Abstract
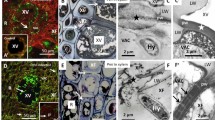
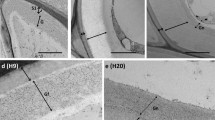
Localization of chitinolytic activities in Fagus sylvatica (beech) mycorrhizas was examined using a range of fluorogenic 4-methylumbelliferyl [4-MU-(GlcNAc)1–4] substrates in order to distinguish between exochitinase, endochitinase and β-N–acetylglucosaminidase activities. The validity of the technique was confirmed using onion epidermis cells. In the beech mycorrhiza, endochitinase activity was not detectable above background fluorescence. Exochitinase activity was detected in the fungal sheath and the Hartig net. β-N–Acetylglucosaminidase activity was also mainly associated with the fungal sheath and Hartig net. Individual fungal hyphae extending from these structures also showed substantial β-N–acetylglucosaminidase activity. The cortical cell walls of the host in the Hartig net region also fluoresced brightly. The localization of β-N–acetylglucosaminidase activity was confirmed using a chromogenic histochemical reagent, 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-N–acetyl-β-d-glucosaminide (X-GlcNAc).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 5 December 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hodge, A., Alexander, I., Gooday, G. et al. Localization of chitinolytic activities in Fagus sylvatica mycorrhizas. Mycorrhiza 6, 181–187 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005720050124
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005720050124