Abstract
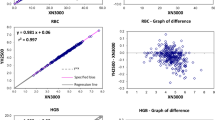
The Sysmex XT-2000iV is a dedicated haematology analyser with full blood count, reticulocyte and five-population differential leucocyte capabilities for several laboratory animal species. The laboratory animal species chosen for this study were rat, dog and mouse. Results from dipotassium ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (K2EDTA) samples from these species were compared with the laboratory’s established haematology analyser, the Bayer (now Siemens) Advia 120™ with multispecies software (Siemens Medical Solutions Diagnostics Europe Limited, Frimley, UK). Imprecision, carry-over between samples, linearity and stability data were also studied. In addition, results obtained for leucocyte differential counts were compared with standard manual 100-cell counts. Throughout this study, the Sysmex XT-2000iV proved to be robust, reliable and dependable. In summary, the Sysmex XT-2000iV has proved capable of accurately and precisely producing haematology results for animal species used within the pharmaceutical industry.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davies D, Fisher GV (1991) The validation and application of the Technicon H*1 for the complete automated evaluation of laboratory animal haematology. Comp Haematol Int 1:91–105
Evans GO, Smith DEC (1992) Preliminary studies with an SLS method for haemoglobin determination in three species. Comp Haematol Int 2:101–102
Grimaldi E, Carandente P, Scopacasa F et al (2005) Evaluation of the monocyte counting by two automated haematology analysers compared to flow cytometry. Clin Lab Haematol 27:91–97
Hur M, Lee YK, Lee KM et al (2004) Pseudobasophilia as an erroneous white cell differential count with a discrepancy between automated cell counters: report of two cases. Clin Lab Haematol 26:287–290
ICSH (1994) International Council for the Standardization in Haematology. Guidelines for the evaluation of blood cell analysers including those used for differential leucocyte and reticulocyte counting and cell marker applications. Clin Lab Haematol 16:157–174
Imazu M (2002) General description of the automated haematology analyser, XT-2000i. Sysmex J Int 12:13–17
Langford K, Luchtman-Jones L, Miller R et al (2003) Performance evaluation of the Sysmex XT-2000i automated haematology analyser. Lab Hematol 9:29–37
Mathers RA, Evans GO, Bleby J et al (2007) Total and differential leucocyte counts in rat and mouse bronchoalveolar lavage fluids using the Sysmex XT-2000iV. Comp Clin Pathol 16:29–39
Tvedten H (1994) Canine automated differential leukocyte count using a hematology analyser system. Vet Clin Pathol 23:90–97
Zelmanovic D, Garcia RA, Leitner T et al (1993) H1*E multi-species haematology. Miles Science Journal 15:7–13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mathers, R.A., Evans, G.O., Bleby, J. et al. Evaluation of the Sysmex XT-2000iV haematology analyser for rat, dog and mouse whole blood samples. Comp Clin Pathol 17, 137–144 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-008-0734-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-008-0734-2