Abstract
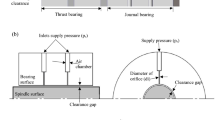
This research proposes the Monte Carlo simulation for manufacturing tolerances in major design variables of fluid dynamic bearings (FDBs) to identify their sensitive design variables on the performance of FDBs and the dynamic performance of a disk-spindle system. Friction torque and critical mass were chosen as the performance indexes of FDBs and the disk-spindle system. The proposed method was applied to the FDBs of a 2.5″ HDD, and the Monte Carlo simulation was performed for 16 major design variables of the FDBs. The clearance of the journal bearing was the most sensitive design variable of both the friction torque and critical mass. Additionally the groove to groove and ridge ratio and groove depth of the grooved journal bearing, which were manufactured by electrochemical machining, were also sensitive to determining the friction torque and critical mass of the FDBs, respectively. This research can be utilized to manage the manufacturing tolerance of FDBs to maintain consistent performance of FDBs and a disk-spindle system in an HDD.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hsia YT, Chang C (1995) Monte-Carlo statistical analysis of non-linear flying attitude. IEEE Trans Magn 31:2988–2990
Jang GH, Kim YJ (1999) Calculation of dynamic coefficients in a hydrodynamic bearing considering five degrees of freedom for a general rotor-bearing system. ASME J Tribol 121:499–505
Jang GH, Lee SH (2006) Determination of the dynamic coefficients of the coupled journal and thrust bearings by the perturbation method. Tribol Lett 22:239–246
Jang GH, Lee SH, Kim HW (2006) Finite element analysis of the coupled journal and thrust bearing in a computer hard disk drive. J Tribol 128:335–340
Kim MG, Jang GH, Kim HW (2010) Stability analysis of a disk-spindle system supported by coupled journal and thrust bearings considering five degrees of freedom. Tribol Int 43:1479–1490
Kim MG, Jang GH, Lee JH (2011) Robust design of a HDD spindle system supported by fluid dynamic bearings utilizing the stability analysis. Microsyst Technol 17:761–770
Koak KY, Jang GH, Kim HW (2009a) Whirling, tilting and axial motions of a HDD spindle system due to the manufacturing errors of FDBs. Microsyst Technol 15:1701–1709
Koak KY, Kim HW, Jung KM, Jang GH (2009b) Dynamic characteristics of a HDD spindle system due to imperfect shaft roundness. IEEE Trans Magn 45:5148–5151
Lee JH, Jang GH, Jung KM (2013) Optimal design of fluid dynamic bearings to develop a robust disk-spindle system in a hard disk drive utilizing modal analysis. Microsyst Technol 19:1495–1504
Lee JH, Lee MH, Jang GH (2014) Effect of an hourglass-shaped sleeve on the performance of the fluid dynamic bearings of a HDD spindle motor. Microsyst Technol 20:1435–1445
Meyer MJ (2003) Monte Carlo Simulation with Java and C++. http://www.javaquant.net. Accessed 20 Feb 2014
Ono K, Murashita S, Yamaura H (2005) Stability analysis of a disk-spindle supported by a plain journal bearing and pivot bearing. Microsyst Technol 11:734–740
Press WH, Teukolsky SA, Vetterling WT, Flannery BP (2007) Numerical recipes, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Acknowledgments
This research was performed at the Samsung-Hanyang Research Center for Precision Motors, sponsored by Samsung Electro-Mechanics Co. Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Lee, M., Kim, K. et al. Monte Carlo simulation of the manufacturing tolerance in FDBs to identify the sensitive design variables affecting the performance of a disk-spindle system. Microsyst Technol 21, 2649–2656 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2518-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2518-3