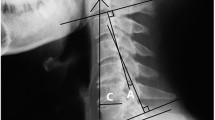
Abstract
The objective of the study was to investigate the comorbidity of degenerative spondylolisthesis (DS), in elderly cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) patients in our hospital, and the correlation between surgical results and preoperative DS. There are few studies on the outcome of laminoplasty for CSM with DS. A total of 49 elderly patients (>65 years old) who eventually had surgical treatment for CSM were evaluated. A slippage displacement of more than 2.5 mm at least at one level was classified to have a positive DS on flexion/extension radiographs (DS group). A slippage displacement less than 1.0 mm was considered a negative DS (non-DS group). Seventeen patients who had slippage of 1.0–2.5 mm were excluded from the study. The DS group (n = 15) included cases with DS at preoperation, while the remaining cases (n = 17) belonged to the non-DS group. The flexion/extension radiographs of the two groups were compared for range of motion and clinical results at 3 years after the operation. Of all elderly patients, 30.6% had DS. There was no significant difference between the two groups based on the clinical results. The range of motion of all cervical spines (DS group and non-DS group) was significantly limited. However, there was no significant difference between the two groups. New postoperative DS appeared in four patients, of which two were from the DS group and two from the non-DS group. These data suggest that degenerative spondylolisthesis does not influence surgical results in elderly cervical spondylotic myelopathy patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
al-Mefty O, Harkey HL, Marawi I, Haines DE, Peeler DF, Wilner HI, Smith RR, Holaday HR, Haining JL, Russell WF (1993) Experimental chronic compressive myelopathy. J Neurosurg 79:550–561
Boulos AS, Lovely TJ (1996) Degenerative cervical spondylolisthesis: diagnosis and management in five cases. J Spinal Disord 9:241–245
Dawley JA (1971) Spondylolisthesis of the cervical spine: case report. J Neurosurg 34:99–101
Deburg A, Mazda K, Guigui P (1995) Unstable degenerative spondylolisthesis of the cervical spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br 77:122–125
Durbin FC (1956) Spondylolisthesis of the cervical spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br 38:734–735
Ebersold MJ, Pare MC, Quast LM (1995) Surgical treatment for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Neurosurg 82:745–751
Fukui K, Kataoka O, Sho T, Sumi M (1990) Pathomechanism, pathogenesis, and results of treatment in cervical spondylotic myelopathy caused by dynamic canal stenosis. Spine 15:1148–1152
Harkey HL, Al-Mefty O, Marawi I, Peeler DF, Haines DE, Alexander LF (1995) Experimental chronic compressive myelopathy: effects of decompression. J Neurosurg 83:336–341
Hayashi H, Okada K, Hamada M, Tada K, Ueno R (1987) Etiologic factors of myelopathy: a radiographic evaluation of the ageing changes in the cervical spine. Clin Orthop 214:200–209
Hayashi H, Okada K, Hashimoto J, Tada K, Ueno R (1988) Cervical spondylotic myelopathy in the aged patient: a radiographic evaluation of the aging changes in the cervical spine and etiologic factors of myelopathy. Spine 13:618–625
Hirabayashi K, Miyakawa J, Satomi K, Maruyama T, Wakano K (1981) Operative results and postoperative progression of ossification among patients with ossification of cervical posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine 6:354–364
Japanese Orthopedic Association. Scoring system for cervical myelopathy. (1994) J Jpn Ortop Assoc 68: 490–503
Kawakami M, Tamaki T, Iwasaki H, Yoshida M, Ando M, Yamada H (2000) A comparative study of surgical approaches for cervical compressive myelopathy. Clin Orthop 381:129–136
Kawasaki M, Tani T, Ushida T, Ishida K (2007) Anterolisthesis and retrolisthesis of the cervical spine in cervical spondylotic myelopathy in the elderly. J Ortho Sci 12:207–213
Kikuchi Y, Baba H, Tomita K, Umeda S (1991) Radiographic studies of the cervical spine after expansive laminoplasty. Seikei Saigaigeka 34:165–170 (Japanese)
Kokubun S, Sato T, Ishii Y, Tanaka Y (1996) Cervical myelopathy in Japan. Clin Orthop Relat Res 323:129–138
Kosnik EJ, Johnson JC, Scoles PV, Rossel CW (1979) Cervical spondylolisthesis. Spine 4:203–205
Matsuzaki H, Hoshino M, Kiuchi T, Toriyama S (1989) Dome-like expansive laminoplasty for the second cervical vertebra. Spine 14:1198–1203
Murone I (1974) The importance of the sagittal diameters of the cervical spinal canal in relation to spondylosis and myelopathy. J Bone Joint Surg Br 56:30–36
Omura F, Shirai Y, Nakagawa S, Yamaguchi J, Fujiwara A, Ooba S (1989) Cervical spine motion after expansive laminoplasty: open-door laminoplasty vs split spinous process method. Rinsho Seikei Geka 24:453–459 (Japanese)
Penning L (1978) Normal movements of the cervical spine. AJR Am J Roentogenol 130:317–326
Pierre G, Michel B, Alain D (1998) Spinal deformity and instability after multilevel cervical laminectomy for spondylotic myelopathy. Spine 23:440–447
Sakai Y, Matsuyama Y, Inoue K, Ishiguro N (2005) Postoperative instability after laminoplasty for cervical myelopathy with spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech 18:1–5
Shigematsu H, Ueda Y, Koizumi M, Takeshima T, Tanaka Y, Satoh N, Matsumori H, Oshima T, Matsuyama E, Kugai A, Takakura Y (2008) Does developmental canal stenosis influence surgical results of bilateral open-door laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy? J Neurosurg Spine 9:358–362
Suda K, Abumi K, Ito M, Shono Y, Kaneda K, Fujiya M (2003) Local kyphosis reduces surgical outcomes of expansive open-door laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine 28:1258–1262
Sumi M, Kataoka O, Sawamura S, Ikeda M, Mukai H (1998) Radiological analysis of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Rinsho Seikeigeka 33:1277–1286 (Japanese)
Sunago K, Kawai S, Oda Y (1989) Postoperative radiographic evaluation of cervical laminoplasty (Hattori’s method). Rinsho Seikeigeka 24:445–452 (Japanese)
Tani T, Kawasaki M, Taniguchi S, Ushida T (2003) Functional importance of degenerative spondylolisthesis in cervical spondylotic myelopathy in the elderly. Spine 28:1128–1134
White AA, Panjabi MM (1988) Biomechanical considerations in the surgical management of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine 13:15–20
Woiciechowsky C, Thomale U, Kroppenstedt S (2004) Degenerative spondylolisthesis of cervical spine-symptoms and surgical strategies depending on disease progress. Eur Spine J 13:680–684
Yonenobu K (2000) Cervical radiculopathy and myelopathy: when and what can surgery contribute to treatment? Eur Spine J 9:1–7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00586-010-1426-6
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shigematsu, H. Degenerative spondylolisthesis does not influence surgical results of laminoplasty in elderly cervical spondylotic myelopathy patients. Eur Spine J 19, 720–725 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-010-1338-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-010-1338-5