Abstract
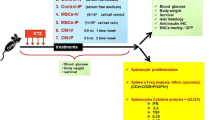
The purpose of this study is to determine if intraventricular injection of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells (hADSC) are effective in treating streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes mellitus (DM) in nude rats. Twenty-two adult, male nude rats (strain Crl:NIH-Fox1RNU) were used to induce diabetes using streptozotocin. A single, 150 mg/kg STZ was injected intraperitoneally. Severity of the induced diabetic state was assessed by daily monitoring of body weight, clinical signs, and blood glucose levels. C-peptide was assessed before ADSC injection (T0) and at 3, 5, and 21 days after ADSC injection. Eight rats (40%) developed DM within 24 h after STZ injection. Of the eight rats that developed DM, five were given 2 million freshly prepared ADSC intraventricularly under echocardiography guidance 10 days after STZ injection and three were only given sterile saline for comparison. Surviving rats were humanly sacrificed 21 days after ADSC injection. The average weight of diabetic rats decreased significantly after STZ injection. ADSC injection had no effect on the body weight of rats. Non-fasting serum glucose levels increased significantly in both groups. In diabetic rats, C-peptide decreased significantly before ADSC injection and seemed to return to normal 21 days after ADSC administration. Results of this preliminary study might suggest a beneficial effect of using hADSC for the treatment of STZ-induced diabetes in adult nude rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu Abeeleh M, Bani Ismail Z, Alzaben KR, Abu-Halaweh SA, Al-Essa MK, Abuabeeleh J, Alsmady MM (2009) Induction of diabetes mellitus in rats using intraperitoneal streptozotocin: a comparison between 2 strains of rats. Eur J Sci Res 32:398–402
Akbarzadeh A, Norouzian D, Mehrabi MR, Jamshidi S, Farhangi A, Allah A, Mofidian S, Lame Rad B (2007) Induction of diabetes by streptozotocin in rats. IJCB 22:60–64
Brosky G, Logothetopoulos J (1969) Streptozotocin diabetes in the mouse and guinea pig. Diabetes 8:606–611
Choi JB, Uchino H, Azuma K, Iwashita N, Tanaka Y, Mochizuki H, Migita M, Shimada T, Kawamori R, Watada H (2003) Little evidence of transdifferentiation of bone marrow-derived cells into pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 46:1366–1374
Elias D, Prigozin H, Polak N, Rapoport M, Lohse AW, Cohen IR (1994) Autoimmune diabetes induced by the b-Cell toxin STZ. Diabetes 43:992–998
Hayashi K, Kojima R, Ito M (2006) Strain differences in the diabetogenic activity of streptozotocin in mice. Biol Pharm Bull 29:1110–1119
Hess D, Li L, Martin M, Sakano S, Hill D, Strutt B, Thyssen S, Gray DA, Bhatia M (2003) Bone marrow-derived stem cells initiate pancreatic regeneration. Nat Biotechnol 21:763–770
Ianus A, Holz GG, Theise ND, Hussain MA (2003) In vivo derivation of glucose-competent pancreatic endocrine cells from bone marrow without evidence of cell fusion. J Clin Invest 111:843–850
Lechner A, Yang YG, Blacken RA, Wang L, Nolan AL, Habener JF (2004) No evidence for significant transdifferentiation of bone marrow into pancreatic beta-cells in vivo. Diabetes 53:616–623
Lee RH, Seo MJ, Reger RL (46) Multipotent stromal cells from human marrow home to and promote repair of pancreatic islets and renal glomeruli in diabetic NOD/scid mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:17438–17443
Rastellini C, Shapiro R, Corry R, Fung JJ, Starzl TE, Rao AS (1997) An attempt to reverse diabetes by delayed islet cell transplantation in humans. Transplantation 29:2238–2239
Szkudelski T (2001) The mechanism of alloxan and streptozotocin action in B cells of the rat pancreas. Physiol Res 50:537–546
Takeshita F, Kodama M, Yamamoto H, Ikarashi Y, Ueda S, Teratani T, Yamamoto Y, Tamatani T, Kanegasaki S, Ochiya T, Quinn G (2006) Streptozotocin-induced partial beta cell depletion in nude mice without hyperglycaemia induces pancreatic morphogenesis in transplanted embryonic stem cells. Diabetologia 49:2948–2958
Taneera J, Rosengren A, Renstrom E, Nygren JM, Serup P, Rorsman P, Jacobsen SE (2006) Failure of transplanted bone marrow cells to adopt a pancreatic beta-cell fate. Diabetes 55:290–296
Voltarelli JC, Couri CEB, Stracieri ABPL (2007) Autologous nonmyeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 297:1568–1576, Vol. 297 No. 14
Weiss RB (1982) Streptozotocin: a review of its pharmacology, efficacy and toxicity. Canc Treat Rep 66:427–438
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, Huang J, Futrell JW, Katz AJ, Benhaim P, Lorenz HP, Hedrick MH (2001) Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng 7:211–228
Acknowledgments
This project was sponsored by Bioheart, Inc., USA. The authors would like to thank the sponsors, Prof. Abdallah Abbadi, University of Jordan, Jordan University of Science and Technology, The Animal House staff and animal care takers, Mr. Mohammad Al-Zo’ubi, and Miss Shereen Kklouf for their help and hard work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abu-Abeeleh, M., Bani Ismail, Z.A., Alzaben, K.R. et al. A preliminary study of the use of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells for the treatment of streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus in a rat model. Comp Clin Pathol 19, 1–4 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-009-0912-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-009-0912-x