Closing-opening wedge osteotomy to correct angular kyphotic deformity by a single posterior approach. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26:391–402
Debarge R, Demey G, Roussouly P (2011) Sagittal balance analysis after pedicle subtraction osteotomy in ankylosing spondylitis. Eur Spine J 20(Suppl 5):619–625
Lafage V, Schwab F, Vira S, Hart R, Burton D, Smith JS, Boachie-Adjei O, Shelokov A, Hostin R, Shaffrey CI, Gupta M, Akbarnia BA, Bess S, Farcy JP (2011) Does vertebral level of pedicle subtraction osteotomy correlate with degree of spinopelvic parameter correction? J Neurosurg Spine 14:184–191
Fu KM, Smith JS, Polly DW, Ames CP, Berven SH, Perra JH, Glassman SD, McCarthy RE, Knapp DR, Shaffrey CI (2011) Morbidity and mortality associated with spinal surgery in children: a review of the Scoliosis Research Society morbidity and mortality database. J Neurosurg Pediatr 7:37–41
Gokce A, Ozturkmen Y, Mutlu S, Caniklioğlu M (2008) Spinal osteotomy: correcting sagittal balance in tuberculous spondylitis. J Spinal Disord Tech 21:484–488
Chang KW, Chen YY, Lin CC, Hsu HL, Pai KC (2005) Closing wedge osteotomy versus opening wedge osteotomy in ankylosing spondylitis with thoracolumbar kyphotic deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30:1584–1593
Lehmer SM, Keppler L, Biscup RS, Enker P, Miller SD, Steffee AD (1994) Posterior transvertebral osteotomy for adult thoracolumbar kyphosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 19:2060–2067
Zhang XS, Zhang YG, Wang Z, Chen C, Wang Y (2010) Correction of severe post-traumatic kyphosis by posterior vertebra column resection. Chin Med J (Engl) 123:680–685
Benazet JP, Chamberlin B, Lazennec JY, Saillant G (1996) Surgical treatment of deformities of the thoracic and lumbar spine by posterior spinalosteotomy. Chirurgie 121:616–621
Thiranont N, Netrawichien P (1993) Transpedicular decancellation closed wedge vertebral osteotomy for treatment of fixed flexion deformity of spine in ankylosing spondylitis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 18:2517–2522
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30300357, 39830100) and National High Technology Development Foundation of China (863) (No. 2003AA205021, 2006AA02Z4E3, 2006AA02A122).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest concerning this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Q., Xu, J. Transpedicular closing wedge osteotomy in the treatment of thoracic and lumbar kyphotic deformity with different etiologies. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 23, 863–871 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-012-1089-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-012-1089-6