Abstract
Background
Acute kidney injury (AKI) after cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a well-known postoperative complication. Remifentanil, which is a commonly used ultra-short-acting opioid, has antiinflammatory and sympatholytic effects with improvement of microcirculation.
Methods
A retrospective study was conducted to clarify the effect of the use of remifentanil during CPB on the incidence of postoperative AKI. Patients who underwent valve surgery while under cardiopulmonary bypass between January 2012 and December 2014 in our hospital were enrolled in this study. The incidences of postoperative AKI were compared in patients who received remifentanil during CPB (group R) and those who did not (group N). Univariate and multivariate regression analyses were performed to determine risk factors for AKI.
Results
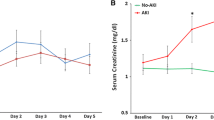
Eighty patients received remifentanil (group R) and 50 patients did not (group N). The incidences of AKI were not significantly different in group R and group N (51% vs. 36%, P = 0.10). In multivariate regression analysis, age [adjusted odds ratio (OR) 1.048, 95% CI 1.008–1.089, P = 0.017], male gender (adjusted OR 3.101, 95% CI 1.303–7.378, P = 0.011), and use of preoperative calcium channel blockers (adjusted OR 3.240, 95% CI 1.302–8.063, P = 0.011) and diuretics (adjusted OR 2.673, 95% CI 1.178–6.066, P = 0.019) were associated with the incidence of AKI. The use of remifentanil was not associated with AKI (adjusted OR 2.321, 95% CI 0.997–5.402, P = 0.051).
Conclusion
The use of remifentanil during CPB did not decrease the incidence of postoperative AKI after cardiac surgery.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosner MH, Okusa MD. Acute kidney injury associated with cardiac surgery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;1:19–32.
Hu J, Chen R, Liu S, Yu X, Zou J, Ding X. Global incidence and outcomes of adult patients with acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2016;30:82–9.
Hansen MK, Gammelager H, Jacobsen CJ, Hjortdal VE, Layton JB, Rasmussen BS, Andreasen JJ, Johnsen SP, Christiansen CF. Acute kidney injury and long-term risk of cardiovascular events after cardiac surgery: a population-based cohort study. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2015;29:617–25.
Xu JR, Zhu JM, Jiang J, Ding XQ, Fang Y, Shen B, Liu ZH, Zou JZ, Liu L, Wang CS, Ronco C, Liu H, Teng J. Risk factors for long-term mortality and progressive chronic kidney disease associated with acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Medicine (Baltim). 2015;94:e2025.
Karkouti K, Wijeysundera DN, Yau TM, Callum JL, Cheng DC, Crowther M, Dupuis JY, Fremes SE, Kent B, Laflamme C, Lamy A, Legare JF, Mazer CD, McCluskey SA, Rubens FD, Sawchuk C, Beattie WS. Acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: focus on modifiable risk factors. Circulation. 2009;119:495–502.
Lassnigg A, Schmidlin D, Mouhieddine M, Bachmann LM, Druml W, Bauer P, Hiesmayr M. Minimal changes of serum creatinine predict prognosis in patients after cardiothoracic surgery: a prospective cohort study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:1597–605.
Kumar AB, Suneja M. Cardiopulmonary bypass-associated acute kidney injury. Anesthesiology. 2011;114:964–70.
Myles PS, Hunt JO, Fletcher H, Watts J, Bain D, Silvers A, Buckland MR. Remifentanil, fentanyl, and cardiac surgery: a double-blinded, randomized, controlled trial of costs and outcomes. Anesth Analg. 2002;95:805–12.
Winterhalter M, Brandl K, Rahe-Meyer N, Osthaus A, Hecker H, Hagl C, Adams HA, Piepenbrock S. Endocrine stress response and inflammatory activation during CABG surgery. A randomized trial comparing remifentanil infusion to intermittent fentanyl. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2008;25:326–35.
Ouattara A, Boccara G, Köckler U, Lecomte P, Leprince P, Léger P, Riou B, Rama A, Coriat P. Remifentanil induces systemic arterial vasodilation in humans with total artificial heart. Anesthesiology. 2004;100:602–7.
De Blasi RA, Palmisani S, Boezi M, Arcioni R, Collini S, Troisi F, Pinto G. Effects of remifentanil-based general anaesthesia with propofol or sevoflurane on muscle microcirculation as assessed by near-infrared spectroscopy. Br J Anaesth. 2008;101:171–7.
Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, Molitoris BA, Ronco C, Warnock DG, Levin A, Acute Kidney Injury Network. Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care. 2007;11:R31.
Demir A, Yılmaz FM, Ceylan C, Doluoglu OG, Uçar P, Züngün C, Guclu CY, Ünal U, Karadeniz U, Günertem E, Lafci G, Çağlı K, Özgök A. A comparison of the effects of ketamine and remifentanil on renal functions in coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Ren Fail. 2015;37:819–26.
Thakar CV, Arrigain S, Worley S, Yared JP, Paganini EP. A clinical score to predict acute renal failure after cardiac surgery. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:162–8.
Carrel T, Englberger L, Mohacsi P, Neidhart P, Schmidli J. Low systemic vascular resistance after cardiopulmonary bypass: incidence, etiology, and clinical importance. J Card Surg. 2000;15:347–53.
Philbin DM, Coggins CH, Wilson N, Sokoloski J. Antidiuretic hormone levels during cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1977;73:145–8.
Edwards RM, Trizna W, Kinter LB. Renal microvascular effects of vasopressin and vasopressin antagonists. Am J Physiol. 1989;256:F274–8.
Watanabe K, Kashiwagi K, Kamiyama T, Yamamoto M, Fukunaga M, Inada E, Kamiyama Y. High-dose remifentanil suppresses stress response associated with pneumoperitoneum during laparoscopic colectomy. J Anesth. 2014;28:334–40.
Ng RR, Chew ST, Liu W, Shen L, Ti LK. Identification of modifiable risk factors for acute kidney injury after coronary artery bypass graft surgery in an Asian population. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;147:1356–61.
Parolari A, Pesce LL, Pacini D, Mazzanti V, Salis S, Sciacovelli C, Rossi F, Alamanni F, Monzino Research Group on Cardiac Surgery Outcomes. Risk factors for perioperative acute kidney injury after adult cardiac surgery: role of perioperative management. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;93:584–91.
Benstein JA, Dworkin LD. Renal vascular effects of calcium channel blockers in hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 1990;3:305S–12S.
Amano J, Suzuki A, Sunamori M, Tofukuji M. Effect of calcium antagonist diltiazem on renal function in open heart surgery. Chest. 1995;107:1260–5.
Young EW, Diab A, Kirsh MM. Intravenous diltiazem and acute renal failure after cardiac operations. Ann Thorac Surg. 1998;65:1316–9.
Hayashi K, Wakino S, Sugano N, Ozawa Y, Homma K, Saruta T. Ca2+ channel subtypes and pharmacology in the kidney. Circ Res. 2007;100:342–53.
Wu X, Zhang W, Ren H, Chen X, Xie J, Chen N. Diuretics associated acute kidney injury: clinical and pathological analysis. Ren Fail. 2014;36:1051–5.
James MK, Vuong A, Grizzle MK, Schuster SV, Shaffer JE. Hemodynamic effects of GI 87084B, an ultra-short acting mu-opioid analgesic, in anesthetized dogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992;263:84–91.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
About this article
Cite this article
Sakai, W., Yoshikawa, Y., Hirata, N. et al. Effect of remifentanil during cardiopulmonary bypass on incidence of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. J Anesth 31, 895–902 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-017-2419-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-017-2419-y