Abstract
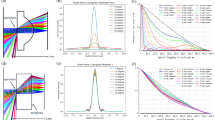
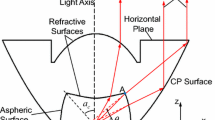
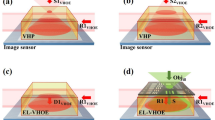
In this paper, we propose a novel optics design for improving the thickness tolerance of a super-hemispherical solid immersion lens (SIL) that is usually used in near-field recording for high data density. To obtain the improved thickness tolerance of a SIL and a high numerical aperture simultaneously, an aspheric replicated lens is added on the SIL. Using an additional aspheric replicated lens, spherical aberration which induces the tight thickness tolerance of the SIL is effectively reduced, therefore it was able to improve the thickness tolerance of the SIL, maintaining high NA equal to that of super-hemispherical SIL. In addition, in this paper, other various tolerances such as decenter and tilt are considered to make sure of the possibility of fabrication.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ichimura I, Hayashi S, Kino GS (1997) High-density optical recording using a solid immersion lens. Appl Opt 36(19):4339–4348
Ishimoto T, Saito K, Shinoda M, Kondo T, Yamamoto M (2003) Gap servo system for a biaxial device using an optical gap signal in a near filed readout system. Jpn J Appl Phys 42:2719–2724
Kim Sm, Kang S (2003) Replication qualities and optical properties of UV-moulded microlens arrays. J Phys D Appl Phys 36:2451–2456
Lee J-I, Aa MAH, Verschuren CA, Zijp F, Mark MB (2005) Development of an air gap servo system for high data transfer rate near field optical recording. Jpn J Appl Phys 44:3423–3426
Shinoda M, Saito K, Ishimoto T, Kondo T, Nakaoki A, Ide N, Furuki M, Takeda M, Akiyama Y, Shimouma T, Yamamoto M (2005) High density near field optical disk recording. Jpn J Appl Phys 44:3537–3541
Smith WJ (2000) Modern optical engineering. McGraw-Hill, New York
Zijp F, Lee J-I, Verschuren CA, Eerenbeemd JMA, Bruls DM (2006) Improved near-field recording system for first-surface media with an NA = 1.9 solid immersion lens. Jpn J Appl Phys 45:1336–1340
Zwiers RJM, Dortant GCM (1985) Aspherical lenses produced by a fast high-precision replication process using UV-curable coatings. Appl Opt 24(24):4483–4488
Acknowledgment
The support of Yonsei Center for Opto-Mechatronics, which is designated as a Specialization Project by Yonsei University, for this research is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, YJ., Choi, H., Kim, WC. et al. Thickness tolerance compensation of SIL first surface near-field recording with replicated lens on SIL. Microsyst Technol 13, 1289–1295 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-006-0353-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-006-0353-2