Abstract
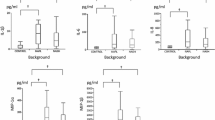
Liver disease is the main cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The spectrum of the disease ranged from fatty liver to hepatic inflammation, necrosis, progressive fibrosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. We evaluated the serum levels of soluble tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor 1, total B-hexosaminidase and its isoenzymes Hex A and B activities, and nitric oxide in patients with liver diseases and their association with aminotransferase level. Seventy patients and 12 healthy subjects were recruited. Patients were divided into three groups: chronic hepatitis group (20 patients), liver cirrhosis group (30 patients), and malignant liver group (20 patients). Serum levels of soluble tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor 1, total B-hexosaminidase and its isoenzymes Hex A and B activities, and nitric oxide were measured. Serum levels of soluble tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor 1, total B-hexosaminidase activity, and nitric oxide were significantly higher in the liver disease patients. Serum levels of isoenzymes Hex A and B were significantly higher in malignant liver patients. Total B-hexosaminidase and its isoenzyme Hex A activity levels were significantly higher in positive HBsAg and positive anti-HCV patients. Serum levels of soluble tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor 1 were positively correlated with aminotransferase level. Taken together, these findings suggested that these biochemical indices might reflect ongoing disease activity and played an important role in the pathophysiology of liver diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardebili SM, Yeghaneh T, Gharesouran J, Rezazadeh M, Farhoudi M, Ayromlou H, Talebi M, Ghojazadeh M (2011) Genetic association of TNF-α-308 G/A and −863 C/A polymorphisms with late onset Alzheimer's disease in Azeri Turk population of Iran. J Res Med Sci 16:1006–1013
Arkenau HT, Stichtenoth DO, Frölich JC, Manns MP, Böker KH (2001) Elevated nitric oxide levels in patients with chronic liver disease and cirrhosis correlate with disease stage and parameters of hyperdynamic circulation. Z Gastroenterol 40:907–913
Bateman KS, Cherney MM, Mahuran DJ, Tropak M, James MN (2011) Crystal structure of β-hexosaminidase B in complex with pyrimethamine, a potential pharmacological chaperone. J Med Chem 54:1421–1429
Belarbi K, Jopson T, Tweedie D, Arellano C, Luo W, Greig NH, Rosi S (2012) TNF-alpha protein synthesis inhibitor restores neuronal function and reverses cognitive deficits induced by chronic neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation 9(1):23
Bierć M, Minarowski Ł, Woźniak Ł, Chojnowska S, Knaś M, Szajda S, Zwierz K (2010) The activity selected glycosidases in salivary gland tumors. Fol Histochem Cytobiol 48:471–474
Chatterjee SK, Bhattacharya M, Barlow JJ (1979) Glycosyltransferase and glycosidase activities in ovarian cancer patients. Cancer Res 39:1943–1951
Chen D, Liu JL, Liu Y, Zhu J, Wang SW (2011) Lack of an association between -308G>A polymorphism of the TNF-α gene and liver cirrhosis risk based on a meta-analysis. Genet Mol Res 10:2765–2774
Choromańska B, Luto M, Szajda SD, Waszkiewicz N, Kępka A, Janica J, Ladny JR, Dadan J, Myśliwiec P, Zwierz K (2011) Activity of N-acetyl-β-hexosaminidase and its isoenzymes A and B in cancer. Postepy Hig Med Dosw 23:752–758
Ergün Y, Kurutaş EB, Ozdil B, Güneşaçar R, Ergün Y (2011) Evaluation of nitrite/nitrate levels in relation to oxidative stress parameters in liver cirrhosis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 35:303–308
Hultberg B, Floren CH, Isaksson A, Jensen E (1995) Liver disease and serum hexosaminidase levels. Studies in a human hepatoma cell-line (Hep G2 cells). Liver 15:99–103
Ibrahim M, Gomaa W, Ibrahim Y, El Hadad H, Shatat M, Aleem AA, Essawy M, Fouad YM (2010) Nitric oxide levels and sustained virological response to pegylated-interferon alpha2a plus ribavirin in chronic HCV genotype 4 hepatitis: a prospective study. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 19:387–392
Ikeguchi M, Ueta T, Yamane Y, Hirooka Y, Kaibara N (2002) Inducible nitric oxide synthase and survivin messenger RNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 8:3131–3136
Itoh Y, Okanoue T, Ohnishi N, Sakamoto M, Nishioji K, Nakagawa Y, Minami M, Murakami Y, Kashima K (1999) Serum levels of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors and effects of interferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Am J Gastroenterol 94:1332–1340
Jorge LG, Francisco GR, Ramon F, Francisco CC, Elena R, Enrique GO (2004) Osteoporosis, mineral metabolism, and serum soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor p55 in viral cirrhosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:4325–4330
