Abstract
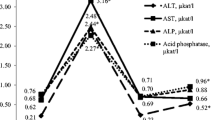
Echinacea preparations are widely used in the prevention or treatment of upper respiratory tract infections. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of a standardized Echinacea extract in experimentally induced liver toxicity and whether this herb would have a modulating effect on the silymarin-induced hepatoprotection in rats. Liver damage was induced by the administration of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). Echinacea extract (18 or 36 mg/kg) alone or combined with silymarin (25 mg/kg), silymarin only (25 mg/kg), or saline (control) was given once daily orally simultaneously with CCl4 and for 1 week thereafter. Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) or aspartate aminotransferase were not significantly changed by treatment with Echinacea, but alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in serum decreased by 23.6% by the extract at 36 mg/kg. Silymarin given in combination with either dose of Echinacea resulted in 34.9% and 57.8% reduction in AST, 42.7% and 58% reduction in ALT and 41% and 60% reduction in ALP, compared with CCl4 control group. Silymarin alone reduced ALT, AST, and ALP levels by 58.8%, 61.2%, and 62.2%, respectively. Histopathological examination revealed a mild decrease in degenerated hepatocytes after treatment with 36 mg/kg of Echinacea. Noticeable improvement in the liver damage was observed upon the addition of silymarin to Echinacea. A marked decrease of intracellular protein and glycogen staining was evident after the administration of CCl4. Slight improvement in protein and glycogen staining was noted after 36 mg/kg of Echinacea. Increased hepatic protein and glycogen staining intensity was observed after silymarin and Echinacea co-treatment compared with Echinacea-only treated groups. Silymarin only treatment resulted in more or less normal histopathological and histochemical findings. The present results suggest that administration of Echinacea extract reduces the hepatoprotective effect of silymarin. Such finding is likely to have important clinical significance in patients with hepatic disease on silymarin treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel Salam OME, Sleem AA, Omara EA, Hassan N (2007) Effect of ribavirin alone or combined with silymarin on carbon tetrachloride induced hepatic damage in rats. Drug Target Insights 1:19–27
Ali EH (2008) Protective effects of Echinacea on cyproterone acetate induced liver damage in male rats. Pak J Biol Sci 11:2464–2471
Batey RG, Salmond SJ, Bensoussan A (2005) Complementary and alternative medicine in the treatment of chronic liver disease. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 7:63–70
Bauer R (1998) Echinacea: biological effects and active principles. Chapter 12. In: Lawson LD, Bauer R (eds) Phytomedicines of Europe. Chemistry and biological activity. ACS Symposium Series 691. American Chemical Society, Washington DC, pp 140–175
Bauer R, Woelkart K (2005) Echinacea. In: Coates P (ed) Encyclopedia of dietary supplements. Dekker, New York, pp 177–187
Belfield A, Goldberg DM (1971) Revised assay for serum phenyl phosphatase activity using 4-amino-antipyrine. Enzyme 12:561–573
Bielory L (2004) Complementary and alternative interventions in asthma, allergy, and immunology. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 93(2 Suppl 1):S45–S54
Boigk G, Stroedter L, Herbst H, Waldschmidt J, Riecken EO, Schuppan D (1997) Silymarin retards collagen accumulation in early and advanced biliary fibrosis secondary to complete bile duct obliteration in rats. Hepatology 26:643–649
Carr RR, Nahata MC (2006) Complementary and alternative medicine for upper-respiratory-tract infection in children. Am J Health Syst Pharm 63:33–39
Castro JA, Gómez MI, de Castro CR, de Fenos OM, de Ferreyra EC, D'Acosta N (1975) Carbon tetrachloride induced polysome breakdown. Relative importance of lipid peroxidation and of binding to ribosomal components in the process. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 10:93–104
Cech NB, Tutor K, Doty BA, Spelman K, Sasagawa M, Raner GM, Wenner CA (2006) Liver enzyme-mediated oxidation of Echinacea purpurea alkylamides: production of novel metabolites and changes in immunomodulatory activity. Planta Med 72:1372–1377
Changani KK, Jalan R, Cox IJ, Ala-Korpela M, Bhakoo K, Taylor-Robinson SD, Bell JD (2001) Evidence for altered hepatic gluconeogenesis in patients with cirrhosis using in vivo 31-phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Gut 49:557–564
