Abstract
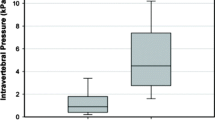
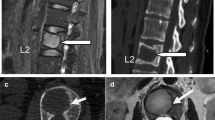
A biomechanical study comparing simulated lytic vertebral metastases treated with laser-induced thermotherapy (LITT) and vertebroplasty versus vertebroplasty alone. To investigate the effect of tumor ablation using LITT prior to vertebroplasty on biomechanical stability and cement fill patterns in a standardized model of spinal metastatic disease. Vertebroplasty in the metastatic spine is aimed at reducing pain, but is associated with risk of cement extravasation in up to 10%. Six pairs of fresh-frozen cadaveric thoracolumbar spinal motion segments were tested in axial compression intact, with simulated metastases and following percutaneous vertebroplasty with or without LITT. Canal narrowing under load, pattern of cement fill, load to failure, and LITT temperature and pressure generation were collected. In all LITT specimens, cement filled the defect without extravasation. The canal extravasation rate was 33% in specimens treated without LITT. LITT and vertebroplasty yielded a trend toward improved posterior wall stability (P = 0.095) as compared to vertebroplasty alone. Moderate rises in temperature and minimal pressure generation was seen during LITT. In this model, elimination of tumor by LITT, facilitates cement fill, enhances biomechanical stability and reduces the risk of cement extravasation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barr JD, Barr MS, Lemley TJ, McCann RM (2000) Percutaneous vertebroplasty for pain relief and spinal stabilization. Spine 25:923–928
Belkoff SM, Malloy S (2003) Temperature measurement during polymerization of polymethylmethacrylate cement used for vertebroplasty. Spine 28:1555–1559
Belkoff SM, Mathis JM, Jasper LE, Deramond H (2001) The biomechanics of vertebroplasty. The effect of cement volume on mechanical behavior. Spine 26:1537–1541
Berman AT, Reid JS, Yanicko DR Jr, Sih GC, Zimmerman MR (1984) Thermally induced bone necrosis in rabbits. Relation to implant failure in humans. Clin Orthop Relat Res 186:284–292
Boland PJ, Lane JM, Sundaresan N (1982) Metastatic disease of the spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res 169:95–102
Bridwell KH, Jenny AB, Saul T, Rich KM, Grubb RL (1998) Posterior segmental spinal instrumentation (PSSI) with posterolateral decompression and debulking for metastatic thoracic and lumbar disease: limitations of the technique. Spine 13:13831394
Chiras J, Depriester C, Weill A, Sola-Martinez MT, Deramond H (1997) Percutaneous vertebral surgery. Technics and indications. J Neuroradiol 24:45–59
Constans JP, de Divitiis E, Donzelli R, Spaziante R, Meder JF, Haye C (1983) Spinal metastases with neurologic manifestations: review of 600 cases. J Neurosurg 59:111–118
Cotten A, Dewatre F, Cortet B, Assaker R, Leblond D, Duquesnoy B, et al (1996) Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteolytic metastases and myeloma: effects of the percentage of lesion filling and the leakage of methyl methacrylate at clinical follow-up. Radiology 200:525–530
DeWald RL, Bridwell KH, Prodromas C, Rodts MF (1985) Reconstructive spinal surgery as palliation for metastatic malignancies of the spine. Spine 10:21–26
Deramond H, Wright NT, Belkoff SM (1999) Temperature elevation caused by bone cement polymerization during vertebroplasty. Bone 25(2 Suppl):17S–21S
Halpin RJ, Bendok BR, Sato KT, Liu JC, Patel JD, Rosen ST (2005) Combination treatment of vertebral metastases using image-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and vertebroplasty: a case report. Surg Neurol 63:469–474
Hammerberg KW (1991) Surgical treatment of metastatic spine disease. Spine 17:11481153
Harrington KD (1986) Current concepts review: metastatic disease of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am 68:1110–1115
Hatrick NC, Lucas JD, Timothy AR, Smith MA (2000) The surgical treatment of metastatic disease of the spine. Radiother Oncol 56:335–339
Izzo F (2003) Other thermal ablation techniques: microwave and interstitial laser ablation of liver tumors. Ann Surg Oncol 10:491497
