Abstract
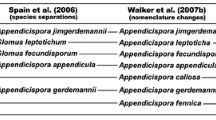
Morphological and molecular characters were analysed to investigate diversity within isolates of the Glomus claroideum/Glomus etunicatum species group in the genus Glomus. The inter- and intra-isolate sequence diversity of the large subunit (LSU) rRNA gene D2 region of eight isolates of G. claroideum and G. etunicatum was studied using PCR-single strand conformational polymorphism (SSCP)-sequencing. In addition, two isolates recently obtained from Southern China were included in the analysis to allow for a wider geographic screening. Single spore DNA isolation confirmed the magnitude of gene diversity found in multispore DNA extractions. An apparent overlap of spore morphological characters was found between G. claroideum and G. etunicatum in some isolates. Analysis of the sequence frequencies in all G. etunicatum and G. claroideum isolates (ten) showed that four LSU D2 sequences, representing 32.1% of the clones analysed for multispore extraction (564) were found to be common to both species, and those sequences were the most abundant in four of the ten isolates analysed. The frequency of these sequences ranged between 23.2% and 87.5% of the clones analysed in each isolate. The implications for the use of phenotypic characters to define species in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi are discussed. The current position of G. claroideum/G.etunicatum in the taxonomy of the Glomeromycota is also discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoniolli ZI, Schachtman DP, Ophel-Keller K, Smith SE (2000) Variation in rDNA ITS sequences in Glomus mosseae and Gigaspora margarita spores from a permanent pasture. Mycol Res 104:708–715
Bentivenga SP, Morton JB (1994) Stability and heritability of fatty-acid methyl-ester profiles of glomalean endomycorrhizal fungi. Mycol Res 98:1419–1426
Bentivenga SP, Bever JD, Morton JB (1997) Genetic variation of morphological characters within a single isolate of the endomycorrhizal fungus Glomus clarum. Am J Bot 84:1211–1216
Clapp JP, Young JPW, Fitter AH (1999) Ribosomal small subunit sequence variation within spores of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus, Scutellospora sp. Mol Ecol 9:915–921
Clapp JP, Rodriguez A, Dodd JC (2001) Inter- and intra-isolate rRNA large subunit variation in Glomus coronatum spores. New Phytol 149:539–554
Clapp JP, Rodriguez A, Dodd JC (2002) Glomales rRNA gene diversity—all that glistens is not necessarily glomalean? Mycorrhiza 12:269–270
Declerck S, Strullu DG, Plenchette C (1996) In vitro mass-production of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus, Glomus versiforme, associated with Ri T-DNA transformed carrot roots. Mycol Res 100:1237–1242
Dodd JC, Rosendahl S, Giovannetti M, Broome A, Lanfranco L, Walker C (1996) Inter- and intraspecific variation within the morphologically-similar arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi Glomus mosseae and Glomus coronatum. New Phytol 133:113–122
Feldmann F (1998) The strain inherent variability of arbuscular mycorrhizal effectiveness: II. Effectiveness of single spores. Symbiosis 25:131–143
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 133:783–793
Helgason T, Daniell TJ, Husband R, Fitter AH, Young JPW (1998) Ploughing up the wood-wide web? Nature 394:431
Hosny M, Hijri M, Passerieux E, Dulieu H (1999) rDNA units are highly polymorphic in Scutellospora castanea (Glomales, Zygomycetes). Gene 226:61–71
Jansa J, Mozafar A, Banke S, McDonald B, Frossard E (2002) Intra- and intersporal diversity of ITS rDNA sequences in Glomus intraradices assessed by cloning and sequencing, and by SSCP analysis. Mycol Res 106:670–681
Kjoller R, Rosendahl S (2000) Detection of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomales) in roots by nested PCR and SSCP (single stranded conformation polymorphism). Plant Soil 226:189–196
Kjoller R, Rosendahl S (2001) Molecular diversity of glomalean (arbuscular mycorrhizal) fungi determined as distinct Glomus specific DNA sequences from roots of field grown peas. Mycol Res 105:1027–1032
Kramadibrata K, Walker C, Schwarzott D, Schüßler A (2000) A new species of Scutellospora with a coiled germination shield. Ann Bot 86:21–27
Lloyd-MacGilp SA, Chambers SM, Dodd JC, Fitter AH, Walker C, Young JPW (1996) Diversity of the internal transcribed spacers within and among isolates of Glomus mosseae and related arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 133:103–111
Millner PD, Mulbry WW, Reynolds SL (2001) Taxon-specific oligonucleotide primers for the detection of Glomus etunicatum. Mycorrhiza 10:259–265
Morton JB (2000) Evolution of endophytism in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi of glomales. In: Bacon CW, White JF Jr (eds) Microbial endophytes. Dekker, New York, pp 121–140
Morton JB (2003) Glomeromycota http://invam.caf.wvu.edu/fungi/taxonomy/glomales.htm
Morton JB, Redecker D (2001) Two new families of Glomales, Archaeosporaceae and Paraglomaceae, with two new genera Archaeospora and Paraglomus, based on concordant molecular and morphological characters. Mycologia 93:181–195
Page RDM (1996) TREEVIEW: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Pringle A, Moncalvo JM, Vilgalys R (2000) High levels of variation in ribosomal DNA sequences within and among spores of a natural population of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Acaulospora colossica. Mycologia 92:259–268