Conti M, Malandrino S, Magistretti MJ (1992) Protective activity of silipide on liver damage in rodents. Jpn J Pharmacol 60:315–321
Crowley LV (1967) The Reitman–Frankel colorimetric transaminase procedure in suspected myocardial infarction. Clin Chem 13:482–487
De La Puerta R, Martinez E, Bravo L, Ahumada MC (1996) Effect of silymarin on different acute inflammation models and on leukocyte migration. J Pharm Pharmacol 48:968–970
Dehmlow C, Erhard J, Groot H (1996) Inhibition of Kupffer cell functions as explanation for the protective properties of silibinin. Hepatology 23:749–754
Diaz-Gomes MI, Decastro CR, Dacosta N, Defenos OM, Deferreyra EC, Castro JA (1975) Species differences in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity: the role of CCl4 activation and of lipid peroxidation. J Appl Pharmacol 34:102–114
Drury RVA, Walligton EA (1980) Carltons Histological techniques, 5th edn. Oxford University Press, New York, Pronto, p 206
Everett LL, Birmingham PK, Williams GD, Brenn BR, Shapiro JH (2005) Herbal and homeopathic medication use in pediatric surgical patients. Paediatr Anaesth 15:455–460
Fehér J, Lengyel G, Blázovics A (1998) Oxidative stress in the liver and biliary tract diseases. Scand J Gastroenterol 228(Suppl):38–46
Flora K, Hahn M, Rosen H, Benner K (1998) Milk thistle (Silybum marianum) for the therapy of liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol 93:139–143
Gupta OP, Sing S, Bani S, Sharma N, Malhotra S, Gupta BD, Banerjee SK, Handa SS (2000) Anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic activities of silymarin acting through inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase. Phytomedicine 7:21–24
Huntimer ED, Halaweish FT, Chase CC (2006) Proliferative activity of Echinacea angustifolia root extracts on cancer cells: interference with doxorubicin cytotoxicity. Chem Biodivers 3:695–703
Jacobsson I, Jönsson AK, Gerdén B, Hägg S (2009) Spontaneously reported adverse reactions in association with complementary and alternative medicine substances in Sweden. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 18:1039–1047
Jeong DH, Lee GP, Jeong WI, Do SH, Yang HJ, Yuan DW, Park HY, Kim KJ, Jeong KS (2005) Alterations of mast cells and TGF-β1 on the silymarin treatment for CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 11:1141–1148
Jia JD, Bauer M, Cho JJ, Ruehl M, Milani S, Boigk G, Riecken EO, Schuppan D (2001) Antifibrotic effect of silymarin in rat secondary biliary fibrosis is mediated by downregulation of procollagen alpha1(I) and TIMP-1. J Hepatol 35:392–398
Kligler B (2003) Echinacea. Am Fam Physician 67:77–80
Kocaman O, Hulagu S, Senturk O (2008) Echinacea-induced severe acute hepatitis with features of cholestatic autoimmune hepatitis. Eur J Intern Med 19:148
Krahenbuhl S, Weber FL Jr, Brass EP (1991) Decreased hepatic glycogen content and accelerated response to starvation in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced cirrhosis. Hepatology 14:1189–1195
Lee AN, Werth VP (2004) Activation of autoimmunity following use of immunostimulatory herbal supplements. Arch Dermatol 140:723–727
Lee PY, McCay PB, Hornbrook KR (1982) Evidence for carbon tetrachloride-induced lipid peroxidation in mouse liver. Biochem Pharmacol 31:405–409
Liatsos G, Elefsiniotis I, Todorova R, Moulakakis A (2006) Severe thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) induced or exacerbated by the immunostimulatory herb Echinacea. Am J Hematol 81:224
Lucena MI, Andrade RJ, De la Cruz JP, Rodriguez Mendizabal M, Blanco E, Sanchez de la Cuesta F (2002) Effects of silymarin MZ-80 on oxidative stress in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. Results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 40:2–8
Mac-Manus JPA, Cason JE (1950) Carbohydrate histochemistry studies by acetylation technique. Periodic acid method. J Exp Med 91:651
Mazia D, Drewer PA, Alfert M (1953) The cytochemical staining and measurement of protein with mercaric bromophenol blue. Biol Bull 104:57–67
McCullough AJ, Tavill AS (1991) Disordered energy and protein metabolism in liver disease. Semin Liver Dis 11:265–277
Miller LG (1998) Herbal medicinals: selected clinical considerations focusing on known or potential drug–herb interactions. Arch Intern Med 158:2200–2211
Morales MR (2004) Echinacea: uses as a medicine. In: Goodman R (ed) Encyclopedia of plant and crop science. Marcel Dekker, New York, United States, pp 395–400
