Abstract
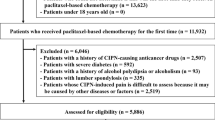
Paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy (PIPN) is one of the serious adverse events associated with paclitaxel-based cancer treatments. A recent case study showed that the antiplatelet agent clopidogrel inhibits paclitaxel metabolism via cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C8, resulting in severe PIPN. The aim of this study was to determine the impact of clopidogrel as a risk factor for the development of PIPN, using a retrospective cohort study. Data from paclitaxel-treated patients with or without clopidogrel and low-dose aspirin treatment were retrieved from medical charts. A total of 161 adult patients were included in this study: 135 were controls, 9 were clopidogrel-treated and 17 were aspirin-treated. The clopidogrel group had a greater proportion of males and a higher rate of comorbidities, such as diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia, than the control group. However, patient characteristics were similar between the clopidogrel and aspirin groups. Severe PIPN was diagnosed in 3 (2.2%) and 2 (22.2%) patients in the control and clopidogrel groups, respectively (odds ratio: 12.0; p = 0.031). No patients in the aspirin group presented with severe neuropathy. These pilot data suggest that concomitant treatment with clopidogrel leads to a greater risk of PIPN. The avoidance of concomitant clopidogrel use may be effective in reducing clopidogrel-associated PIPN.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee JJ, Swain SM. Peripheral neuropathy induced by microtubule-stabilizing agents. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1633–42.
Rivera E, Cianfrocca M. Overview of neuropathy associated with taxanes for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015;75:659–70.
Necchi A, Pond GR, Raggi D, Giannatempo P, Vogelzang NJ, Grivas P, Galsky MD, Bellmunt J, Sonpavde G. Efficacy and safety of gemcitabine plus either taxane or carboplatin in the first-line setting of metastatic urothelial carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2017;15:23–30.
Hershman DL, Lacchetti C, Dworkin RH, Lavoie Smith EM, Bleeker J, Cavaletti G, Chauhan C, Gavin P, Lavino A, Lustberg MB, Paice J, Schneider B, Smith ML, Smith T, Terstriep S, Wagner-Johnston N, Bak K, Loprinzi CL. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:1941–67.
Boora GK, Kanwar R, Kulkarni AA, Abyzov A, Sloan J, Ruddy KJ, Banck MS, Loprinzi CL, Beutler AS. Testing of candidate single nucleotide variants associated with paclitaxel neuropathy in the trial NCCTG N08C1 (Alliance). Cancer Med. 2016;5:631–9.
Backman JT, Filppula AM, Niemi M, Neuvonen PJ. Role of cytochrome P450 2C8 in drug metabolism and interactions. Pharmacol Rev. 2016;68:168–241.
Wang ZY, Chen M, Zhu LL, Yu LS, Zeng S, Xiang MX, Zhou Q. Pharmacokinetic drug interactions with clopidogrel: updated review and risk management in combination therapy. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015;11:449–67.
Tornio A, Filppula AM, Kailari O, Neuvonen M, Nyrönen TH, Tapaninen T, Neuvonen PJ, Niemi M, Backman JT. Glucuronidation converts clopidogrel to a strong time-dependent inhibitor of CYP2C8: a phase II metabolite as a perpetrator of drug-drug interactions. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2014;96:498–507.
Bergmann TK, Filppula AM, Launiainen T, Nielsen F, Backman J, Brosen K. Neurotoxicity and low paclitaxel clearance associated with concomitant clopidogrel therapy in a 60-year-old Caucasian woman with ovarian carcinoma. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;81:313–5.
Kanda Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48:452–8.
Shinoda Y, Kimura M, Usami E, Asano H, Yoshimura T. Potential drug interaction between paclitaxel and clopidogrel. Biomed Rep. 2016;5:141–5.
Alberti P, Rossi E, Cornblath DR, Merkies IS, Postma TJ, Frigeni B, Bruna J, Velasco R, Argyriou AA, Kalofonos HP, Psimaras D, Ricard D, Pace A, Galiè E, Briani C, Dalla Torre C, Faber CG, Lalisang RI, Boogerd W, Brandsma D, Koeppen S, Hense J, Storey D, Kerrigan S, Schenone A, Fabbri S, Valsecchi MG. Cavaletti G Physician-assessed and patient-reported outcome measures in chemotherapy-induced sensory peripheral neurotoxicity: two sides of the same coin. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(1):257–64.
Tozaki-Saitoh H, Tsuda M, Miyata H, Ueda K, Kohsaka S, Inoue K. P2Y12 receptors in spinal microglia are required for neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury. J Neurosci. 2008;28:4949–56.
Gu N, Eyo UB, Murugan M, Peng J, Matta S, Dong H, Wu LJ. Microglial P2Y12 receptors regulate microglial activation and surveillance during neuropathic pain. Brain Behav Immun. 2016;55:82–92.
Gu N, Peng J, Murugan M, Wang X, Eyo UB, Sun D, Ren Y, DiCicco-Bloom E, Young W, Dong H, Wu LJ. Spinal microgliosis due to resident microglial proliferation is required for pain hypersensitivity after peripheral nerve injury. Cell Rep. 2016;16:605–14.
Lou N, Takano T, Pei Y, Xavier AL, Goldman SA, Nedergaard M. Purinergic receptor P2RY12-dependent microglial closure of the injured blood-brain barrier. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:1074–9.
Agergaard K, Mau-Sørensen M, Stage TB, Jørgensen TL, Hassel RE, Steffensen KD, Pedersen JW, Milo ML, Poulsen SH, Pottegård A, Hallas J, Brøsen K, Bergmann TK. Clopidogrel paclitaxel drug-drug interaction: a pharmacoepidemiologic study. Clin Pharmacol Ther. published online. doi:10.1002/cpt.674.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Mariko Takebe, Dr. Akiyo Kameyama and Mr. Toshio Fujimori for their helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuo, M., Ito, H., Takemura, Y. et al. Increased risk of paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients using clopidogrel: a retrospective pilot study. J Anesth 31, 631–635 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-017-2362-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-017-2362-y