Redecker D, Hijri M, Dulieu H, Sanders IR (1999) Phylogenetic analysis of a dataset of fungal 5.8S rDNA sequences shows that highly divergent copies of internal transcribed spacers reported from Scutellospora castanea are of ascomycete origin. Fungal Genet Biol 28:238–244
Redecker D, Kodner R, Graham LE (2000a) Glomalean fungi from the Ordovician. Science 289:1920–1921
Redecker D, Morton JB, Bruns TD (2000b) Ancestral lineages of arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi (Glomales). Mol Phylogenet Evol 14:276–284
Robinson L, Rodriguez A, Clapp JP, Knight E, Wong YH, Jeffries P, Dodd JC (2002) Diversity of the D2 domain of the LSU rRNA gene of several Chinese Glomus species. In: Avio L, Sbrana C, Strani P (eds) AM Research in Europe—the dawning of a new millennium. Cost 838 meeting. Area della Ricerca Pisa, 10–12th October 2002, session 1, S.T.A.R. Servizio Tecnografico Area della Ricerca del CNR, Pisa, pp 28
Rodriguez A, Dougall T, Dodd JC, Clapp JP (2001) The large sub-unit ribosomal RNA genes of Entrophospora infrequens comprise sequences related to two different glomalean families. New Phytol 152:159–167
Rosendahl S, Dodd JC, Walker C (1994) Taxonomy and phylogeny of Glomales. In: Gianinazzi S, Schüepp H (eds) Impact of arbuscular mycorrhizas on sustainable agriculture and natural ecosystems. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 1–12
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sawaki H, Sugawara K, Saito M (1998) Phylogenetic position of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus, Acaulospora gerdemannii, and its synanamorph Glomus leptotichum, based upon 18S rRNA gene sequence. Mycoscience 39:477–480
Schüßler A (1999) Glomales SSU rRNA gene diversity. New Phytol 144:205–207
Schüßler A, Gehrig H, Schwarzott D, Walker C (2001a) Analysis of partial Glomales SSU rRNA gene sequences: implications for primer design and phylogeny. Mycol Res 105:5–15
Schüßler A, Schwarzott D, Walker C (2001b) A new fungal phylum, the Glomeromycota: phylogeny and evolution. Mycol Res 105:1413–1421
Schüßler A, Schwarzott D, Walker C (2003) Glomeromycota rRNA genes—the diversity of myths? Mycorrhiza 13:233–236
Schwarzott D, Schüßler A (2001) A simple and reliable method for SSU rRNA gene DNA extraction, amplification, and cloning from single AM fungal spores. Mycorrhiza 10:203–207
Schwarzott D, Walker C, Schüßler A (2001) Glomus, the largest genus of the arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi (Glomales), is non-monophyletic. Mol Phylogenet Evol 21:190–197
Simon L (1996) Phylogeny of the Glomales: deciphering the past to understand the present. New Phytol 133:95–101
Simon L, Bousquet J, Lévesque RC, Lalonde M (1993a) Origin and diversification of endomycorrhizal fungi and coincidence with vascular land plants. Nature 363:67–69
Simon L, Lévesque RC, Lalonde M (1993b) Identification of endomycorrhizal fungi colonizing roots using fluorescent SSCP-PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 5:4211–4215
Stürmer SL, Morton JB (1997) Developmental patterns defining morphological characters in spores of four species in Glomus. Mycologia 89:72–81
Swofford DL (1999) PAUP*. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods). Sinauer, Sunderland, Mass
Walker C (1992) Systematics and taxonomy of the arbuscular endomycorrhizal fungi (Glomales)—a possible way forward. Agronomie 12:887–897
Walker C, Trappe JM (1993) Names and epithets in the Glomales and Endogonales. Mycol Res 97:339–344
Walker C, Vestberg M (1998) Synonymy amongst the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: Glomus claroideum, G. maculosum, G. multisubstenum and G. fistulosum. Ann Bot 82:601–624
Wyss P, Bonfante P (1993) Amplification of genomic DNA of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi by PCR using short arbitrary primers. Mycol Res 97:1351–1357
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by funds contributed from the following sources: The International Institute of Biotechnology (IIB), the BEGNET project EU Framework IV, contract number BIO4-CT97-2225 and NATO grant ENVIR.LG.950923. Alia Rodriguez wishes to express her thanks to COLFUTURO, Carrera 15 No. 37–15, Santafe de Bogota (Colombia), Research School of Biosciences, University of Kent and IIB for the financial support of her Ph.D. studies. The authors would like to thank Drs. David Sylvia, Miroslav Vosatka and Mauritz Vestberg for providing some of the isolates included in this study. Professors Xiaolin Li (China Agricultural University, Beijing), Bin Zhao (Hauzhong Agricultural University, Wuhan) and Yuen Ha Wong (Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, P.R. China) are also acknowledged for the provision of original Chinese soil samples or cultures. The Mychintec (ICA4-CT-2000-30014) project (partner IIB) from the EU INCO-DEV FP5 programme supported Louisa Robinson and the sequencing of Chinese isolates of AMF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodriguez, A., Clapp, J.P., Robinson, L. et al. Studies on the diversity of the distinct phylogenetic lineage encompassing Glomus claroideum and Glomus etunicatum . Mycorrhiza 15, 33–46 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-003-0291-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-003-0291-0