Abstract
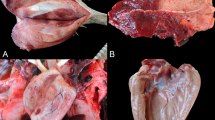
Narasin poisoning was reported in 15 camels, 7 adults and 8 young, after accidental access to poultry feed medicated with 60 g narasin per ton. Fourteen camels died between 3 and 20 days, and one young animal survived the dose after developing a chronic course of a disease. The main clinical signs of narasin toxicity in the dromedary include: weakness of hind limbs, lack of coordination, oedema of dependent parts, inappetence, ruminal atony, myoglobinuria, profound depression, tachycardia, sternal recumbency and death. The lesions were mainly in the heart and skeletal muscles and consisted of multifocal degeneration and necrosis of heart and skeletal muscle fibres with areas of regeneration and lung oedema. There was high enzyme activity for creatine kinase (CK), lactate dehydrogenase, aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase and an increase in urea concentration and white blood cells, neutrophil and platelet counts. Cardiac markers, troponin T, CK-MB and C-reactive protein, showed slight or no changes terminally.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABVT (2003) Ionophore toxicosis. The American Board of Veterinary Toxicology, 1–9
Adam SEI (1972) A review of drug hepatotoxicity in animals. Vet Bull 42:683–689
Alpharma (1998) Safety and toxicity of polyether ionophores in livestock and poultry. Technical Bulletin No CD331; Al Pharma Animal Health Division, pp 1–12
Behr KP, Luders H, Glunder G, Friederichs M (1988) Narasin poisoning in turkey. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr 95:107–108
Bengoumi M, Faye B, De La Farge F, Olson WG, Rico AG (1997) Clinical enzymology in the dromedary camel (Camelus dromedaries). Part 1. Enzyme activities and distributions of AST, ALT, GGT, ALP and LDH in liver kidney, muscles, myocardium and blood. J Camel Pract Res 4:19–23
Bergen WG, Bates DB (1984) Ionophores: their effect on production efficiency and mode of action. J Anim Sci 58:1465–1483
Boyd JW (1962) The comparative activity of some enzymes in sheep, cattle and rats—normal serum and tissue levels and changes during experimental liver necrosis. Res Vet Sci 3:256–268
Chaudhry ZI, Iqbal J, Raza M, Qandil MI (1998) Acute monensin toxicity in dromedary camels. J Camel Pract Res 5:271–273
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) (2007) Opinion of the scientific panel on contaminants in the food chain on a request from the European Commission on cross-contamination of non-target feeding-stuffs by narasin authorized for use as a feed additive. The EFSA Journal 552:1–35
Fraser CM, Bergeron JA, Mays A, Aiello SE (1991) The Merck veterinary manual, 7th edn. Merck, Rahway, p 1474
Fry JM, Allen JG, Speijers EJ, Roberts WD (1994) Muscle enzymes in the diagnosis of ovine weaner nutritional myopathy. Aust Vet J 71:146–150
Langston UC, Galey F, Lovell R, Buck WB (1985) Toxicity and therapeutics of monensin: a review. J Vet Med 80:75–84
Manefield GW, Tinson A (1996) Camels A compendium. The TG Hungertord Vade Mecum series for domestic animals series G, no 22, pp. 157–158
Matsuoka T (1976) Evaluation of monensin toxicity in the horse. J Am Vet Med Assoc 169:1098–1100
Mousa HM, El-Sheikh HA (1992) Monensin poisoning in dromedary camels (short report). Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr 99:464
Nagaraja TG, Avery TB, Bartley EE, Galitzer SJ, Dayton AD (1981) Prevention of lactic acidosis in cattle by lasalocid or monensin. J Anim Sci 53:206–215
Novilla MN, Owen NV, Todd GC (1994) The comparative toxicity of narasin in laboratory animals. Vet Hum Toxicol 36:318–323
Ordidge RM, Schubert FK, Stoker JW (1979) Death of horses after accidental feeding of monensin. Vet Rec 104:375
Peeters JE, Geeroms R, Antoine O, Mammerickx O, Halen P (1981) Efficacy of narasin against hepatic and intestinal coccidiosis in rabbits. Parasitology 83:293–301
Riddell FG, Tompsett SJ (1990) The transport of Na+ and K+ ions through phospholipid bilayers mediated by the antibiotics salinomycin and narasin studied by 23Na- and 39K-NMR spectroscopy. Biochimic Biophysi Acta 1024:193–197
Salles MS, Lombardo de Barros CS, Barros SS (1994) Ionophore antibiotic (narasin) poisoning in rabbits. Vet Hum Toxicol 36:437–444
Val Vleet JF, Amustutz HE, Weirich WE, Rebar AH, Ferrans VJ (1983) Clinical, clinicopathologic and pathologic alterations in acute monensin toxicosis in cattle. Am J Vet Res 44:2133–2144
Wernery U, Tinson A, Kinne J, Masri JAl (1998) Salinomycin poisoning in a dromedary breeding herd in the United Arab Emirates. J Camel Pract Res 5:275–279
Wouters ATB, Wouters F, Barros CSL (1997a) Experimental narasin poisoning in cattle. Pesquisa Veterinaria Brasileira 17:82–88
Wouters ATB, Wouters F, Barros CSL (1997b) Experimental narasin poisoning in sheep. Pesquisa Veterinaria Brasileira 17:89–95
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Mr. Mohamed ET Tayab and the staff of the Histopathology Section, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, UAE University, Al-Ain for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abu Damir, H., Ali, M.A., Abbas, T.A. et al. Narasin poisoning in the dromedary camel (Camelus dromedarius). Comp Clin Pathol 22, 305–311 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-011-1403-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-011-1403-4