Abstract
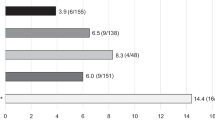
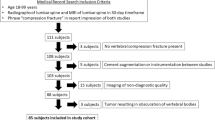
Percutaneous vertebroplasty is widely discussed in the management of osteoporotic spinal compression fracture, but few reports are available concerning salvage procedures after failure of this technique. We studied 22 percutaneous vertebroplasty patients who required revision surgery upon presentation of new symptoms postoperatively. The indications for revision surgery included recurrent intractable back pain with no response to medical treatment, infectious spondylitis, cement leakage with neurologic deficit, and cement dislodgement and/or fragmentation. Five patients underwent repeated percutaneous vertebroplasty of the initially cemented vertebrae. Seventeen patients underwent anterior, posterior, or combined anterior and posterior surgery. Four patients required a third surgical procedure because of poor augmentation with cement, subsidence of the anterior bone graft, or pullout of the instrumentation. Finally, four (18%) patients underwent repeat vertebroplasty, two (9%) patients underwent anterior surgery only, one (5%) patient underwent posterior surgery only, and 15 (68%) patients underwent combined anterior and posterior surgery; all but one regained ambulatory status equivalent to that prior to surgery. In conclusion, percutaneous vertebroplasty is a simple and effective, but not risk- or complication-free procedure for the treatment of osteoporotic spinal compression fracture. The spine surgeon should be familiar with varied approaches and techniques for revision surgery. Combined anterior and posterior surgery seems to be the most secure salvage method to treat severely osteoporotic patients in whom percutaneous vertebroplasty initially failed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Jalil Y, Bartels J, Alberti O, Becker R (2007) Delayed presentation of pulmonary polymethylmethacrylate emboli after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Spine 32(20):E589–E593
Alvarez L, Alcaraz M, Perez-Higueras A, Granizo JJ, de Miguel I, Rossi RE, Quinones D (2006) Percutaneous vertebroplasty: functional improvement in patients with osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine 31(10):1113–1118
Amar AP, Larsen DW, Esnaashari N, Albuquerque FC, Lavine SD, Teitelbaum GP (2001) Percutaneous transpedicular polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty for the treatment of spinal compression fractures. Neurosurgery 49(5):1105–1114
Askew MJ, Steege JW, Lewis JL, Ranieri JR, Wixson RL (1984) Effect of cement pressure and bone strength on polymethylmethacrylate fixation. J Orthop Res 1(4):412–420
Baroud G, Steffen T (2005) A new cannula to ease cement injection during vertebroplasty. Eur Spine J 14:474–479
Barr JD, Barr MS, Lemley TJ, McCann RM (2000) Percutaneous vertebroplasty for pain relief and spinal stabilization. Spine 25(8):923–928
Baumann C, Fuchs H, Kiwit J, Westphalen K, Hierholzer J (2007) Complications in percutaneous vertebroplasty associated with puncture or cement leakage. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 30(2):161–168
Bohner M, Gasser B, Baroud G, Heini P (2003) Theoretical and experimental model to describe the injection of a polymethylmethacrylate cement into a porous structure. Biomaterials 24:2721–2730
Bostrom MP, Lane JM (1997) Future directions. Augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral bodies. Spine 22(24):S38–S42
Burval DJ, McLain RF, Milks R, Inceoglu S (2007) Primary pedicle screw augmentation in osteoporotic lumbar vertebrae:biomechanical analysis of pedicle fixation strength. Spine 32(10):1077–1083
Chen LH, Lai PL, Chen WJ (2005) Unipedicle percutaneous vertebroplasty for spinal intraosseous vacuum cleft. Clin Orthop Relat Res 435:148–153
Deramond H, Depriester C, Galibert P, Le Gars D (1998) Percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate. Technique, indications, and results. Radiol Clin North Am 36(3):533–546
Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P, Le Gars D (1987) Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty. Neurochirurgie 33(2):166–168
Harrington KD (2001) Major neurological complications following percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83(7):1070–1073
Huang KY, Yan JJ, Lin RM (2005) Histopathologic findings of retrieved specimens of vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate cement: case control study. Spine 30(19):E585–E588
Krause WR, Krug W, Miller J (1982) Strength of the cement–bone interface. Clin Orthop Relat Res 163:290–299