Kallinowski B, Haseroth K, Marinos G, Hanck C, Stremmel W, Theilmann L, Singer MV, Rossol S (1998) Induction of tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptor type p55 and p75 in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Clin Exp Immunol 111:269–277
Lee KC, Yang YY, Wang YW, Lee FY, Loong CC, Hou MC, Lin HC, Lee SD (2010) Increased plasma malondialdehyde in patients with viral cirrhosis and its relationships to plasma nitric oxide, endotoxin, and portal pressure. Dig Dis Sci 55:2077–2085
Leung TM, Fung ML, Liong EC, Lau TY, Nanji AA, Tipoe GL (2011) Role of nitric oxide in the regulation of fibrogenic factors in experimental liver fibrosis in mice. Histol Histopathol 26:201–211
Li CJ, Li RW, Kahl S, Elsasser TH (2012) Alpha-tocopherol alters transcription activities that modulates tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) induced inflammatory response in bovine cells. Gene Regul Syst Biol 6:1–14
Liu ZG, Han J (2001) Cellular responses to tumor necrosis factor. Curr Issues Mol Biol 3:79–90
López-Sánchez LM, Corrales FG, Barcos M, Espejo I, Muñoz-Castañeda JR, Rodríguez-Ariza A (2010) Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis during induced cholestasis ameliorates hepatocellular injury by facilitating S-nitrosothiol homeostasis. Lab Investig 90:116–127
Marusi CJ, Podlipnik C, Jevsevar S, Kuzman D, Vesnaver G, Lah J (2012) Recognition of human tumor necrosis factor TNF-α by a therapeutic antibody fragment: energetics and structural features. J Biol Chem 287:8613–8620
Matsuoka K, Tamura T, Tsuji D, Dohzono Y, Kitakaze K, Ohno K, Saito S, Sakuraba H, Itoh K (2011) Therapeutic potential of intracerebroventricular replacement of modified human β-hexosaminidase B for GM2 gangliosidosis. Mol Ther 19:1017–1024
Moura AS, Ricardo AC, Antonio LT, Manoel OCR (2009) Soluble inflammatory markers as predictors of hepatocellular damage and therapeutic response in chronic hepatitis C. Braz J Infect Dis 13:375–382
Napoleon W, Beata Z, Sławomir DS, Alina K, Magdalena W, Wiesława R, Marzena W, Anna JM, Jacek D, Agata S, Krzysztof Z, Jerzy RŁ (2012) Lysosomal exoglycosidases and cathepsin D in colon adenocarcinoma. Pol Arch Med Wewn 122:551–556
Pérez LF, Casal JA, Rojas P, Tutor JC (2000) Relationship between plasma ammonia concentration and beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase isoenzyme activities in liver. Clin Chem Lab Med 38:1237–1241
Shiraki M, Yoichi T, Junpei I, Masahito S, Yoshiyuki M, Nobuo M, Masahito N, Hisataka M (2010) Elevated serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha and soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors correlate with aberrant energy metabolism in liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 26:269–275
Szajda SD, Waszkiewicz N, Stypułkowska A, Dadan J, Zwierz K (2010) Lysosomal exoglycosidases in serum and urine of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Fol Histochem Cytobiol 48:351–357
Szajda SD, Waszkiewicz N, Chojnowska S, Zwierz K (2011) Carbohydrate markers of pancreatic cancer. Biochem Soc Trans 39:340–343
Tirapelli LF, Batalhão ME, Jacob-Ferreira AL, Tirapelli DP, Carnio EC, Tanus-Santos JE, Queiroz RH, Uyemura SA, Padovan CM, Tirapelli CR (2011) Chronic ethanol consumption induces histopathological changes and increases nitric oxide generation in the rat liver. Tissue Cell 43:384–391
Titheradge A (1998) The enzymatic measurement of nitrate and nitrite. Methods Mol Biol 100:83–91
Trebicka J, Krag A, Gansweid S, Appenrodt B, Schiedermaier P, Sauerbruch T, Spengler U (2010) Endotoxin and tumor necrosis factor-receptor levels in portal and hepatic vein of patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis receiving elective transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Nutrition 26:269–275
von Baehr V, Döcke WD, Plauth M, Liebenthal C, Küpferling S, Lochs H, Baumgarten R, Volk HD (2000) Mechanisms of endotoxin tolerance in patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis: role of interleukin 10, interleukin 1 receptor antagonist, and soluble tumour necrosis factor receptors as well as effector cell desensitisation. Gut 47:281–287
Zylberberg H, Rimaniol A, Pol S, Masson A, De Groote D, Berthelot P, Bach J, Brechot C, Zavala F (1999) Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors in chronic hepatitis C: a correlation with histological fibrosis and activity. J Hepatol 30:185–191
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Idriss, N.K., Sayyed, H.G., Zakhary, M.M. et al. Implication of tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor 1 and hexosaminidase: relationship to pathogenesis of liver diseases. Comp Clin Pathol 23, 1095–1102 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-013-1747-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-013-1747-z