Abstract
Purpose
Global sagittal alignment is considered as an important aspect in the management of spinal disorders, but the evidence establishing its clinical impact in lumbosacral spondylolisthesis is still poor. This study evaluated the impact of global sagittal alignment on the health-related quality of life (HRQOL) of patients with spondylolisthesis.
Methods
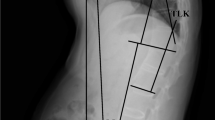
A retrospective study of 149 consecutive unoperated children and adolescents presenting with lumbosacral spondylolisthesis (117 low-grade and 32 high-grade) was performed. Two global sagittal alignment parameters were measured on standing lateral radiographs: spinal tilt (ST) and C7 plumbline deviation (C7P deviation). All patients completed the SRS-22 questionnaire to assess HRQOL. Pearson’s correlations were calculated between parameters of global sagittal alignment and HRQOL. Multiple regression analyses were also undertaken to account for slip percentage and lumbosacral kyphosis (LSK).
Results
Both global sagittal alignment parameters were correlated with the SRS-22 total score. When analyzed separately, the correlation was absent in patients with a low-grade slip but remained significant for patients with a high-grade slip (r = 0.35 for ST; r = −0.35 for C7P deviation). The relation was strengthened in high-grade spondylolisthesis when considering only patients with a C7P in front of the posterior corner of upper sacral endplate (r = 0.48 for ST; r = –0.48 for C7P deviation) and was also positive for the SRS-22 pain and appearance domains. For these last patients, the relationship with global sagittal alignment remained significant in the multiple regression analysis. HRQOL was particularly worse for high-grade patients with a C7P in front of the hip axis.
Conclusions
In high-grade spondylolisthesis, an increasing positive sagittal alignment was related to a poorer SRS-22 total score, especially when the C7P is in front of the hip axis. Global sagittal alignment should particularly be assessed in patients with high-grade spondylolisthesis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angevine PD, McCormick PC (2007) The importance of sagittal balance: how good is the evidence? J Neurosurg Spine 6:101–103
Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, Horton W, Berven S, Schwab F (2005) The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine 30:2024–2029
Glassman SD, Berven S, Bridwell K, Horton W, Dimar JR (2005) Correlation of radiographic parameters and clinical symptoms in adult scoliosis. Spine 30:682–688
Mac-Thiong JM, Transfeldt EE, Mehbod AA, Perra JH, Denis F, Garvey TA, Lonstein JE, Wu C, Dorman CW, Winter RB (2009) Can c7 plumbline and gravity line predict health related quality of life in adult scoliosis? Spine 34:E519–E527
Berven S LH, Deriven V, O’Brien MF, Roussouly P (2007) Spondylolisthesis and lumbopelvic parameters: defining the relationship between radiographic measurements and health-related quality of life (HRQL). Presented at the 42nd International Meeting of the Scoliosis Research Society, Edinburgh, 5–8 September 2007
Jackson RP, Phipps T, Hales C, Surber J (2003) Pelvic lordosis and alignment in spondylolisthesis. Spine 28:151–160
Rajnics P, Templier A, Skalli W, Lavaste F, Illes T (2002) The association of sagittal spinal and pelvic parameters in asymptomatic persons and patients with isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Techniques 15:24–30
Mac-Thiong JM, Wang Z, de Guise JA, Labelle H (2008) Postural model of sagittal spino-pelvic alignment and its relevance for lumbosacral developmental spondylolisthesis. Spine 33:2316–2325
Labelle H, Mac-Thiong JM, Roussouly P (2011) Spino-pelvic sagittal balance of spondylolisthesis: a review and classification. Eur Spine J 20(Suppl 5):641–646
Horton WC, Brown CW, Bridwell KH, Glassman SD, Suk SI, Cha CW (2005) Is there an optimal patient stance for obtaining a lateral 36″ radiograph? A critical comparison of three techniques. Spine 30:427–433
Roussouly P, Gollogly S, Noseda O, Berthonnaud E, Dimnet J (2006) The vertical projection of the sum of the ground reactive forces of a standing patient is not the same as the C7 plumb line: a radiographic study of the sagittal alignment of 153 asymptomatic volunteers. Spine 31:E320–E325
Bago J, Perez-Grueso FJ, Les E, Hernandez P, Pellise F (2009) Minimal important differences of the SRS-22 Patient Questionnaire following surgical treatment of idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J 18:1898–1904
Labelle H RP, Mac-Thiong J-M, et al. 2010 Relationship between HRQL measures and spino-pelvic alignment in adolescent spondylolisthesis compared to a control population. Presented at the Scoliosis Research Society 45th annual meeting and combined course, Kyoto, 21–24 September 2010
Tanguay F, Labelle H, Wang Z, Joncas J, de Guise JA, Mac-Thiong JM (2012) Clinical significance of lumbosacral kyphosis in adolescent spondylolisthesis. Spine 37:304–308
Vialle R, Ilharreborde B, Dauzac C, Guigui P (2006) Intra and inter-observer reliability of determining degree of pelvic incidence in high-grade spondylolisthesis using a computer assisted method. Eur Spine J 15:1449–1453
Parent S, Joncas J, Roy-Beaudry M, Beausejour M, Grimard G, Forcier M, Labelle H, (2008) The SRS Outcome Questionnaire can discriminate between patients with spondylolisthesis and normal healthy adolescents. 15th International meeting on advanced spine techniques, Hong Kong, 8–11 July 2008
Cheung EV, Herman MJ, Cavalier R, Pizzutillo PD (2006) Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents: II. Surg Manag JAAOS 14:488–498
Conflict of interest
This study has been funded by the Fonds de Recherche Québec - Santé (FRQS) and by the Ressources humaines et développement des compétences Canada (RHDCC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harroud, A., Labelle, H., Joncas, J. et al. Global sagittal alignment and health-related quality of life in lumbosacral spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 22, 849–856 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2591-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2591-6