Lane JI, Maus TP, Wald JT, Thielen KR, Bobra S, Luetmer PH (2002) Intravertebral clefts opacified during vertebroplasty: pathogenesis, technical implications, and prognostic significance. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23(10):1642–1646
Layton KF, Thielen KR, Koch CA, Luetmer PH, Lane JI, Wald JT, Kallmes DF (2007) Vertebroplasty, first 1000 levels of a single center: evaluation of the outcomes and complications. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28(4):683–689
Maldague BE, Noel HM, Malghem JJ (1978) The intravertebral vacuum cleft: a sign of ischemic vertebral collapse. Radiology 129(1):23–29
Martin JB, Jean B, Sugiu K, San Millan Ruiz D, Piotin M, Murphy K, Rufenacht B, Muster M, Rufenacht DA (1999) Vertebroplasty: clinical experience and follow-up results. Bone 25(2):S11–S15
McKiernan F, Faciszewski T (2003) Intravertebral clefts in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Arthritis Rheum 48(5):1414–1419
McKiernan F, Jensen R, Faciszewski T (2003) The dynamic mobility of vertebral compression fractures. J Bone Miner Res 18(1):24–29
Mirovsky Y, Anekstein Y, Shalmon E, Blankstein A, Peer A (2006) Intradiscal cement leak following percutaneous vertebroplasty. Spine 31(10):1120–1124
Murphy KJ, Deramond H (2000) Percutaneous vertebroplasty in benign and malignant disease. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 10(3):535–545
Nussbaum DA, Gailloud P, Murphy K (2004) A review of complications associated with vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty as reported to the Food and Drug Administration medical device related web site. J Vasc Interv Radiol 15(11):1185–1192
Olmos MA, Gonzalez AS, Clemente JD, Tome CV (2006) Infected vertebroplasty due to uncommon bacteria solved surgically: a rare and threatening life complication of a common procedure. Report of a case and a review of the literature. Spine 31(20):E770–E773
Patel AA, Vaccaro AR, Martyak GG, Harrop JS, Albert TJ, Ludwig SC, Youssef JA, Gelb DE, Mathews HH, Chapman JR, Chung EH, Grabowski G, Kuklo TR, Hilibrand AS, Anderson DG (2007) Neurologic deficit following percutaneous vertebral stabilization. Spine 32(16):1728–1734
Peters KR, Guiot BH, Martin PA, Fessler RG (2002) Vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures: current practice and evolving techniques. Neurosurgery 51(5):S96–S103
Ploeg WT, Veldhuizen AG, The B, Sietsma MS (2006) Percutaneous vertebroplasty as a treatment for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a systematic review. Eur Spine J 15(12):1749–1758
Ratliff J, Nguyen T, Heiss J (2001) Root and spinal cord compression from methylmethacrylate vertebroplasty. Spine 26(13):E300–E302
Renner SM, Lim TH, Kim WJ, Katolik L, An HS, Andersson GB (2004) Augmentation of pedicle screw fixation strength using an injectable calcium phosphate cement as a function of injection timing and method. Spine 29(11):E212–E216
Tohmeh AG, Mathis JM, Fenton DC, Levine AM, Belkoff SM (1999) Biomechanical efficacy of unipedicular versus bipedicular vertebroplasty for the management of osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine 24(17):1772–1776
Tsai TT, Chen WJ, Lai PL, Chen LH, Niu CC, Fu TS, Wong CB (2003) Polymethylmethacrylate cement dislodgment following percutaneous vertebroplasty: a case report. Spine 28(22):E457–E460
Vats HS, McKiernan FE (2006) Infected vertebroplasty: case report and review of literature. Spine 31(22):E859–E862
Wuisman PI, Van Dijk M, Staal H, Van Royen BJ (2000) Augmentation of (pedicle) screws with calcium apatite cement in patients with severe progressive osteoporotic spinal deformities: an innovative technique. Eur Spine J 9(6):528–533
Yeom JS, Kim WJ, Choy WS, Lee CK, Chang BS, Kang JW (2003) Leakage of cement in percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic compression fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 85(1):83–89
Yu SW, Chen WJ, Lin WC, Chen YJ, Tu YK (2004) Serious pyogenic spondylitis following vertebroplasty—a case report. Spine 29(10):E209–E211
Yu SW, Lee PC, Ma CH, Chuang TY, Chen YJ (2004) Vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic compression spinal fracture: comparison of remedial action at different stages of injury. J Trauma 56(3):629–632
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
No funds were received in support of this work. No benefits in any form have been or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, SC., Chen, WJ., Yu, SW. et al. Revision strategies for complications and failure of vertebroplasties. Eur Spine J 17, 982–988 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-008-0680-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-008-0680-3