Lieberman IH, Dudeney S, Reinhardt MK, Bell G (2001) Initial outcome and efficacy of “kyphoplasty” in the treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine 26:1631–1638
Martin JB, Wetzel SG, Seium Y, Dietrich PY, Somon T, Gailloud P, et al (2003) Percutaneous vertebroplasty in metastatic disease: transpedicular access and treatment of lysed pedicles—initial experience. Radiology 229:593–597
Masala S, Roselli M, Massari F, Fiori R, et al (2004) Radiofrequency heat ablation and vertebroplasty in the treatment of neoplastic vertebral body fractures. Anticancer Res 24:3129–3133
McGraw JK, Lippert JA, Minkus KD, Rami PM, Davis TM, Budzik RF (2002) Prospective evaluation of pain relief in 100 patients undergoing percutaneous vertebroplasty: results and follow-up. J Vasc Interv Radiol 13:883–886
Mousavi P, Roth S, Finkelstein J, Cheung G, Whyne C (2003) Volumetric quantification of cement leakage following percutaneous vertebroplasty in metastatic and osteoporotic vertebrae. J Neurosurg Spine 99:56–59
Muralidharan V, Christophi C (2001) Interstitial laser thermotherapy in the treatment of colorectal liver metastases. J Surg Oncol 76:73–81
Phillips FM, Ho E, Campbell-Hupp M, McNally T, Todd Wetzel F, Gupta P (2003) Early radiographic and clinical results of balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine 28:2260–2265
Reidy D, Ahn H, Mousavi P, Finkelstein J, Whyne CM (2003) A biomechanical analysis of intravertebral pressures during vertebroplasty of cadaveric spines with and without simulated metastases. Spine 28:1534–1539
Roth SE, Mousavi P, Finkelstein J, Chow E, Kreder H, Whyne CM (2004) Metastatic burst fracture risk prediction using biomechanically based equations. Clin Orthop Relat Res 419:83–90
Toksvig-Larsen S, Johnsson R, Stromqvist B (1995) Heat generation and heat protection in methylmethacrylate cementation of vertebral bodies. A cadaver study evaluating different clinical possibilities of dural protection from heat during cement curing. Eur Spine J 4:15–17
Tschirhart CE, Roth SE, Whyne CM (2005) Biomechanical assessment of stability in the metastatic spine following percutaneous vertebroplasty: effects of cement distribution patterns and volume. J Biomech 38:1582–1590
Vogl TJ, Muller PK, Mack MG, Straub R, Engelmann K, Neuhaus P (1999) Liver metastases: interventional therapeutic techniques and results, state of the art. Eur Radiol 1999:675–684
Wai EK, Finkelstein JA, Tangente RP, Holden L, Chow E, Ford M, et al (2003) Quality of life in surgical treatment of metastatic spine disease. Spine 28:508–512
Weill A, Chiras J, Simon JM, Rose M, Sola-Martinez T, Enkaoua E (1996) Spinal metastases: indications for and results of percutaneous injection of acrylic surgical cement. Radiology 199:241–247
Whyne CM, Hu SS, Lotz JC (2003) Biomechanically derived guideline equations for burst fracture risk prediction in the metastatically involved spine. J Spinal Disord Tech 16:180–185
Whyne CM, Hu SS, Lotz JC (2003) Burst fracture in the metastatically involved spine: development, validation, and parametric analysis of a three-dimensional poroelastic finite-element. Spine 28:652–660
Whyne CM, Hu SS, Workman KL, Lotz JC (2000) Biphasic material properties of lytic bone metastases. Ann Biomed Eng 28:1154–1158
Whyne CM, Hu SS, Lotz JC (2001) Parametric finite element analysis of vertebral bodies affected by tumors. J Biomech 34:1317–1324
Wong DA, Fornasier VL, McNab I (1990) Spinal metastases: the obvious, the occult, and the imposters. Spine 15:1–3
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by US Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Breast Cancer Research Award DAMD 17-00-1-0693. Simplex P Cement was provided by Stryker-Howmedica, Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, H., Mousavi, P., Chin, L. et al. The effect of pre-vertebroplasty tumor ablation using laser-induced thermotherapy on biomechanical stability and cement fill in the metastatic spine. Eur Spine J 16, 1171–1178 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-007-0375-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-007-0375-1