Abstract
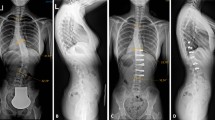
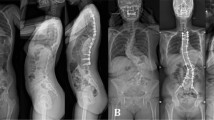
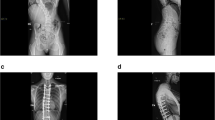
Fifteen skeletally immature patients with double major adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with large lumbar curves and notable L4 and L5 coronal plane obliquity were retrospectively studied. Seven patients who underwent anterior release and fusion of the lumbar curve with segmental anterior instrumentation and subsequent posterior instrumentation ending at L3 were compared with eight patients treated with anterior release and fusion without anterior instrumentation followed by posterior instrumentation to L3 or L4. At 4.5 years follow-up (range 2.5–7 years), curve correction, coronal balance and fusion rate were not statistically different between the two groups; however, the group with anterior instrumentation had improved coronal plane, near normalangulation in the distal unfused segment compared with the group without anterior instrumentation. In cases involving severe lumbar curvatures in the context of double major scoliosis, when as a first stage anterior release is chosen, the addition of instrumentation appears to restore normal coronal alignment of the distal unfused lumbar segment, and may in certain cases save a level compared with traditional fusions to L4.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Betz RR, Harms J, Clements DH III, Lenke LG, Lowe TG, Shufflebarger HL, Jeszenszky D, Bruno B (1999) Comparison of anterior and posterior instrumentation for correction of adolescent thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 24:225–239
Bradford DS (1979) Anterior spinal surgery in the management of scoliosis: Indications-techniques-results. Orthop Clin North Am 10:801–12
Bridwell KH, McAllister JW, Betz RR, Huss G, Clancy M, Schoenecker PL (1991) Coronal decompensation produced by Cotrel–Dubousset “derotation” maneuver for idiopathic right thoracic Scoliosis. Spine 16:769–77
Cochran T, Irstam L, Nachemson A (1983) Long-term anatomic and functional changes in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis treated with Harrington rod fusion. Spine 8: 576–84
Dobbs MB, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH (2005) Comparison of combined anterior/posterior fusion alone for the treatment of adolescent idiopathic curves greater than 90 degrees. Book of abstracts. Scoliosis Research Society. 40th annual meeting, October 2005, pp 44–45
Dwyer AF, Schafer MF (1974) Anterior approach to scoliosis: results of treatment in 51 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br 56:218–224
Edwards CC, Lenke LG, Peele M, Sides B, Rinella A, Bridwell KH (2004) Selective thoracic fusion for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with C Modifier Lumbar curves: 2–16 year radiographic and clinical results. Spine 29:536–546
Ginsburg HH, Goldstein LA, Robinson SC, et al (1979) Back pain in postoperative idiopathic scoliosis: long-term follow up study. Spine 4:518
Kaneda K, Shono Y, Satoh S, Abumi K (1997) Anterior correction of thoracic scoliosis with Kaneda anterior spinal system: a preliminary report. Spine 22:1358–68
Kaneda K, Shono Y, Satoh S, Abumi K (1996) New anterior instrumentation for the management of thoracolumbar and lumbar scoliosis: application of the Kaneda two-rod system. Spine 21:1250–1261
King HA, Moe JH, Bradford DS, Winter RB (1983) The selection of fusion levels in thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 65:1302–1313
Lenke LG, Bridwell K, Baldus C, Blanke K (1992) Preventing decompensation in King Type II curves treated with Cotrel–Dubousset instrumentation: strict guidelines for selective fusion. Spine 17S:274–81
Lenke LG, Betz RR, Bridwell KH, Harms J, Clements DH, Lowe TG (1999) Spontaneous lumbar curve coronal correction after selective anterior or posterior thoracic fusion in adolescent scoliosis. Spine 24:1663–72
Lenke LG, Betz RR, Haher TR, Lapp MA, Merola AA, Harms J, Shufflebarger HL (2001) Multisurgeon assessment of surgical decision-making in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 26:2347–2353
Lenke L, Betz R, Harms J, Bridwell KH, Clements DH, Lowe TG, Blanke K (2001) Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a new classification to determine extent of spinal arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83:1169–81
