Abstract
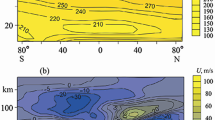
The coupled thermosphere-ionosphere-plasmasphere model CTIP is used to study the global three-dimensional circulation and its effect on neutral composition in the midlatitude F-layer. At equinox, the vertical air motion is basically up by day, down by night, and the atomic oxygen/molecular nitrogen [O/N2] concentration ratio is symmetrical about the equator. At solstice there is a summer-to-winter flow of air, with downwelling at subauroral latitudes in winter that produces regions of large [O/N2] ratio. Because the thermospheric circulation is influenced by the high-latitude energy inputs, which are related to the geometry of the Earth’s magnetic field, the latitude of the downwelling regions varies with longitude. The downwelling regions give rise to large F2-layer electron densities when they are sunlit, but not when they are in darkness, with implications for the distribution of seasonal and semiannual variations of the F2-layer. It is also found that the vertical distributions of O and N2 may depart appreciably from diffusive equilibrium at heights up to about 160 km, especially in the summer hemisphere where there is strong upwelling.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Rishbeth, H., Müller-Wodarg, I.C.F. Vertical circulation and thermospheric composition: a modelling study. Annales Geophysicae 17, 794–805 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00585-999-0794-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00585-999-0794-x