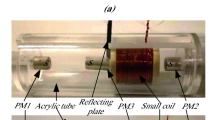
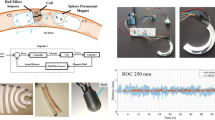
Abstract
Capsule endoscopes used for diagnosis in the gastro intestinal tract have gained much popularity in recent years due to the minimized patient discomfort and available operating range. New therapeutic applications of these devices are surgical interventions or medication at specific locations. So far capsule endoscopic devices are passively propelled prohibiting these new approaches. To overcome this issue we presented a Magnet Drive Unit (MDU) for external actuation for robotic capsule devices in our previous work. While MDU is used for manipulation of a capsule-robot, there has not been any information of the current location of the robot within the patient. Therefore, we propose a novel ultrasound based tracking system for the capsule-robot and endoscopic devices in this manuscript. The tracking system consists of a Cartesian robot actuating a transcutaneous sonographic probe in two degrees of freedom. While the capsule-robot is propelled by MDU, our tracking system generates sonographic images through the back of the patient showing the current location of the capsule. The results of our experiments unveil that our concept is feasible and can be used to navigate a robotic capsule device inside the human body.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We abbreviated the indices, i.e., w = water, s = silicone, t = tissue, a = aluminum.
References
Bley H (1994) Ultraschalldiagnostik (Sonographie), Ultraschalltherapie, Lithotripsie. Kompendium Medizin + Technik. FORUM-MEDIZIN Verlagsgesellschaft mbH. Graefelfing, Germany, pp 305–319
Gong F, Swain P, Mills T (2000) Wireless endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 51:725–729. doi:10.1067/mge.2000.105724
Gregersen H (2003) Biomechanics of the gastrointestinal tract: new perspectives in motility research and diagnostics. Springer, Heidelberg
Gumprecht JDJ, Maier T, Eckl R et al (2010) A new ultrasound imaging concept for laparoscopy in urology. In: Proceedings of 32nd annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC). Buenos Aires, pp 5991–5994
Gumprecht JDJ, Bauer T, Stolzenburg J-U, Lueth TC (2011) A robotics-based flat-panel ultrasound device for continuous intraoperative transcutaneous imaging. In: Proceedings of 33rd annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC). Boston, MA, USA, pp 2152–2155
Gumprecht JDJ, Geiger F, Stolzenburg J-U, Lueth TC (2012a) A flat-panel ultrasound robot to align an abdominal ultrasound probe during laparoscopic partial nephrectomy. In: Proceedings of ASME 2012 international mechanical engineering congress and exposition (IMECE 2012), accepted for publication
Gumprecht JDJ, Lueth TC, Khamesee MB (2012b) Tracking of a magnetic capsule-robot inside the human esophagus based on a novel ultrasound navigation system. In: 2012 ASME-ISPS/JSME-IIP joint international conference on micromechatronics for information and precision equipment (MIPE2012). Santa Clara, CA, USA, pp 20–22
Hopkins HH, Kapany NS (1954) A flexible fibrescope, using static scanning. Nature 173:39–41. doi:10.1038/173039b0
Hosseini S, Khamesee MB (2009) Design and control of a magnetically driven capsule-robot for endoscopy and drug delivery. In: IEEE Toronto international conference on science and technology for humanity, pp 697–702
Hosseini S, Mehrtash M, Khamesee MB (2011) Design, fabrication and control of a magnetic capsule-robot for the human esophagus. Microsyst Technol 17:1145–1152
Huaming L, Jindong T, Mingjun Z (2009) Dynamics modeling and analysis of a swimming microrobot for controlled drug delivery. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 6:220–227. doi:10.1109/TASE.2008.917137
Iddan G, Meron G, Glukhovsky A, Swain P (2000) Wireless capsule endoscopy. Nature 405:417
Khamesee MB, Kato N, Nomura Y, Nakamura T (2002) Design and control of a microrobotic system using magnetic levitation. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 7:1–14
Kim B, Park S, Park J-O (2009) Microrobots for a capsule endoscope. In: 2009 IEEE/ASME international conference on advanced intelligent mechatronics. IEEE, pp 729–734
Leighton JA (2011) The role of endoscopic imaging of the small bowel in clinical practice. Am J Gastroenterol 106:27–36; quiz 37. doi:10.1038/ajg.2010.410
Mackay RS, Jacobson B (1957) Endoradiosonde. Nature 179:1239–1240. doi:10.1038/1791239a0
Mehrtash M, Tsuda N, Khamesee MB (2011) Bilateral macro–micro teleoperation using magnetic levitation. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 16:459–469. doi:10.1109/TMECH.2011.2121090
Moglia A, Menciassi A, Schurr MO, Dario P (2007) Wireless capsule endoscopy: from diagnostic devices to multipurpose robotic systems. Biomed Microdevices 9:235–243. doi:10.1007/s10544-006-9025-3
Noller HG (1960) Die endoradiosonde. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 85:1707
Park H, Park S, Yoon E et al (2007) Paddling based microrobot for capsule endoscopes. In: Proceedings 2007 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 3377–3382
Selfridge AR (1985) Approximate material properties in isotropic materials. IEEE Trans Sonics Ultrasonics 32:381–394
Simi M, Valdastri P, Quaglia C et al (2010) Design, fabrication, and testing of a capsule with hybrid locomotion for gastrointestinal tract exploration. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 15:170–180. doi:10.1109/TMECH.2010.2041244
Swain P (2003) Wireless capsule endoscopy. Gut 52(Suppl 4):iv48–iv50
Welch G, Foxlin E (2002) Motion tracking: no silver bullet, but a respectable arsenal. IEEE Comput Graph Appl 22:24–38. doi:10.1109/MCG.2002.1046626
Zworykin VK (1957) A “Radio Pill”. Nature 179:898. doi:10.1038/179898a0
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Kai Wang for the support during the performance of the experiments. The support of the German research foundation (Grant PAK 404) for the development of the flat-panel ultrasound robot is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gumprecht, J.D.J., Lueth, T.C. & Khamesee, M.B. Navigation of a robotic capsule endoscope with a novel ultrasound tracking system. Microsyst Technol 19, 1415–1423 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-013-1828-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-013-1828-6