Abstract
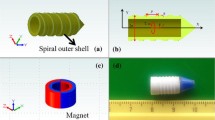
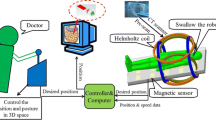
This paper proposes a new type of microrobot that can move along a narrow area such as blood vessels which has great potential for application in microsurgery. Also, the development of a wireless microrobot that can be manipulated inside a pipe by adjusting an external magnetic field has been discussed. The model microrobot utilizes an electromagnetic actuator as the servo actuator to realize movement in biomedical applications. The structure, motion mechanism, and evaluation characteristic of motion of the microrobot have been discussed, and the directional control can be realized via the frequency of the input current. The moving experiments have been carried out in branching points in the horizontal direction, and the moving speed of the robot has been measured in vertical direction by changing frequency. Based on the results, the microrobot has a rapid response, and it can clear out dirt which is adhering to the inner wall of pipe. This microrobot will play an important role in both industrial and medical applications such as microsurgery.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JM, Triantafyllou MS, Kerrebrock PA (1997) Concept design of a flexible-hull unmanned undersea vehicle. In: Proceedings of the international offshore and polar engineering conference, pp 82–88
Barrett D, Yue DKP, Grosenbaugh, Wolfgang MJ (1999) Drag reduction in fish-like locomotion. J Fluid Mech 392:183–212
Bone Q, Marshall NB (1982) Biology of fishes. Blackie and Son Limited, London, 167 p
Domenici P, Blake RW (1997) The kinematics and performance of fish fast-start swimming. J Exp Biol 200(8):1165–1178
Fearing L (1992) Micro structures and micro actuator for implementing submillimetres robots, precision sensors, actuators and systems. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 39–72
Fukuda T, Kawamoto A, Arai F, Matsuura H (1994) Mechanism and swimming experiment of micro mobile robot in water. Proc IEEE Int Conf Robot Autom 1:814–819
Fukuda T, Kawamoto A, Arai F, Matsuura H (1995) Steering mechanism of underwater micro mobile robot. Proc IEEE Int Conf Robot Autom 1:363–368
Guo S, Pan Q (2007) Mechanism and control a novel type of microrobot for biomedical application. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, pp 187–192, Roma, Italy
Gray J (1936) Studies in animal locomotion. VI. The propulsive powers of the dolphin. J Exp Biol 13:192–199
Guo S, Pan Q (2006) Design and control of a novel type of microrobot moving in pipe. In: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE international conference on mechatronics and automation, pp 649–653, China
Guo S, Fukuda T, Kosuge K, Arai F, Oguro K, Negoro M (1995) Micro catheter system with active guide wire. In: Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE international conference on robotic and automation, vol 1, Nagoya, Japan, pp 79–84
Guo S, Fukuda T, Kato N, Oguro K (1998) Development of underwater micro robot using ICPF actuator. In: Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, Belgium, pp 1829–1834
Guo S, Sugimoto K, Hata S, Su J, Oguro K (2000) A new type of underwater fish-like micro robot. In: Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE international conference on intelligent robotics and systems, Kagawa, Japan, pp 867–862
Guo S, Fukuda T, Asaka K (2002) Fish-like underwater micro robot with 3 DOF. In: Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, Washington, DC, pp 738–743
Guo S, Sasaki Y, Fukuda T (2002) A fin type of microrobot in pipe. Proceedings of the 2002 international symposium on micro machine and human science (MHS’ 22), Nagoya, Japan, pp 93–98
Guo S, Fukuda T, Asaka K (2003) A new type of fish-like underwater microrobot. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron 8(1):35–40
Guo S, Sasaki Y, Fukuda T (2003) A new kind of microrobot in pipe using driving fin. In: IEEE/ASME international conference on advanced intelligent mechatronics (AIM 2003), Kobe, Japan, pp 667–702
Guo S, Sakamoto J, Pan Q (2005) A novel type of microrobot for biomedical application. In: IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS2005), Canada, pp 2265–2270
Guo S, Pan Q, Khamesee MB (2006) Development of a novel type of microrobot for biomedical application. ASME/JSME joint conference (MIPE 2006), Santa Clara, CA, USA
Guo S, Pan Q, Zhang W (2006) Characteristics of the microrobot moving in the vertical pipe. Proceedings of the 6th World Congress on Control and Automation, pp 9282–9286, China
Harper KA, Berkemeier MD, Grace S (1998) Modeling the dynamics of spring-driven oscillating-foil propulsion. IEEE J Ocean Eng 23:285–296
Hirose Y, Shiga T, Okada A, Kurauchi T (1992) Gel actuators driven by an electric field. In: Proceedings of the 3rd international symposium on micro machine and human science, pp 21–26
Laurent G, Piat E (2001) Efficiency of swimming microrobots using ionic polymer metal composite actuators. In: Proceedings of 2001 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, pp 3914–3919
Maddock L, Bone Q et al (1994) Mechanics and physiology of animal swimming. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Mojarrad M, Shahinpoor M (1997) Biomimetic robot propulsion using polymeric artificial muscles. In: Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, New Mexico, USA, pp 2152–2157
Oguro K, Asaka K, Takenaka H (1993) Polymer film actuator driven by a low voltage. In: Proceedings of the 4th international symposium on micro machine and human science, Japan, pp 39–40
Osada Y, Okuzaki H, Hori H (1992) A polymer gel of electrically driven moiety. Nature 355:242–244
Pan Q, Guo S (2006) A novel type of microrobot moving in the vertical pipe. In: The 24th annual conference of the robotics society of Japan, 2G22, Japan
Sendoh M, Yamazaki A, Ishiyama K (2000) Wireless controlling of the swimming direction of the spiral-type magnetic micro-machines. Trans IEEE Jpn 120-A:301–306
Sfakiotakis M, Lane DM, Davies JBC (1999) Review of fish swimming modes for aquatic locomotion. IEEE J Ocean Eng 24:237–252
Tadokoro S, Takamori T et al (1998) Development of a distributed actuation device consisting of soft gel actuator elements. In: Proceedings of 1998 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, Leuven, Belgium, pp 2155–2160
Tadokoro S, Yamagami S et al (1999) Multi-DOF device for soft micromanipulation consisting of soft gel actuator elements. In: Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, Detroit, MI, USA, pp 2177–2182
Tadokoro S, Yamagami S, Takamori T (2000) An actuator model of ICPF for robotic applications on the basis of physicochemical hypotheses. In: Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, Seoul, Korea, pp 1340–1345
Triantafyllou MS, Triantafyllou GS (1995) An efficient swimming machine. Sci Am 272(3):64–70
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, S., Pan, Q. & Khamesee, M.B. Development of a novel type of microrobot for biomedical application. Microsyst Technol 14, 307–314 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-007-0430-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-007-0430-1