Abstract
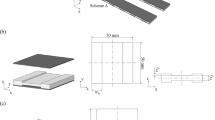
In order to improve the working stroke of micro/nano-transmission platform (MNTP) , a unidirectional multi-driven compliant mechanism based on the right-angle flexure hinges is designed. Applying the compliant mechanisms, elastic mechanics, and combining the working principle of MNTP, the mechanics models of bridge-type amplification mechanism (BTAM) and MNTP are built. Stiffness matrices, stress and strain, natural frequency, and sensitivity are derived. Also, the posture state equations of MNTP are established to predict the mechanism behavior. Then a few simulation calculations through Matlab software are carried out. In terms of Ansys 14.5 software, the simulation motions of the MNTP are acquired. The MNTP is machined through wire cut electrical discharge machining, and the measurement experiments of MNTP are established to verify the computational predictions, and the ability of the proposed mechanism with large working stroke is demonstrated in the experimental study. Finally, the theoretical values, finite element values and experimental values are comparatively analyzed, especially the output results of X/Y-direction in single-driven and double-driven mode. As a result, the reasonability of theoretical model of MNTP is verified. And a reference basis in the study of large stroke micro platform is provided.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark L, Shirinzadeh B, Bhagat U (2015) Development and control of a two DOF linear–angular precision transmission stage. Mechatronics 32:34–43
Codourey A, Rodriguez M, Pappas I (1997) A task-oriented teleoperation system for assembly in the microworld. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Advanced Robotics, Monterey pp 235–240
Howell LL (2013) Compliant Mechanisms 21st Century Kinematics. Springer, London, pp 457–463
Jia X (2011) Inverse Dynamics of 3-RRPR Compliant Precision Positioning Stage Based on the Principle of Virtue Work. J Mech Eng 47(1):68–74
Kim JH, Kim SH, Kwak YK (2004) Development and optimization of 3-D bridge-type hinge mechanisms. Sens Actuators A 116(3):530–538
Kim D, Kang D, Shim J et al (2005) Optimal design of a flexure hinge-based XYZ, atomic force microscopy scanner for minimizing Abbe errors. Rev Sci Instrum 76(7):073706–073707
Li Y, Xu Q (2008) Design of a new decoupled XY flexure parallel kinematic manipulator with actuator isolation//Ieee/rsj International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. IEEE, 470–475
Lin C, Cai L, Shao J et al (2015) Posture error analysis and precision compensation of 6-DOF micro transmission platform. Nongye Jixie Xuebao/Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach 46(5):357–364
Ma HW, Yao SM, Wang LQ et al (2006) Analysis of the displacement amplification ratio of bridge-type flexure hinge. Sens Actuators A 132(2):730–736
Russell RA (1993) Development of a robotic manipulator for micro-assembly operations. Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Yokohama pp 471–474
Shan MC, Wang WM, Shu-Yuan MA et al (2012) Analysis and design of large stroke series flexure mechanism. Nami Jishu Yu Jingmi Gongcheng/nanotechnol Precis Eng 10(3):268–272
Sun X, Chen W, Zhou R et al (2013) A decoupled 2-DOF flexure-based microtransmission stage with large stroke. Robotica 32(5):677–694
Wang F, Liang C, Tian Y et al (2015) Design of a piezoelectric-actuated microgripper with a three-stage flexure-based amplification. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 20(5):2205–2213
Xu HG, Okamoto K, Zhang DY et al (2006) Monolithic PZT microstage with multidegrees of freedom for high-precision transmission. Proc Spie 6032:603205–603206
Yun Y (2008) Survey on parallel manipulators with micro/nano manipulation technology and applications. Chin J Mech Eng 44(12):12–23
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, C., Wu, Z., Ren, Y. et al. Characteristic analysis of unidirectional multi-driven and large stroke micro/nano-transmission platform. Microsyst Technol 23, 3389–3400 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3130-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3130-x