Abstract
Purpose
At present, most spinal surgeons undertake pedicle screw implantation using either anatomical landmarks or C-arm fluoroscopy. Reported rates of screw malposition using these techniques vary considerably, though the evidence generally favors the use of image-guidance systems. A miniature spine-mounted robot has recently been developed to further improve the accuracy of pedicle screw placement. In this systematic review, we critically appraise the perceived benefits of robot-assisted pedicle screw placement compared to conventional fluoroscopy-guided technique.
Methods
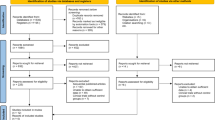
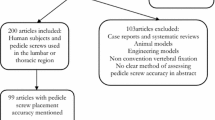
The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, PubMed, and EMBASE databases were searched between January 2006 and January 2013 to identify relevant publications that (1) featured placement of pedicle screws, (2) compared robot-assisted and fluoroscopy-guided surgery, (3) assessed outcome in terms of pedicle screw position, and (4) present sufficient data in each arm to enable meaningful comparison (>10 pedicle screws in each study group).
Results
A total of 246 articles were retrieved, of which 5 articles met inclusion criteria, collectively reporting placement of 1,308 pedicle screws (729 robot-assisted, 579 fluoroscopy-guided). The findings of these studies are mixed, with limited higher level of evidence data favoring fluoroscopy-guided procedures, and remaining comparative studies supporting robot-assisted pedicle screw placement.
Conclusions
There is insufficient evidence to unequivocally recommend one surgical technique over the other. Given the high cost of robotic systems, and the high risk of spinal surgery, further high quality studies are required to address unresolved clinical equipoise in this field.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barzilay Y, Liebergall M, Fridlander A, Knoller N (2006) Miniature robotic guidance for spine surgery—introduction of a novel system and analysis of challenges encountered during the clinical development phase at two spine centres. Int J Med Robot Comput Assist Surg 2(2):146–153
Barzilay Y, Liebergall M, Fridlander A, Knoller N (2006) Miniature robotic guidance for spine surgery—introduction of a novel system and analysis of challenges encountered during the clinical development phase at two spine centres. Int J Med Robot 2(2):146–153. doi:10.1002/rcs.90
Benmessaoud C, Kharrazi H, MacDorman KF (2011) Facilitators and barriers to adopting robotic-assisted surgery: contextualizing the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. PLoS ONE 6(1):e16395. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016395
Devito DP, Kaplan L, Dietl R, Pfeiffer M, Horne D, Silberstein B, Hardenbrook M, Kiriyanthan G, Barzilay Y, Bruskin A, Sackerer D, Alexandrovsky V, Stuer C, Burger R, Maeurer J, Donald GD, Schoenmayr R, Friedlander A, Knoller N, Schmieder K, Pechlivanis I, Kim IS, Meyer B, Shoham M (2010) Clinical acceptance and accuracy assessment of spinal implants guided with SpineAssist surgical robot: retrospective study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35(24):2109–2115. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181d323ab
Gelalis ID, Paschos NK, Pakos EE, Politis AN, Arnaoutoglou CM, Karageorgos AC, Ploumis A, Xenakis TA (2012) Accuracy of pedicle screw placement: a systematic review of prospective in vivo studies comparing free hand, fluoroscopy guidance and navigation techniques. Eur Spine J 21(2):247–255. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-2011-3
Gertzbein SD, Robbins SE (1990) Accuracy of pedicular screw placement in vivo. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 15(1):11–14
Hicks JM, Singla A, Shen FH, Arlet V (2010) Complications of pedicle screw fixation in scoliosis surgery: a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35(11):E465–E470. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181d1021a
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJM, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ (1996) Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials 17(1):1–12
Kantelhardt SR, Martinez R, Baerwinkel S, Burger R, Giese A, Rohde V (2011) Perioperative course and accuracy of screw positioning in conventional, open robotic-guided and percutaneous robotic-guided, pedicle screw placement. Eur Spine J 20(6):860–868. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-1729-2
Kosmopoulos V, Schizas C (2007) Pedicle screw placement accuracy: a meta-analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 32(3):E111–E120. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000254048.79024.8b
