Abstract
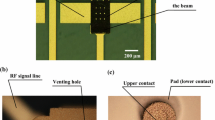
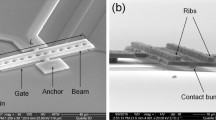
This document presents a push-pull double-contact MEMS (Micro ElectroMechanical System) relay. The MEMS relay is electrostatic driven and laterally actuating. Two push-pull structures form two parallel contacts for the proposed MEMS relay, which can make the contact resistance of the MEMS relay be smaller. The push and pull actions of the push-pull actuators can be accomplished simultaneously using only one action signal. In addition, high inductance DC bias line and substrate removal are used for additional electrical and/or thermal isolation. The fabrication of the proposed switch is based on the standard MetalMUMPs process. The measured pull-in voltage is 116 V and the switch-ON delay is 44 μs. Contact resistance of the MEMS relay is less than 1 Ω when the stress voltage exceeds 120 V.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida L, Ramadoss R, Jackson R, Ishikawa K, Yu Q (2007) Laterally actuated multicontact MEMS relay fabricated using MetalMUMPS process experimental characterization and multiscale contact modelling. J Micro/Nanolith MEMS MOEMS 6(2):02300901–02300910
Cao A, Yuen P, Lin L (2007) Microrelays With Bidirectional Electrothermal Electromagnetic Actuators and Liquid Metal Wetted Contacts. J Microelectromech S 16(3):700–708
Hah D, Yoon E, Hong S (2000) A low-voltage actuated micromachined microwave switch using torsion springs and leverage. IEEE T Microw Theory 48(12):2540–2545
He SY, Chang JS, Li LH, Ho H (2009) Characterization of Young’s modulus and residual stress gradient of MetalMUMPs electroplated nickel film. Sensor Actuat A-Phys 154:149–156
Ma B, You Z, Ruan Y, Chang S, Zhang G (2015) Electrostatically actuated MEMS relay arrays for high-power applications. Microsyst Technol. doi:10.1007/s00542-015-2660-y
MUMPs® process (2014) MetalMUMPs Design Handbook Rev. 4.0. http://www.memscap.com/products/mumps/metalmumps/reference-material, accessed June 2014
Peterson KE (1976) Micromechanical membrane switches on silicon. IEEE T Electron Dev 23(4):376–386
Rangra K, Margesin B, Lorenzelli L, Giacomozzi F, Collini C, Zen M, Soncini G, Tin L, Gaddi R (2005) Symmetric toggle switch- a new type of rf MEMS switch for telecommunication applications: design and fabrication. Sensor Actuat A Phys 123–124:505–514
Rebeiz GM (2003) RF MEMS Theory Design and Technology. Wiley, Hoboken
Song YH, Han CH, Kim MW, Lee JO, Yoon JB (2012) An Electrostatically Actuated Stacked-Electrode MEMS Relay With a Levering and Torsional Spring for Power Applications. J Microelectromech S 21(5):1209–1217
Wang LF, Han L, Tang JY, Huang Q A (2012) Fabrication of a Push-Pull Type Electrostatic Comb-Drive RF MEMS Switch. IEEE 11th Int Conf on Sensors, Taipei, pp. 331–334
Wang LF, Han L, Tang JY, Huang QA (2013) Lateral contact Three-State RF MEMS switch for ground wireless communication by actuating rhombic structures. J Microelectromech S 22(1):10–12
Wu YB, Ding GF, Zhang CC, Wang J, Mao SP, Wang H (2010) Magnetostatic bistable MEMS switch with electrothermal actuators. Electron Lett 46(15):1074–1075
Young WC, Budynas RG (2002) Roark’s Formulas for Stress and Strain, 7th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Zavracky PM, McGruer NE, Morrison RH, Potter D (1999) Microswitches and microrelays with a view toward microwave applications. Int J RF Microw C E 9(4):338–347
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61401084) and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2015AA042602).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Jin, Y. A push-pull double-contact MEMS relay fabricated by MetalMUMPs process. Microsyst Technol 23, 2257–2262 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3001-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3001-5