Abstract
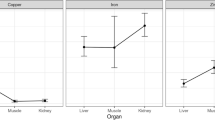
There were 26 male and female (nonpregnant and nonlactating) apparently healthy adult (5 to 10 years) field camels (Camelus dromedarius) studied to provide data regarding the normal values of trace elements in serum and different tissues. Blood samples were collected by jugular venepuncture and serum was separated by centrifugation. Tissue samples (liver, heart, striated muscle, spleen, kidney, and hair) were collected during postmortem examinations. All the samples were digested and analyzed for copper, iron, cobalt, and molybdenum using atomic absorption spectrophotometry. The results showed that the highest concentration of iron was present in the spleen and that the concentrations of this element in the liver and kidney were higher than those in the heart, striated muscle, serum, and hair (p<0.05). The lowest mean iron concentration was observed in the serum (p<0.05). The mean copper concentration was highest in liver in comparison to other tissues (p<0.05). No significant differences in cobalt concentrations were detected among different compartments. The mean molybdenum concentration of striated muscle, heart, kidney, spleen, and liver were significantly higher than those of serum and hair (p<0.05). No difference due to sex was detected in different tissue and serum concentrations of trace elements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla OM, Wasfi IA, Gadir FA (1988) The Arabian race camel normal parameters—I. Haemogram, enzymes and minerals. Comp Biochem Physiol A 90:237–239
Abu Damir H (1998) Mineral deficiencies, toxicities and imbalances in the camel (Camelus dromedarius). Vet Bull 63:1103–1119
Al-Busadah KA (2003) Trace-elements status in camels, cattle and sheep in Saudi Arabia. Pak J Biol Sci 6:1856–1859
Benemariya, H, Robberecht H, Deelstra H (1993) Zinc, copper, and selenium in milk and organs of cow and goat from Burundi, Africa. Sci Total Environ 128:83–98
Deen A, Bhati A, Sahani M (2004) Trace mineral profiles of camel blood and sera. J Camel Pract Res 11:135–136
El-Kasmi K (1989) Constribution a I’etude des proteines seriques et de certains mineraux chez le dromadaire: influence de I’age et du sexe (Investigation of serum proteins and some minerals in dromedaries: influence of age and sex). Mem (Prem. cycle) Inst Agrom Vet 11:46
Faye B, Bengoumi M (1994) Trace-elements status in camels. A review. Biol Trace Elem Res 41:1–11
Faye B, Bengoumi M (1997) Donnee es nouvelles sur le metabolisme des principaux elements-traces chez le dromadaire. Rev Élev Méd Vét Pays Trop 50:47–53
Faye B, Saint-Martin G, Cherrier R et al (1992) The influence of high dietary protein, energy and mineral intake on deficient young camel (Camelus dromedarius)—II. Changes in mineral status. Comp Biochem Physiol Comp Physiol 102:417–424
Haroun EM (1994) Normal concentrations of some blood constituents in young Najdi camels (Camelus dromedarius). Comp Biochem Physiol Comp Physiol 108:619–622
Hill AD, Patterson KY, Veillon C et al (1986) Digestion of biological materials for mineral analyses using a combination of wet and dry ashing. Anal Chem 58:2340–2342
Kaneko JJ (1980) Clinical biochemistry of domestic animals. Academic, London, pp 263–264
Liu ZP, Ma Z, Zhang YJ (1994) Studies on the relationship between sway disease of Bactrian camels and copper status in Gansu province. Vet Res Commun 18:251–260
Mohamed HE (2004) The zinc and copper content of the plasma of Sudanese camels (Camelus dromedarius). Vet Res Commun 28:359–363
Nazifi S, Tadjalli M, Bedeltavana AR (1998) Normal haematopoiesis, cellular components and stainable iron content in the bone marrow of camels (Camelus dromedarius). Vet Res Commun 22:11–20
Osman TEA, Al-Busadah KA (2003) Normal concentrations of twenty serum biochemical parameters of she-camel, cows and ewes in Saudi arabia. Pak J Biol Sci 6:1253–1256
Puls R (1988) Mineral levels in animal health. Sherpa International, British Columbia
Radostits OM, Blood DC, Gay CC (1994) Veterinary medicine, 8th edn. Baillier Tindall, London, p 1389
Radostits OM, Gay CC, Blood DC et al (2000) Veterinary medicine, 8th edn. Harcourt Brace, London, pp 1487–1502
Saeed A, Hussain MM, Khan IA et al (2004) Effect of sex and age on blood biochemical profile in camel. J Camel Pract Res 11:73–77
Underwood EJ (1981) The mineral nutrition of livestock, 2nd edn. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux, London, pp 31–48
Zongping L (2003) Studies on the haematology and trace element status of adult Bactrian camels (Camelus bactrianus) in China. Vet Res Commun 27:397–405
Acknowledgements
We thank the financial support of Shiraz University during the period of this study. We also wish to thank Shiraz Central Veterinary Laboratory for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badiei, K., Mostaghni, K., Pourjafar, M. et al. Serum and tissue trace elements in Iranian camels (Camelus dromedarius). Comp Clin Pathol 15, 58–61 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-006-0610-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-006-0610-x