Abstract
Background
Surgical treatment of spinal deformities in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is influenced by a number of factors which have proven to be a difficult challenge. Each case should be carefully evaluated, considering not only the natural history of the spinal deformity, but also the patient’s general condition. These should be thoroughly assessed through clinical and radiographic investigations together with other medical specialists. Life expectancy should be determined according to the cardio-respiratory function, and both preoperative and postoperative quality of life should be taken into consideration, trying to imagine the functional status of each patient after surgery.
Methods
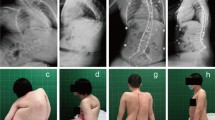
From February 1985 to February 2000, 58 patients with spinal deformity in DMD were surgically treated. Of 25 patients that were operated on between 1985 and 1995, only 20 were followed-up after 5 years because 5 of them had died during this time. Therefore, the present study focuses on the results obtained in 20 cases. The 20 cases reviewed presented with a mean angular value of scoliosis equal to 48° (range 10–92°). Spinal fusion with our modified Luque technique [6] was performed in 19 cases, whereas CD instrumentation was applied in only one case.
Results
At the 5 year follow-up (range 5.6–10 years), the age ranged from 18 to 24 years and averaged 20.4 years. The postoperative angular value of scoliosis averaged 22° (58%, range 0–43°), the mean correction at follow-up was 28° (range 0–60°), and the mean loss of correction was equal to 6° (range, 0–11°). Vital capacity showed a slow progression, slightly inferior to its natural evolution in untreated patients. The severest complication was the death that occurred in one of the patients.
Conclusions
According to the present study, an early surgery (angular value lower than 35–40°) dramatically reduces the rate of risk factors associated with spinal deformities in DMD, and its advantages far exceed the disadvantages, above all in terms of quality of life.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alman BA, Kim HK (1999) Pelvic obliquity after fusion of the spine in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Bone Joint Surg Br 81:821–824
Bellen P, Hody JL, Clairbois J et al. (1993) The surgical treatment of spinal deformities in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Orthop Surg 7:48–57
Bradford DS (1987) Neuromuscular spinal deformity. In: Bradford DS, Lonstein JE, Moe JA, Winter RB (eds) Moe’s textbook of scoliosis and other spinal deformities, Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 284–296
Bridwell KH, Baldus C, Iffrig TM, Lenke LG, Blanke K (1999) Process measures and patient/parent evaluation of surgical management of spinal deformities in patients with progressive flaccid neuromuscular scoliosis (Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy and spinal muscular atrophy). Spine 24:1300–1309
Cambridge W, Drennan JC (1987) Scoliosis associated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Pediatr Orthop 7:436–440
Cervellati S, Bettini N, Bianco T, Greggi T, Lollini ME, Parisini P (1995) Il sistema di Luque. Prog Pat Vert 18:17–27
Chataigner G, Gretet V, Onimus M (1998) Surgery of the spine in Duchenne’s dystrophy. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 84:224–230
Colbert AP, Craig C (1987) Scoliosis management in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: prospective study of modified Jewett hyperextension brace. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 68:302–304
Drennan JC (1984) Surgical management of neuromuscular scoliosis. In: Serratrice G et al. (eds) Neuromuscular disease, Raven, New York, p 551
Dubousset J (1996) Les déformations rachidiennes d’origine neuromusculaire. Analyse et traitement. Prog Pat Vert XIX:177–191
Dubousset J, Queneau P (1983) Place et indication de la chirurgie dans la dystrophie musculaire de Duchenne de Bologne à évolution rapide. Rev Chir Orthop 69:207–220
Dubowitz V (1978) Muscle disorders in childhood, Saunders, Philadelphia
Dweyr AF, Newton NC, Sherwood AA (1969) An anterior approach to scoliosis: a preliminary report. Clin Orthop 62:192–202
Forst R, Forst J, Heller KD, Hengstler K (1997) Characteristics in the treatment of scoliosis in muscular diseases. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 135:95–105
Galasko CSB (1977) Incidence of orthopaedic problems in children with muscle disease. Isr J Med Sci 13:165–176
Galasko CSB (1987) The orthopaedic management of the dystrophies, myopathies, atrophies, neuropathies and ataxias. In: Galasko CSB (ed) Neuromuscular problems in orthopaedics, Blackwell, Oxford, pp 83–105
Galasko CSB, Delaney C, Morris P (1992) Spinal stabilisation in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Bone Joint Surg Br 74:210–214
Galasko CSB, Williamson JB, Delaney C (1995) Lung function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Eur Spine J 4:263–267
Gardner-Medwin D (1980) Clinical features and classification of the muscular dystrophies. Br Med Bull 36:109–115
Gayet LE (1999) Surgical treatment of scoliosis due to Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Chirurgie 124:423–431
Gibson DA, Koreska J, Robertson D, Khan A III, Albisser AM (1978) The management of spinal deformities in Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy. Orthop Clin North Am 9:437–450
Gibson DA, Wilkins KE (1975) The management of spinal deformities in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a new concept of spinal bracing. Clin Orthop 108:41–51
