Abstract
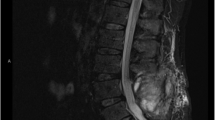
Spontaneous spinal subdural haematoma is a rare cause of spinal cord compression, usually confined to a few vertebral levels. When the haematoma extends over several spinal segments, surgical decompression is a major undertaking. Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) has previously been used in a number of surgical procedures, but not in the setting of acute spinal subdural haematoma. A minimally invasive technique of decompression, using topical rt-PA, is presented in two patients with extensive spinal intradural haematoma. Two patients receiving long-term anticoagulation therapy presented with acute-onset back pain progressing to paraparesis. Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine demonstrated spinal subdural haematomas extending over 15 vertebral levels in one patient and 12 in the other. An angiography catheter was introduced into the subdural space through a limited laminectomy. Thrombolysis and evacuation of haematoma was then achieved by intermittent irrigation of the subdural space with rt-PA, followed by saline lavage. Postoperative imaging demonstrated satisfactory decompression in both patients. There was significant improvement of neurological function in one patient. Topical application of rt-PA for spinal subdural haematoma allows evacuation of the haematoma through a limited surgical exposure. Decompression of the subdural space by this minimally invasive technique may be advantageous over extensive surgery by minimising surgical exposure, reducing postoperative pain and risk of neuronal injury. This technique may be useful in patients presenting with compression extending over several vertebral levels or poor surgical candidates.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anagnostopoulos DI, Gortvai P (1972) Spontaneous spinal subdural haematoma. BMJ 30:791
Doll A, Neugroschl C, Jacques C, Chassagnon S, Kehril P, Dietemenn JL (2000) Spontaneous regression of an acute spinal subdural haematoma. MR imaging. J Neuroradiol 27:192–195
Edelson RN, Chernik NL, Posner JB (1974) Spinal subdural haematomas complicating lumbar puncture. Occurrence in thrombocytopenic patients. Arch Neurol 31:134–137
Hann PP, Theodore N, Porter RW, Detwiler PW, Lawton MT, Spetzler RF (1991) Subdural haematoma from a type I spinal arteriovenous malformation. Case report. J. Neurosurg 90:255–257
Kulkarni AV, Willinsky RA, Gray T, Cusimano MD (1998) Serial magnetic resonance imaging findings for a spontaneously resolving spinal subdural haematoma: case report. Neurosurgery 43:1495
Lao TT, Halpern SH, MacDonald D, Huh C (1993) Spinal subdural haematoma in a parturient after attempted epidural anaesthesia. Can J Anaesth 40:340–345
Maeda M, Mochida J, Toh E, Nishimura K, Nomura T (2001) Nonsurgical treatment of an upper thoracic spinal subdural haemorrhage. Spinal Cord 39:657–661
Russell NA, Benoit BG (1983) Spinal subdural haematoma: A review. Surg Neurol 20:133–137
Swann KW, Ropper AH, New PFJ, Poletti CE (1984) Spontaneous spinal subarachnoid haemorrhage and subdural haematoma. J Neurosurg 61:975–980
Vinters HV, Barnett HJ, Kaufmann JC (1980) Subdural haematoma of the spinal cord and widespread subarachnoid haemorrhage complicating anticoagulant therapy. Stroke 11:459–464
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Little, C.P., Patel, N., Nagaria, J. et al. Use of topically applied rt-PA in the evacuation of extensive acute spinal subdural haematoma. Eur Spine J 13, 380–383 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-003-0529-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-003-0529-8