Abstract
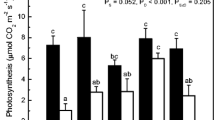
This study examined select, naturally-occurring tree mycorrhizae for differences related to efficiency of organic phosphorus hydrolysis in forest soils. We investigated the activity of several phosphatases and root respiration in field-collected ectomycorrhizae of American beech and gray birch and VAM of red maple. Root materials were collected in the early and late growing season from a common soil type. American beech occurred in a late-successional stand, whereas gray birch and red maple grew in a mid-successional stand. All of the root types examined had phosphatase activities with p-nitrophenyl phosphate, bis-p-nitrophenyl phosphate and phytic acid and thus the potential to mineralize monoester and diester forms of organic phosphorus. Rates of hydrolysis at pH 5.0 were greatest with p-nitrophenyl phosphate. Although enzyme activity varied with season and ectomycorrhizal morphotype, VAM roots of red maple consistently had the lowest enzyme activities on a length and dry weight basis. Comparison of 32P uptake from inositol phosphate by gray birch and red maple roots suggested that phosphomonoesterase activity was linked to P uptake from this source. Differences between species in oxygen consumption rates were less pronounced than those observed for enzymatic activities, suggesting similar short-term energy demands by the root types examined. The quantitative differences observed between plants growing on a common soil potentially relate to differences in host demand or reflect differences in basic morphology and/or physiology of associated mycobionts. Further study is necessary to understand the importance of these enzymes in the functional ecology of mycorrhizal fungi.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 20 December 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antibus, R., Bower, D. & Dighton, J. Root surface phosphatase activities and uptake of 32P-labelled inositol phosphate in field-collected gray birch and red maple roots. Mycorrhiza 7, 39–46 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005720050161
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005720050161