Granata C, Merlini L, Cervellati S, Ballestrazzi A, Giannini S, Corbascio M, Lari S (1996) Long-term results of spine surgery in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul Disord 6:61–68
Harrington PR (1962) Treatment of scoliosis: correction and internal fixation by spine instrumentation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 44:591–610
Heller KD, Forst R, Forst J, Hengstler K (1997) Scoliosis in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: aspects of orthotic treatment. Prosthet Orthot Int 21:202–209
Hopf C, Forst R, Forst J, Eysel P, Reitter B (1994) Multi-segmental fusion of scoliosis in Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 132:377–382
Hsu JD (1983) The natural history of spine curvature progression in the non-ambulatory Duchenne muscular patient. Spine 8:771–775
Kennedy JD, Staples AJ, Brook PD, Parsons DW, Sutherland AD, Martin AJ, Stern LM, Foster BK (1995) Effect of spinal surgery on lung function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Thorax 50:1173–1178
Kurz LT, Mubarak SJ, Schultz P, Park SM, Leach J (1983) Correlation of scoliosis and pulmonary function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Pediatr Orthop 3:347–353
Ledoux P (1980) La scoliose du miopathe Duchenne de Bulogne. Caractéristiques et incidences thérapeutiques. Kinesiter Scient 177:51–55
Luque ER (1982) The anatomical basis and development of segmental spinal instrumentation. Spine 7:256–259
Marchesi D, Arlet V, Stricker U, Aebi M (1997) Modification of the original Luque technique in the treatment of Duchenne’s neuromuscular scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop 17:743–749
Matsumura T, Kang J, Nozaki S, Takahashi MP (1997) The effect of spinal fusion on respiratory function and quality of life in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 37:87–92
McCarthy RE (1999) Management of neuromuscular scoliosis. Orthop Clin North Am 30:435–449
Miller F, Moseley CF, Koreska J (1992) Spinal fusion in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Dev Med Child Neurol 34:775–786
Miller F, Moseley CF, Koreska J, Levison H (1988) Pulmonary function and scoliosis in Duchenne dystrophy. J Pediatr Orthop 8:133–137
Miller G, O’Connor J (1985) Spinal bracing and respiratory function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Clin Pediatr 24:94
Miller RG, Chalmers AC, Dao H et al. (1991) The effect of spine fusion on respiratory function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neurology 41:38–40
Mubarak SJ, Morrin WD, Leach JL (1993) Spinal fusion in Duchenne muscular dystrophy–Fixation and fusion to the sacropelvis? J Pediatr Orthop 13:752–757
Noble Jamieson CM, Heckmatt JZ, Dubowitz V, Silverman M (1986) The effect of posture and spinal bracing on respiratory function in neuromuscular disease. Arch Dis Child 61:168–171
Pruijs JE, van Tol MJ, van Kesteren RG, van Nieuwenhuizen O (2000) Neuromuscular scoliosis: clinical evaluation pre- and postoperative. J Pediatr Orthop B9:217–220
Rennie MJ, Edwards RHT, Millward DJ et al. (1982) Effects of Duchenne muscular dystrophy on muscle protein synthesis. Nature 296:165–167
Rice JJ, Jeffers BL, Devitt AT, McManus F (1998) Management of the collapsing spine for patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Ir J Med Sci 167:242–245
Rideau Y et al. (1984) The treatment of scoliosis in Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve 7:281–286
Sakai DN, Hsu JD, Bonnett CA, Brown JC (1977) Stabilisation of the collapsing spine in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Clin Orthop 6:256–260
Savini R, Cervellati S, Palmisani M, Spina F (1991) Il ruolo della chirurgia nel trattamento delle deformità vertebrali nella distrofia muscolare di Duchenne. Rivista Italiana di Ortopedia e Traumatologia Pediatrica 7:249–255
Shapiro F, Sethna N, Colan S, Wohl ME, Specht L (1992) Spinal fusion in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a multidisciplinary approach. Muscle Nerve 15:604–614
Siegel IM (1978) The management of muscular dystrophy: a critical review. Muscle Nerve 1:453
Smith PEM, Calverley PMA, Edwards RHT, Evans GA, Campbell EJM (1987) Practical problems in the respiratory care of patients with muscular dystrophy. N Engl J Med 316:1197–1205
Stricker U, Moser H, Aebi M (1996) Predominantly posterior instrumentation and fusion in neuromuscular and neurogenic in children and adolescents. Eur Spine J 5:101–106
Sussman MD (1984) Advantage of early spinal stabilization and fusion in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Pediatr Orthop 4:532–537
Swank SM, Brown JC, Perry RE (1982) Spinal fusion in Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy. Spine 7:484–491
Tunner JM, Whitehouse RH (1976) Clinical longitudinal standards for height, weight, height velocity, weight velocity, and stages of puberty. Arch Dis Child 51:170–179
Weimann RL, Gibson DA, Moseley CF, Jones DC (1983) Surgical stabilization of the spine in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Spine 8:776–780
Yazici M, Asher MA, Hardacker JW (2000) The safety and efficacy of Isola-Galveston instrumentation and arthrodesis in the treatment of neuromuscular spinal deformities. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82:524–543
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank “Telethon” for supporting this project with research funds (no. 1165C)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cervellati, S., Bettini, N., Moscato, M. et al. Surgical treatment of spinal deformities in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a long term follow-up study. Eur Spine J 13, 441–448 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-002-0515-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-002-0515-6