Abstract
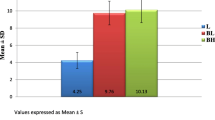
Thirty six patients were received epidural anesthesia with or without buprenorphine (BPN) during upper abdominal surgery. They were divided into three groups of 12 patients as follows; G-I received 20 ml of 1% lidocaine epidurally, G-II received 20 rnl of 1% lidocaine epidurally and 0.6 mg BPN intravenously, G-III received 20 ml of 1% lidocaine with 0.6 mg BPN epidurally. Additional 5 rnl of 1% lidocaine was given to any patient if systolic blood pressure or heart rate increased 10% compared to control value. Trachea was intubated following anesthetic induction with thiopental. The lungs were ventilated with a mixture of N2O/O2 (33%) and pancuronium was used for muscle relaxation. The total required doses of lidocaine in G-II and G-III were decreased 60% compared to control group (G-I) (P< 0.05). The mean period of time until the first administration of pentazocine for postoperative pain was 13 ± 10 hr (mean ± SD) in G-II and 19 ± 24 hr in G-III compared to 5 ± 4 hr in G-I (P< 0.001). The dose of the administration of pentazocine that was required for pain relief during the first 48 postoperative hr in G-III was 54 ± 10 mg (mean ± SD) compared to 150 ± 21 mg in G-I (P< 0.02) and 106 ± 28 mg in G-II (P< 0.05). Recovery from anesthesia in G-III was more rapid than that in G-I (P< 0.05). The\(Pa_{CO_2 } \) values in G-II and G-III increased 15% compared to control group at about 4 hr and 8 hr after administration of BPN, but any clinical treatment was not needed for them. Nonrespiratory side effects, e.g., nausea, vomiting, fatigue and headache, were comparably common in all groups. Mild hematuria associated with acute hypotension occurred in two patients in G-II (17%) immediately after the intravenous injection of 0.6 mg of BPN. The results showed that 0.6 mg of BPN given epidurally demonstrated better anesthetic and more potent postoperative analgesic effects and lesser side effects than 0.6 mg of BPN given intravenously in patients undergoing upper abdominal surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shapiro LA, Hoffman S, Jededeikin R, Kaplan R: Single injection epidural anesthesia with bupivacaine and morphine for prostatectomy. Anesth Analg 60:818–820, 1981
Justin DM, Francis D, Houlton PG, Reynolds F: A controlled trial of extradural fentanyl in labour. Br J Anaesth 54:409–414, 1982
Rucci FS, Cardamone M, Migliori P: Fentanyl and bupivacaine mixture for extradural blockade. Br J Anaesth 57:275–284, 1985
Buprenorphine and anaesthesiology: Internatioinal congress and symposium series, number 65. Edited in chief; HJCJL’Etag, The royal society of medicine, London, 1982
Cahill J, Murphy D, O’Brien D, Mulhall J, Fitzpatrick G: Epidural buprenorphine for pain relief after major abdominal surgery — A controlled comparison with epidural morphine. Anaesthesia 38: 760–764, 1983
Yonemura E, Fukushima K: Epidural buprenorphine analgesia in patients undergoing total hip replacement. Jap J Clin Anesth 12:166–170, 1988
Yonemura E, Shimada M, Fukushima K: Comparison of epidural morphine and epidural buprenorphine for anesthetic effect during upper abdominal surgery. J ap J Clin Pharmacol Ther 19:271–272, 1988
Fukushima K, Yonemura E, Shimada M: Effects of epidural morphine and buprenorphine on EEG during operation. Jpn J Anesth (Masui) 37 (supple) S.173, 1988
Hand CW, Baldwin D, Moore RA: Radioimmunoassay of buprenorphine with iodine label: analysis of buprenorphine and metabolites in human plasma. Ann Clin Biochemist 23:47–53, 1986
Lanz E, Simko G, Theiss D, Glocke MH: Epidural buprenorphine — A double — blind study of postoperative analgesia and side effects. Anesth Analg 63:593–598, 1984
Fukushima K, Yonemura E, Shimada M: Uno studio comparativo tra la morfina e la buprenorfina peridurali durante e dopo intervento chirurgico. La rivista italiana della clinica del dolore 0:7-17, 1989
Watson PJQ, Mcquay HJ, Bullingham RES, Allen MC, Moore RA: Single dose comparison of BPN 0.3 and 0.6 mg LV. given after operation: clinical effects and plasma concentrations. Br J Anaesth 54:37–43, 1982
Papworth DP: High dose buprenorphine for postoperative analgesia. Anaesthesia 38:163, 1983
Forrest AL: Buprenorphine and lorazepam. Anaesthesia 38:598, 1983
Faroqui MH, Cole M, Curran J: Buprenorphine, benzodiazepines and respiratory depression. Anaesthesia 38:1002–1003, 1983
Hambrook JM, Rance MJ: The interaction of buprenorphine and the opiate receptor; lipophilicity as a determining factor in drug receptor kinetics; in Opiates and Endogenous Opioid Peptides (ed. H.W. Kosterlitz), p. 295. Amsterdam: Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press. 1976
Bullingham RES, Mcquay HJ, Moore RA, Bennett MRD: Buprenorphine kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 28:667–672, 1982
Bullingham RES, Mcquay HJ, Dwyer D, Allen MC, Moore RA: Sublingual buprenorphine used postoperatively: clinical observations and preliminary pharmacokinetics analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol 12:117–123, 1981
Glynn CJ, Mather LE, Cousins MJ, Graham JR, Wilson PR: Peridural meperidine in humans: Analgetic response, pharmacokinetics and transmission into CSF. Anesthesiology 55:520–526, 1981
Bromage PR, Camporesi EM, Durant PAC, Nielsen CV: Rostral spread of epidural morphine. Anesthesiology 56:431–436, 1982
Boas RA, Villiger JW: Clinical actions of fentanyl and buprenorphine: The significance of receptor binding. Br J Anaesth 57:192–196, 1985
Colpaert FC, Leysen JE, Michiels M, van den Hoogen RHWM: Epidural and intravenous sufentanil in the rat: analgesia, opiate receptor binding, and drug concentrations in plasma and brain. Anesthesiology 65:41–49, 1986
Yonemura E, Nakamura M, Fukushima K: Comparison of the effect of pain relief following the administration of the intrathecal morphine and buprenorphine. Jap J Soc Clin Anesth 8 (supple): 229, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Yonemura, E., Fukushima, K. Comparison of anesthetic effects of epidural and intravenous administration of buprenorphine during operation. J Anesth 4, 242–248 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/s0054000040242
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s0054000040242