Liljenqvist UR, Allkemper T, Hackenberg L, Link TM, Steinbeck J, Halm HFH (2002) Analysis of vertebral morphology in idiopathic scoliosis with use of magnetic resonance imaging and multiplanar reconstruction. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84:359–368
Lonstein J.Decompensation with Cotrel–Dubousset instrumentation: a multicenter study (1991) 25th Anniversary Meeting of the Scoliosis Research Society, Minneapolis, MN, September, 1991
Lowe TG, Alongi PR, Smith DAB, O’Brien MF, Mitchell SL, Pinteric RJ (2003) Anterior single rod instrumentation for thoracolumbar adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with and without use of structural interbody support. Spine 28:2232–2242
Lowe TG, Betz R, Lenke L, Clements D, Harms J, Newton P, Haher T, Merola A, Wenger D (2003) Anterior single-rod instrumentation of the thoracic and lumbar spine: saving levels. Spine 28:S208–S216
Luk KDK, Lee FB, Leong JCY, Hsu LCS (1987) The effect on the lumbosacral spine of long spinal fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: a minimum of 10 year follow-up. Spine 12:996–1000
Luk KDK, Leong JCY, Reyes L, Hsu LCS (1989) The comparative results of treatment in idiopathic thoracolumbar and lumbar scoliosis using the Harrington, Dwyer, and Zielke instrumentations. Spine 14:275–280
McCance SE, Denis F, Lonstein JE, et al (1998) Coronal and sagittal balance in surgically treated adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with the King II curve pattern: a review of 67 consecutive cases having selective thoracic arthrodesis. Spine 23:2063–72
Moskowitz A, Moe JH, Winter RB, Binner H (1980) Long-term follow-up of scoliosis fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am 62:364–76
Nash CL Jr, Moe JH (1969) A study of vertebral rotation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 51:223–229
Richards BS (1992) Lumbar curve response in type II idiopathic scoliosis after posterior instrumentation of the thoracic curve. Spine 17:S282–6
Richards BS, Birch JG, Herring JA, Johnston CE, Roach JW (1989) Frontal plane and sagittal plane balance following Cotrel–Dubousset instrumentation for idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 14:733–737
Rinella A, Bridwell K, Kim Y, Rudzki J, Edwards C, Roh M, Lenke L, Berra A (2004) Late complications of adult idiopathic scoliosis primary fusions to L4 and above. Spine 29:318–325
Schwender JD, Denis F (2000) Coronal plane imbalance in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with left lumbar curves exceeding 40 degrees: the role of the lumbosacral hemicurve. Spine 25:2368–2363
Suk SI, Choon KL, Chung SS (1993) Comparison of Zielke ventral derotation system and Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation in the treatment of idiopathic lumbar and thoracolumbar scoliosis. Spine 19(4):419–429
Sweet FA, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Blanke KM (1999) Maintaining lumbar lordosis with anterior single solid-rod instrumentation in thoracolumbar and lumbar adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 24:1655–62
Sweet FA, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Blanke KM, Whorton J (2001) Prospective radiographic and clinical outcomes and complications of single solid rod instrumented anterior spinal fusion in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 26:1956–1965
Takahashi S, Delecrin J, Passuti N (1997) Changes in the unfused lumbar spine in patients with idiopathic scoliosis: a 5–9 year assessment after Cotrel–Dubousset instrumentation. Spine 22:517–523
Turi M, Johnston CE, Richards BS (1993) Anterior correction of idiopathic scoliosis using TSRH instrumentation. Spine 18:417–422
Yazici M, Cil A, Pekmezci M, Acaroglu E, et al (2005) The effects of residual lower end vertebral tilt on the outcome of surgical correction in patients with AIS.Book of abstracts. Scoliosis Research Society. 40th annual meeting, October 2005, p 176
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Paper presented at the Scoliosis Research Society, October 2005, Miami, FL.
No funding or grants were used to prepare this manuscript
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeon, H.B., Weinberg, J., Arlet, V. et al. Anterior lumbar instrumentation improves correction of severe lumbar Lenke C curves in double major idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J 16, 1379–1385 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-007-0370-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-007-0370-6