Abstract
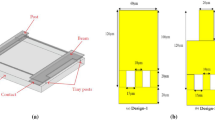
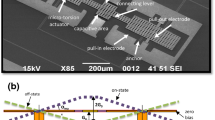
This paper deals with the RF (Radio Frequency)-MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical-System) switches are integrated in CPW topology. Phase shifter is integrated on high resistivity silicon substrate and loading elements are 360 switch design using the coventorware software and its superiority over the existing technologies like PIN Diodes and Field-Effect-Transistors regarding size, power, Isolation The measured down state insertion loss of −0.1 dB up to 40 GHz and switch resistance is 1 Ω. The measured reflection coefficient is dominated bt t-line switch is −20 dB at 30 GHz. This switch used in X-band and K-band phase shifter, switched capacitor bank and tunable filter. The 1-kg class satellite plans to use the MEMS TxRx switch as a functional component on its RF communication board. Application of switch based Phase shifters for satellite based radars (20 billion cycles), missile systems (0.1–1 billion cycles), long-range radars (20–200 billion cycles). By cutting the mass of components onboard the space vehicle, the launch costs and hopefully the overall budget for production can be reduced.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown ER (1998) RF MEMS switches for reconfigurable integrated circuits. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory and Techniques 46(11): 1868−1880
Charalampidis N, Kampitaki D (2009) “On the design of an ohmic RF MEMS switch for reconfigurable microstrip antenna applications”
Grant PD, Mansour RR (2002) A comparison between RF MEMS switches and semiconductor switches. Can J Elect Comput Eng 27(1):33–39
Hung ES, Senturia SD (1999) Extending the travel range of analog-tuned electrostatic actuators. J Microelectromech Syst 8: 847−505
Senturia SD, Osterberg PM (1997) M-TEST: a test chip for MEMS material property measurement using electrostatically actuated test structures. J Microelectromech Syst 6(2):107–118
Sharma AK, Balaji CG, Singh SG (2013) Ohmic RF MEMS switch with low loss and low force on quartz for reconfigurable circuits 3(1): 45–54
Acknowledgments
The devices were simulated in the NPMASS Laboratory at the Physics department of Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University, Aurangabad as NMDC National mems design center. The authors would like to thank SSPL, DRDO, at Nanotechnology for scheduling film depositions, for calibrating RF Switches used in device testing and for advice given for vacuum pressure sensing, and I would like to thanks NPMASS for providing Intellisuit software and necessary guidance Prof. A. G. Murugkar for their proper suggestions. Also to our vice chancellor Dr. V. M. Pandharipande sir for allowing me to use MEMS laboratory for my work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolhare, N. MEMS switches for 0.1–40 GHz for Pico-satellite application. Microsyst Technol 21, 707–717 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2409-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2409-7