Mourelle P, Muriel P, Favari L, Franco T (1989) Prevention of CCl4 induced liver cirrhosis by silymarin. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 3:183–191
Mrozikiewicz PM, Bogacz A, Karasiewicz M, Mikolajczak PL, Ozarowski M, Seremak-Mrozikiewicz A, Czerny B, Bobkiewicz-Kozlowska T, Grzeskowiak E (2010) The effect of standardized Echinacea purpurea extract on rat cytochrome P450 expression level. Phytomedicine 17:830–833
Mullins RJ, Heddle R (2002) Adverse reactions associated with echinacea: the Australian experience. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 88:42–51
Muriel P, Mourelle M (1990) Prevention by silymarin of membrane alterations in acute CCl4 liver damage. J Appl Toxicol 10:275–279
Muriel P, Garciapina T, Perez-Alvarez V, Mourelle M (1992) Silymarin protects against paracetamol induced lipid peroxidation and liver damage. J Appl Toxicol 12:439–442
Muriel P, Alba N, Perez-Alvarez VM, Shibayama M, Tsutsumi VK (2001) Kupffer cells inhibition prevents hepatic lipid peroxidation and damage induced by carbon tetrachloride. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 130:219–226
Neff GW, O'Brien C, Montalbano M, DeManno A, Kahn S, Safdar K, Nishida S, Tzakis A (2004) Consumption of dietary supplements in a liver transplant population. Liver Transpl 10:881–885
Nordlie RC, Foste JD, Lange AJ (1999) Regulation of glucose production by the liver. Annu Rev Nutr 19:379–406
Paget GE, Barnes JM (1964) Toxicity testing. In: Laurence DR, Bacharach AL (eds) Evaluation of drug activities pharmacometrics. Academic, London, pp 1–135
Pár A, Roth E, Rumi G, Kovács Z, Nemes J, Mózsik G (2000) Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense in alcoholic liver disease and chronic hepatitis C. Orv Hetil 141:1655–1659
Postic C, Dentin R, Girard J (2004) Role of the liver in the control of carbohydrate and lipid homeostasis. Diabetes Metab 30:398–408
Pratt DS, Kaplan MM (1999) Laboratory tests. In: Schiff ER, Sorrell MF, Maddrey WC (eds) Schiff’s diseases of the liver, vol. 1, 8th edn. Lippincott–Raven, Philadelphia, pp 205–244
Siddiqui U, Weinshel EH, Bini EJ (2004) Prevalence and predictors of herbal medication use in veterans with chronic hepatitis C. J Clin Gastroenterol 38:605–610
Smalinskiene A, Lesauskaite V, Ryselis S, Abdrakhmanov O, Kregzdyte R, Sadauskiene I, Ivanov L, Savickiene N, Zitkevicius V, Savickas A (2007) Assessment of the effect of Echinacea purpurea (L.) Moench on apoptotic and mitotic activity of liver cells during intoxication by cadmium. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1095:574–584
Soon SL, Crawford RI (2001) Recurrent erythema nodosum associated with Echinacea herbal therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol 44:298–299
Teocharis SE, Margeli AP, Skaltsas SD, Spiliopoulou CA, Koutelinis AS (2001) Induction of metallothionein in the liver of carbon tetrachloride intoxicated rats: an immunohistochemical study. Toxicology 161:129–138
Toselli F, Matthias A, Gillam EM (2009) Echinacea metabolism and drug interactions: the case for standardization of a complementary medicine. Life Sci 85:97–106
Wagner VH, Diesel P, Seitz M (1974) Chemistry and analysis of silymarin from Silybum marianum Gaertn. Arzneimittelforschung 24:466–471
Wellington K, Jarvis B (2001) Silymarin: a review of its clinical properties in the management of hepatic disorders. BioDrugs 15:465–489
Werneke U, Earl J, Seydel C, Horn O, Crichton P, Fannon D (2004) Potential health risks of complementary alternative medicines in cancer patients. Br J Cancer 90:408–413
Whiting PW, Clouston A, Kerlin P (2002) Black cohosh and other herbal remedies associated with acute hepatitis. MJA 177:432–435
Wilson KM, Klein JD, Sesselberg TS, Yussman SM, Markow DB, Green AE, West JC, Gray NJ (2006) Use of complementary medicine and dietary supplements among U.S. adolescents. J Adolesc Health 38:385–394
Wu CG, Chamuleau RA, Bosch KS, Frederiks WM (1993) Protective effect of silymarin on rat liver injury induced by ischemia. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol 64:259–263
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Salam, O.M.E., Sleem, A.A., El-Mosallamy, A.E.M.K. et al. Effect of Echinacea alone or in combination with silymarin in the carbon-tetrachloride model of hepatotoxicity. Comp Clin Pathol 21, 1483–1492 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-011-1317-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-011-1317-1