Lieberman IH, Hardenbrook MA, Wang JC, Guyer RD (2012) Assessment of pedicle screw placement accuracy, procedure time, and radiation exposure using a miniature robotic guidance system. J Spinal Disord Techn 25(5):241–248. doi:10.1097/BSD.0b013e318218a5ef
Lieberman IH, Togawa D, Kayanja MM, Reinhardt MK, Friedlander A, Knoller N, Benzel EC (2006) Bone-mounted miniature robotic guidance for pedicle screw and translaminar facet screw placement: Part I-Technical development and a test case result. Neurosurgery 59(3):641–650. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000229055.00829.5B (discussion 641–650)
Patel PS, Aspinwall EM, Fennell AJ, Trotman SG, Shepherd DE, Hukins DW (2011) Pedicle screw surgery in the UK and Ireland: a questionnaire study. Open Biomed Eng J 5:90–97. doi:10.2174/1874120701105010090
Pechlivanis I, Kiriyanthan G, Engelhardt M, Scholz M, Lucke S, Harders A, Schmieder K (2009) Percutaneous placement of pedicle screws in the lumbar spine using a bone mounted miniature robotic system: first experiences and accuracy of screw placement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34(4):392–398. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e318191ed32
Rampersaud YR, Pik JH, Salonen D, Farooq S (2005) Clinical accuracy of fluoroscopic computer-assisted pedicle screw fixation: a CT analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30(7):E183–E190
Rampersaud YR, Simon DA, Foley KT (2001) Accuracy requirements for image-guided spinal pedicle screw placement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26(4):352–359
Ringel F, Stuer C, Reinke A, Preuss A, Behr M, Auer F, Stoffel M, Meyer B (2012) Accuracy of robot-assisted placement of lumbar and sacral pedicle screws: a prospective randomized comparison to conventional freehand screw implantation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 37(8):E496–E501. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31824b7767
Roser F, Tatagiba M, Maier G (2013) Spinal robotics: current applications and future perspectives. Neurosurgery 72(Suppl 1):12–18. doi:10.1227/NEU.0b013e318270d02c
Schizas C, Michel J, Kosmopoulos V, Theumann N (2007) Computer tomography assessment of pedicle screw insertion in percutaneous posterior transpedicular stabilization. Eur Spine J 16(5):613–617. doi:10.1007/s00586-006-0221-x
Schizas C, Thein E, Kwiatkowski B, Kulik G (2012) Pedicle screw insertion: robotic assistance versus conventional C-arm fluoroscopy. Acta Orthop Belg 78(2):240–245
Shamir R, Freiman M, Joskowicz L, Shoham M, Zehavi E, Shoshan Y (2005) Robot-assisted image-guided targeting for minimally invasive neurosurgery: planning, registration, and in vitro experiment. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 8(Pt 2):131–138
Shoham M, Lieberman IH, Benzel EC, Togawa D, Zehavi E, Zilberstein B, Roffman M, Bruskin A, Fridlander A, Joskowicz L, Brink-Danan S, Knoller N (2007) Robotic assisted spinal surgery—from concept to clinical practice. Comput Aided Surg 12(2):105–115. doi:10.3109/10929080701243981
Slim K, Nini E, Forestier D, Kwiatkowski F, Panis Y, Chipponi J (2003) Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J Surg 73(9):712–716
Sukovich W, Brink-Danan S, Hardenbrook M (2006) Miniature robotic guidance for pedicle screw placement in posterior spinal fusion: early clinical experience with the SpineAssist. Int J Med Robot 2(2):114–122. doi:10.1002/rcs.86
Tian NF, Xu HZ (2009) Image-guided pedicle screw insertion accuracy: a meta-analysis. Int Orthop 33(4):895–903. doi:10.1007/s00264-009-0792-3
Togawa D, Kayanja MM, Reinhardt MK, Shoham M, Balter A, Friedlander A, Knoller N, Benzel EC, Lieberman IH (2007) Bone-mounted miniature robotic guidance for pedicle screw and translaminar facet screw placement: Part 2—Evaluation of system accuracy. Neurosurgery 60(2 Suppl 1):ONS-129–ONS-139
Verma R, Krishan S, Haendlmayer K, Mohsen A (2010) Functional outcome of computer-assisted spinal pedicle screw placement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 23 studies including 5,992 pedicle screws. Eur Spine J 19(3):370–375. doi:10.1007/s00586-009-1258-4
Wiesner L, Kothe R, Ruther W (1999) Anatomic evaluation of two different techniques for the percutaneous insertion of pedicle screws in the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 24(15):1599–1603
Acknowledgments
H. J. Marcus is supported by the Wellcome Trust.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marcus, H.J., Cundy, T.P., Nandi, D. et al. Robot-assisted and fluoroscopy-guided pedicle screw placement: a systematic review. Eur Spine J 23, 291–297 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-2879-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-2879-1