Abstract
Purpose
Perioperative analgesia during thoracotomy is often achieved by combining paravertebral block (PVB) with general anesthesia (GA). Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) can detect changes in cerebral oxygenation resulting from nociceptive stimuli in the awake state or under sedation. We used NIRS to measure changes in cerebral blood flow provoked by thoracotomy incision made under GA and determine how these changes were influenced by supplementation of GA with PVB.
Methods
Thirty-four patients undergoing elective thoracotomy were enrolled. Patients were randomly assigned to a group receiving only GA, or GA combined with PVB (GA + PVB). Changes in cerebral oxygenated hemoglobin (ΔO2Hb), deoxygenated-Hb (ΔHHb), and total-Hb (ΔtotalHb) were evaluated by NIRS as surgery began.
Results
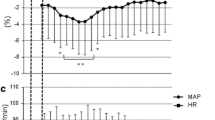
In the GA group, ΔO2Hb was significantly higher in the hemisphere contralateral to the side of surgery when the incision was made and 2 min after incision compared with the ipsilateral side (start of surgery, P < 0.01; 2 min, P < 0.05). In contrast, there were no significant changes in the ΔO2Hb at any of the time points in the GA + PVB group. Comparable with ΔO2Hb, the concentration of ΔtotalHb was significantly higher in the contralateral hemisphere in the GA group at the start of surgery (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
Changes in the cerebral O2Hb concentration were detected by NIRS immediately after surgical incision under GA, but not in the presence of a PNB. NIRS could be used to monitor surgical pain. PVB inhibited changes in oxygenation induced by incision-provoked pain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apkarian AV, Bushnell MC, Treede RD, Zubieta JK. Human brain mechanisms of pain perception and regulation in health and disease. Eur J Pain. 2005;9(4):463–84.
Hsieh JC, Belfrage M, Stone-Elander S, Hansson P, Ingvar M. Central representation of chronic ongoing neuropathic pain studied by positron emission tomography. Pain. 1995;63(2):225–36.
Lorenz J, Cross DJ, Minoshima S, Morrow TJ, Paulson PE, Casey KL. A unique representation of heat allodynia in the human brain. Neuron. 2002;35(2):383–93.
Hsieh JC, Stahle-Backdahl M, Hagermark O, Stone-Elander S, Rosenquist G, Ingvar M. Traumatic nociceptive pain activates the hypothalamus and the periaqueductal gray: a positron emission tomography study. Pain. 1996;64(2):303–14.
Rosen SD, Paulesu E, Nihoyannopoulos P, Tousoulis D, Frackowiak RS, Frith CD, Jones T, Camici PG. Silent ischemia as a central problem: regional brain activation compared in silent and painful myocardial ischemia. Ann Intern Med. 1996;124(11):939–49.
Silverman DH, Munakata JA, Ennes H, Mandelkern MA, Hoh CK, Mayer EA. Regional cerebral activity in normal and pathological perception of visceral pain. Gastroenterology. 1997;112(1):64–72.
Pogatzki-Zahn EM, Wagner C, Meinhardt-Renner A, Burgmer M, Beste C, Zahn PK, Pfleiderer B. Coding of incisional pain in the brain: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study in human volunteers. Anesthesiology. 2010;112(2):406–17.
Muthalib M, Re R, Zucchelli L, Perrey S, Contini D, Caffini M, Spinelli L, Kerr G, Quaresima V, Ferrari M, Torricelli A. Effects of increasing neuromuscular electrical stimulation current intensity on cortical sensorimotor network activation: a time domain fNIRS study. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0131951.
Yennu A, Tian F, Gatchel RJ, Liu H. Prefrontal hemodynamic mapping by functional near-infrared spectroscopy in response to thermal stimulations over three body sites. Neurophotonics. 2016;3(4):045008.
Becerra L, Aasted CM, Boas DA, George E, Yucel MA, Kussman BD, Kelsey P, Borsook D. Brain measures of nociception using near-infrared spectroscopy in patients undergoing routine screening colonoscopy. Pain. 2016;157(4):840–8.
Kussman BD, Aasted CM, Yucel MA, Steele SC, Alexander ME, Boas DA, Borsook D, Becerra L. Capturing pain in the cortex during general anesthesia: near infrared spectroscopy measures in patients undergoing catheter ablation of arrhythmias. PLoS One. 2016;11(7):e0158975.
Lee CH, Sugiyama T, Kataoka A, Kudo A, Fujino F, Chen YW, Mitsuyama Y, Nomura S, Yoshioka T. Analysis for distinctive activation patterns of pain and itchy in the human brain cortex measured using near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e75360.
Yucel MA, Aasted CM, Petkov MP, Borsook D, Boas DA, Becerra L. Specificity of hemodynamic brain responses to painful stimuli: a functional near-infrared spectroscopy study. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9469.
Baliki MN, Chialvo DR, Geha PY, Levy RM, Harden RN, Parrish TB, Apkarian AV. Chronic pain and the emotional brain: specific brain activity associated with spontaneous fluctuations of intensity of chronic back pain. J Neurosci. 2006;26(47):12165–73.
Ji G, Neugebauer V. Pain-related deactivation of medial prefrontal cortical neurons involves mGluR1 and GABA(A) receptors. J Neurophysiol. 2011;106(5):2642–52.
Meyer K. The role of dendritic signaling in the anesthetic suppression of consciousness. Anesthesiology. 2015;122(6):1415–31.
Conti A, Iacopino DG, Fodale V, Micalizzi S, Penna O, Santamaria LB. Cerebral haemodynamic changes during propofol-remifentanil or sevoflurane anaesthesia: transcranial Doppler study under bispectral index monitoring. Br J Anaesth. 2006;97(3):333–9.
Wagner KJ, Willoch F, Kochs EF, Siessmeier T, Tolle TR, Schwaiger M, Bartenstein P. Dose-dependent regional cerebral blood flow changes during remifentanil infusion in humans: a positron emission tomography study. Anesthesiology. 2001;94(5):732–9.
Derbyshire SW, Jones AK, Collins M, Feinmann C, Harris M. Cerebral responses to pain in patients suffering acute post-dental extraction pain measured by positron emission tomography (PET). Eur J Pain. 1999;3(2):103–13.
Morimoto Y, Matsumoto A, Koizumi Y, Gohara T, Sakabe T, Hagihira S. Changes in the bispectral index during intraabdominal irrigation in patients anesthetized with nitrous oxide and sevoflurane. Anesth Analg. 2005;100(5):1370–4 (table of contents).
Zbinden AM, Maggiorini M, Petersen-Felix S, Lauber R, Thomson DA, Minder CE. Anesthetic depth defined using multiple noxious stimuli during isoflurane/oxygen anesthesia. I. Motor reactions. Anesthesiology. 1994;80(2):253–60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Mukaihara, K., Hasegawa-Moriyama, M. & Kanmura, Y. Contralateral cerebral hemoglobin oxygen saturation changes in patients undergoing thoracotomy with general anesthesia with or without paravertebral block: a randomized controlled trial. J Anesth 31, 829–836 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-017-2402-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-017-2402-7